Map of Residents by Birth State in 2020

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
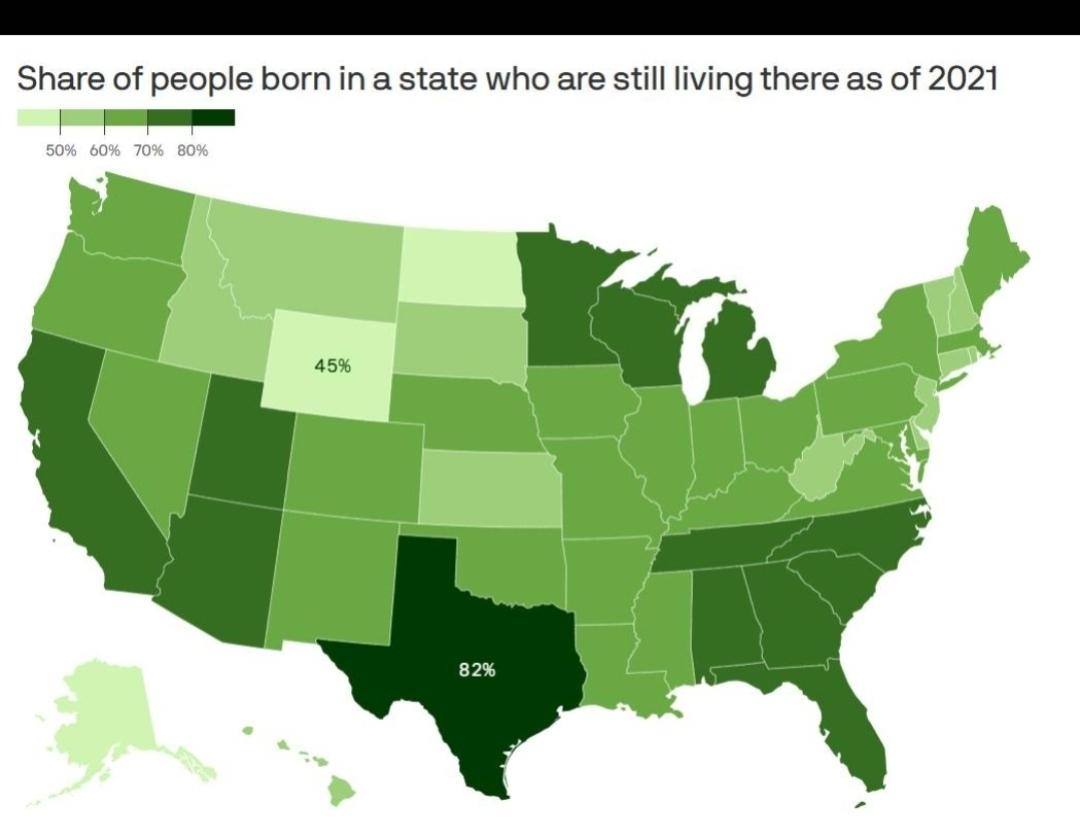
What This Map Shows
The map titled "Share of People Born in a State Who Are Still Living There as of 2020" offers a compelling snapshot of the mobility patterns of the U.S. population. It visualizes the percentage of individuals who remain in their state of birth, providing insights into regional demographics and the factors influencing residential stability. This data is crucial for understanding various social and economic dynamics at play in our society today.
Deep Dive into Population Retention
Population retention is a fascinating topic that reflects the interplay of various factors, including economic opportunities, family ties, cultural influences, and regional amenities. In essence, the map illustrates how many residents remain in the same state where they were born, revealing trends about migration and local attachment.
Interestingly, certain states exhibit high retention rates, suggesting a strong sense of community and connection among residents. For instance, states like North Dakota and Iowa showcase impressive retention figures—often over 70%. What drives this loyalty? One reason could be the smaller community sizes and strong family networks that encourage individuals to stay close to home. Moreover, rural areas often have less economic mobility, prompting residents to remain in the familiar surroundings of their birthplaces.
Conversely, states like California and New York display lower retention rates, often under 50%. Urban centers tend to attract newcomers, creating a melting pot of cultures and lifestyles. The dynamic job markets in these areas entice individuals to relocate for work, education, or new experiences. However, high living costs can also prompt those who were born there to seek opportunities elsewhere, leading to a more transient population.
Furthermore, age plays a significant role in this equation. Younger generations are notably more mobile than their older counterparts, often moving for education or employment. In contrast, older populations tend to settle in their birth states, especially as they approach retirement age. This demographic shift can have lasting implications for local economies, healthcare systems, and community structures.
Additionally, socio-economic factors greatly influence these patterns. States with robust economies, diverse job markets, and high quality of life tend to retain more residents. For instance, Colorado has seen an influx of young professionals attracted to its vibrant economy and outdoor lifestyle, yet it still maintains a relatively high retention rate among those born there, indicating a balance between attracting new residents and keeping locals.
Regional Analysis
Breaking the map down by regions reveals intriguing differences. The Midwest, for example, often reflects higher retention rates compared to the coastal states. This could be attributed to the slower pace of life, lower cost of living, and the strength of community ties in states like Wisconsin and Minnesota. In contrast, the South shows mixed results; while states like Alabama display solid retention rates, others like Florida attract a significant number of newcomers, particularly retirees.
In the Northeast, states like Vermont and Maine report high levels of population retention, influenced by their scenic beauty and tight-knit communities. Meanwhile, New York's bustling urban life presents complex challenges for retention as it constantly attracts new residents driven by the promise of economic opportunity.
Interestingly, the West Coast often sees a dichotomy between urban and rural areas. Urban centers like San Francisco and Los Angeles have lower retention rates due to their transient populations, whereas rural parts of states like Montana and Idaho maintain high retention, emphasizing a lifestyle choice that values tranquility and natural beauty.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the share of people who remain in their birth states has significant implications for various sectors, including urban planning, economic development, and social services. For instance, regions with declining populations may struggle to maintain infrastructure and services, leading to economic challenges. Conversely, states that successfully retain their residents can benefit from stable economies and community cohesion.
Current trends suggest that as remote work becomes more prevalent, patterns of mobility may shift once again. Will more people choose to live in their birth states if they can work from anywhere? Or will the lure of urban environments continue to draw them away? These questions are essential as policymakers and community leaders strive to understand and adapt to the evolving landscape of population dynamics.
In conclusion, the retention rates of individuals in their birth states provide a window into broader societal trends. Whether it's fostering a sense of belonging or grappling with economic challenges, the implications of this data are profound and far-reaching, shaping the future of our communities and economies.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 26, 2025
- Views
- 12
Comments
Loading comments...