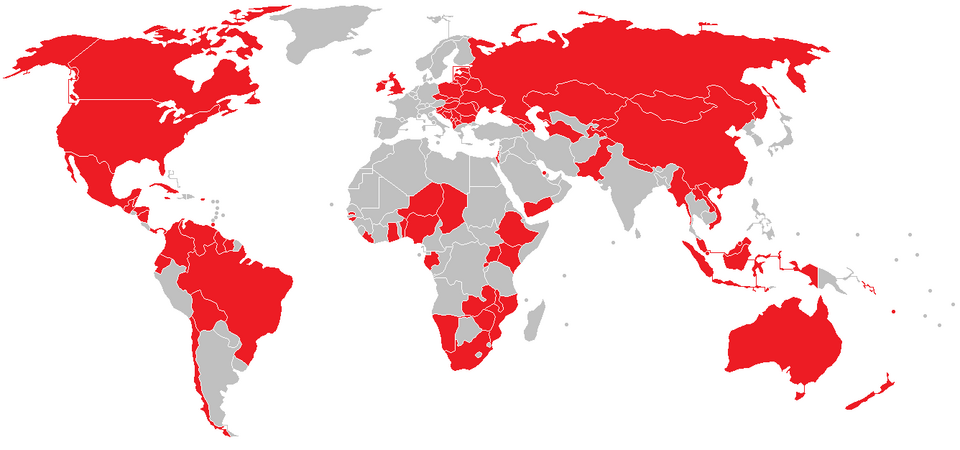
Map of Countries Recording Race and Ethnicity in Censuses

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The map displays countries highlighted in red where race or ethnicity has been recorded in national censuses since the beginning of the 21st century. This visualization illustrates the global landscape of demographic data collection practices, revealing the nations that prioritize understanding the ethnic and racial makeup of their populations. It serves as a crucial starting point for a deeper exploration of how different societies view and categorize their populations.
Deep Dive into Race and Ethnicity Data Collection
Race and ethnicity are fundamental aspects of human identity that influence social, political, and economic dynamics within countries. The practice of recording this information in population censuses provides insights into the demographic composition and diversity of nations. It also reflects prevailing attitudes towards race and ethnicity within different societies.
Interestingly, the collection of race and ethnicity data has varied significantly across countries. In some regions, such as the United States, the census has included questions on race since the first national census in 1790. This data has been pivotal in understanding demographic trends and shaping public policy. In contrast, other countries may have only recently begun to include such questions, often in response to shifting political landscapes or social movements advocating for greater recognition of minority groups.
The reasons for collecting this data can differ widely. For instance, in nations with a history of racial or ethnic conflict, such as Rwanda or Bosnia, enumerating populations by ethnicity can be a sensitive yet necessary practice to promote understanding and reconciliation. In other cases, it aids in resource allocation, ensuring that government services are adequately tailored to meet the needs of diverse communities.
According to the United Nations, about 70 countries have included questions on race or ethnicity in their recent censuses. However, the approach to categorization can vary greatly. Some countries may categorize populations into broad groups, while others may provide options for more nuanced identification. This can affect the interpretation of data and the policies that stem from it.
Have you noticed that in some countries, the terms used to define racial or ethnic groups can be heavily influenced by historical contexts? For example, in Brazil, the census uses a variety of terms to capture the complex racial landscape, reflecting the country's unique history of colonization and slavery. In contrast, in many European countries, the approach is often more rigid, which can oversimplify the diverse backgrounds of citizens.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map, we can see that North America, parts of Africa, and several countries in Asia and Europe actively record race and ethnicity. In North America, the United States and Canada have robust systems in place for collecting this data. The U.S. employs a multi-racial option that allows individuals to identify as belonging to multiple racial groups, reflecting the country's evolving understanding of identity. Canada, on the other hand, has been recognized for its approach to acknowledging Indigenous peoples in its census, which can offer insights into regions with significant Indigenous populations.
In contrast, many African nations, such as South Africa, actively collect data on race due to their historical context of apartheid. The census in South Africa is instrumental in addressing inequalities and implementing policies aimed at redressing past injustices.
Interestingly, some regions in Europe, like the United Kingdom, have made substantial efforts to record race and ethnicity in their censuses, with specific questions designed to capture a wide array of identities. Meanwhile, other European countries, like France, adhere to a policy of colorblindness, avoiding the collection of racial data altogether. This can lead to challenges in addressing issues of inequality and representation.
Significance and Impact
The significance of collecting race and ethnicity data cannot be understated. It shapes how governments understand their populations, informs public policy, and ultimately influences the social fabric of nations. In an era where issues of racial equality and representation are at the forefront of global discourse, having accurate and comprehensive data is crucial.
Moreover, as globalization continues to intertwine societies, the need for nuanced understandings of demographics becomes even more pressing. Countries that actively track and understand their racial and ethnic diversity are better equipped to foster social cohesion and address potential conflicts that may arise from misunderstandings or inequalities.
Looking ahead, the future of race and ethnicity recording in censuses poses both opportunities and challenges. As societies become increasingly diverse, governments will need to adapt their methodologies to reflect these changes accurately. This may involve revising definitions, expanding categories, or even introducing new questions altogether.
In conclusion, the map not only highlights where race and ethnicity data are being collected but also opens up a broader conversation about identity, representation, and the importance of understanding the complexities of human populations in today's world. The data collected can serve as a powerful tool for fostering inclusive societies that recognize and celebrate diversity.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 26, 2025
- Views
- 4
Comments
Loading comments...