World Population Distribution Map by Equal Parts

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
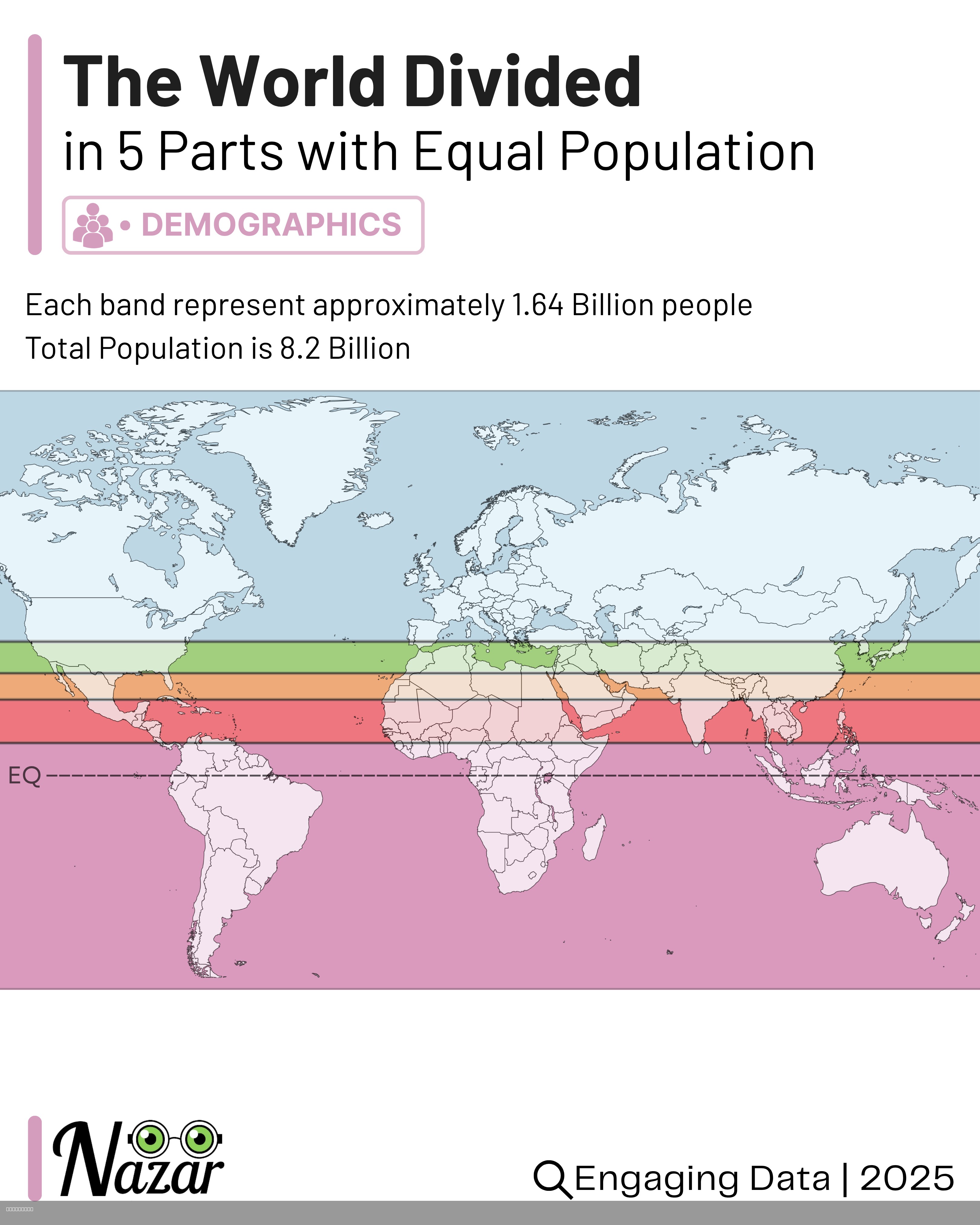
What This Map Shows
This map visualizes the world’s population divided into five horizontal bands, each containing approximately 1.64 billion people. This striking representation illustrates the stark inequalities in human distribution across the globe. While some regions are densely packed with inhabitants, others remain vast and sparsely populated. The bands run through some of the most populous areas such as India, China, and Southeast Asia, while simultaneously encompassing extensive territories like Siberia, Canada, and the Sahara Desert, where human presence is minimal. This visualization is not merely an artistic representation; it serves as a powerful reminder of how unevenly humanity is spread across our planet.
