Climate Comparison Map of Australia and the World

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
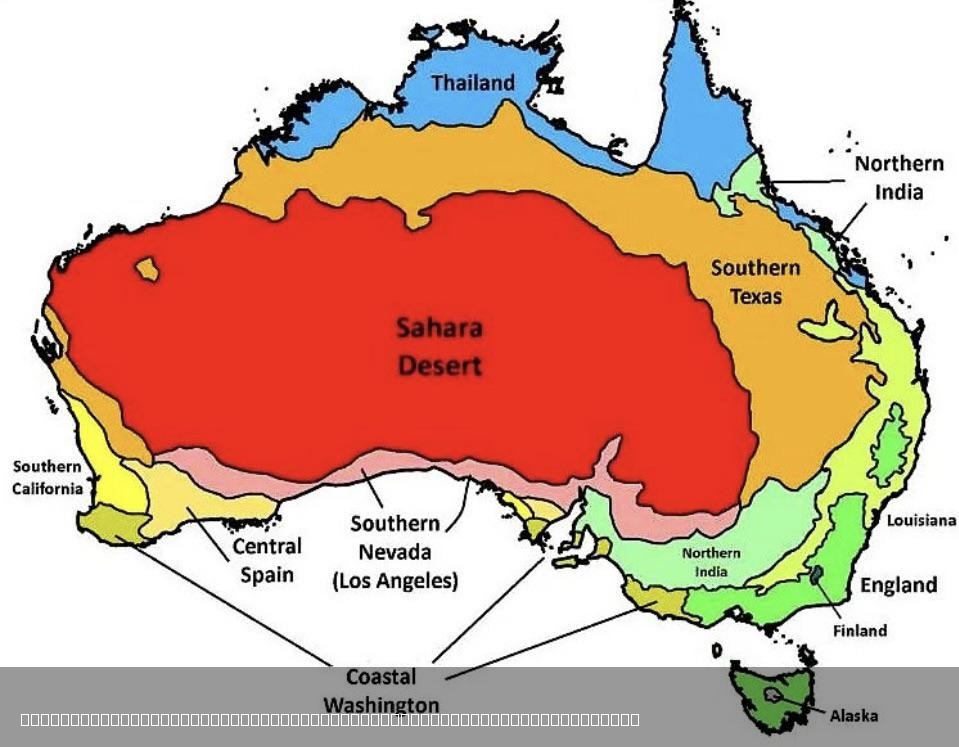
What This Map Shows
The visualization titled "The Climate in Australia Compared to Other Places in the World" presents a comprehensive overview of how Australia's climate stacks up against various regions globally. It highlights temperature ranges, precipitation levels, and distinct climate zones, allowing viewers to grasp the unique environmental characteristics of Australia in a broader context.
However, to fully appreciate these climatic differences, we need to delve deeper into the fundamental aspects of climate itself—specifically how it is defined, the factors that influence it, and the broader implications of these patterns.
Deep Dive into Climate
Climate refers to the long-term patterns of temperature, humidity, wind, and precipitation in a particular area. Unlike weather, which can change from day to day, climate represents the average conditions over extended periods. In Australia, the climate is diverse, ranging from tropical in the north to temperate in the south.
Interestingly, Australia is often characterized by its arid and semi-arid conditions. Approximately 70% of the continent is classified as arid or semi-arid, which significantly influences not only the landscape but also the ecosystems and human activities present there. For instance, the interior regions, known as the Outback, experience high temperatures and low rainfall, making them some of the harshest environments on Earth.
In contrast, coastal areas, particularly in the eastern regions like Queensland, enjoy a more tropical climate, with warm temperatures and abundant rainfall. The Great Barrier Reef, located along this coastline, thrives due to the warm waters and consistent sunlight, showcasing how climatic factors can create rich biodiversity.
Australia's climate is also heavily influenced by phenomena such as El Niño and La Niña. These climatic events can lead to extreme weather patterns, including droughts and floods. For instance, during an El Niño year, parts of Australia may experience significantly reduced rainfall, leading to drought conditions, while La Niña can result in increased rainfall and flooding. This variability is essential for understanding the broader climatic trends and predicting future changes.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map reveals distinct climatic zones across Australia. In the far north, the tropical climate is characterized by wet and dry seasons, with cities like Darwin experiencing significant monsoonal rains. As we move southward, the climate transitions into subtropical regions, such as Brisbane, which enjoy milder winters and more consistent rainfall.
The southeastern coast, including cities like Sydney and Melbourne, presents a temperate climate with four distinct seasons. Here, rainfall is more evenly distributed throughout the year. Interestingly, Melbourne is renowned for its unpredictable weather, often experiencing a single day with multiple weather changes.
In stark contrast, the interior regions, such as Alice Springs, have a desert climate, with extreme temperature fluctuations between day and night. This variability is a defining characteristic of the Outback, where temperatures can soar above 40°C (104°F) during the day and plummet at night, leading to unique adaptations among the flora and fauna.
When comparing Australia’s climate to other places around the world, it’s essential to consider regions like the Mediterranean, which experiences warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters, or the polar regions, where extreme cold dominates. Each of these areas showcases how different factors—including latitude, altitude, and proximity to oceans—shape climatic conditions.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the climate of Australia relative to other regions is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it informs agricultural practices; farmers must adapt to the climate's nuances to ensure crop viability. Additionally, it plays a significant role in biodiversity conservation, as various species are adapted to specific climatic conditions.
Furthermore, as the world grapples with climate change, the implications of these patterns become even more critical. Australia is one of the countries most affected by climate change, with increasing temperatures predicted. This could lead to more frequent droughts and bushfires, impacting wildlife and human populations alike.
As we look to the future, it’s essential to monitor these climatic patterns and their effects on both the environment and human society. Understanding climate in relation to other regions can provide valuable insights into global climate trends and help inform policies aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change.
In conclusion, the climate comparison map serves as a vital tool for understanding not just Australia’s environmental conditions but also the broader climatic influences at play worldwide. It underscores the importance of geographic literacy in navigating the challenges posed by climate variability and change.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 3, 2025
- Views
- 224
Comments
Loading comments...