Deep Dive into Global Population Distribution
Population distribution refers to the way people are spread across the world’s surface. Understanding this distribution is crucial for various reasons, including resource allocation, urban planning, and environmental management. As of 2023, the global population stands at approximately 8.2 billion. This number is not evenly distributed, leading to significant variations in demographics, urbanization, and accessibility to resources.
Interestingly, about 60% of the world’s population lives in just 10 countries. China and India alone account for over a third of the global population. In urban areas, this concentration intensifies; cities like Tokyo, Delhi, and Shanghai are among the most populous in the world, drawing millions of people for economic opportunities and better living standards. The phenomenon of urbanization has led to megacities, which are defined as urban areas with over 10 million inhabitants. As of now, there are over 30 megacities globally, many of which are located in Asia.
What’s fascinating is how historical, social, and economic factors contribute to these patterns. For instance, fertile river valleys and coastal regions have historically attracted populations due to their agricultural viability and trade opportunities. In contrast, areas like the Sahara Desert or Siberia have harsh climates and limited resources, resulting in low population densities.
Furthermore, migration plays a significant role in reshaping population distribution. People often move from rural areas to urban centers in search of better job prospects, education, and quality of life. This movement creates a ripple effect, leading to urban sprawl and the development of new suburbs and satellite towns.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the map into regions reveals intriguing contrasts in population distribution. In Asia, the narrowest bands are densely packed with people, particularly in countries like India and China. For instance, India’s population density is approximately 464 people per square kilometer, making it one of the most crowded countries worldwide. Conversely, China, despite its vast land area, has a similar density due to its large population concentrated in urban areas along the eastern seaboard.
In North America, however, the population is much more spread out. Canada, with its expansive wilderness, has a population density of only 4 people per square kilometer. Most Canadians live in urban areas near the U.S. border, highlighting the stark contrast to the densely populated regions of Asia. Similarly, in Europe, countries like Germany and the United Kingdom have high population densities, while places like Norway and Iceland remain relatively unpopulated due to their geographical features.
In Africa, the population distribution is characterized by rapid urbanization in countries like Nigeria, where Lagos is one of the fastest-growing cities in the world. However, vast areas of the continent, such as the Sahara, are largely uninhabited. This dichotomy underscores the complexities of population movements and the challenges of managing urbanization in emerging economies.
Significance and Impact
Understanding global population distribution is crucial for several reasons. It informs policymakers about where to allocate resources, plan infrastructure, and address issues like housing, healthcare, and education. For instance, the concentration of people in urban areas can lead to challenges such as overcrowding, pollution, and strain on public services. Conversely, rural areas may face issues like depopulation, leading to economic decline and loss of services.
Moreover, population distribution is intrinsically linked to environmental sustainability. As cities expand, they often encroach on natural habitats, leading to biodiversity loss and increased carbon emissions. This highlights the need for sustainable urban planning that balances growth with environmental conservation.
Looking ahead, trends indicate that the world’s population could reach 9.7 billion by 2050, according to the United Nations. This growth will likely exacerbate existing disparities in population distribution, necessitating a comprehensive approach to urban development and resource management. Have you noticed how these patterns affect your community? The implications of population distribution are not just theoretical; they impact daily life and the future of our planet.
Overall, this map serves as a valuable tool for understanding the complexities of human settlement. By recognizing where people live and the factors influencing these patterns, we can better address the challenges and opportunities that come with an ever-evolving global population.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 4, 2025
- Views
- 134
Comments
Loading comments...