World's Thorium Reserves Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
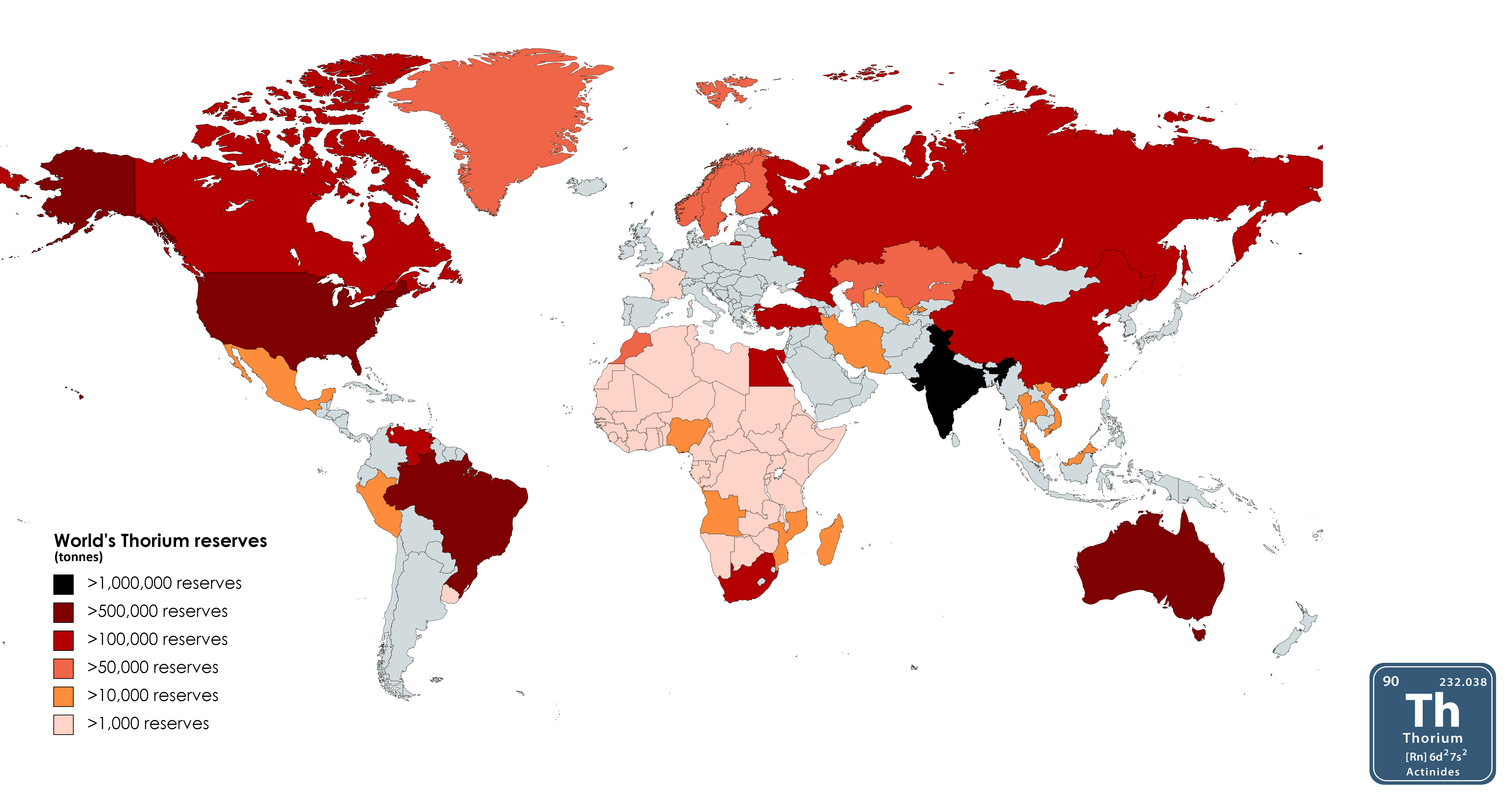
What This Map Shows
This map displays the global distribution of thorium reserves, highlighting countries rich in this alternative nuclear fuel source. Unlike uranium and plutonium, thorium has gained attention for its potential to provide a safer and more efficient means of generating nuclear energy. The map indicates not only the locations of these reserves but also their estimated quantities, offering insights into where the future of nuclear energy might be headed.
Deep Dive into Thorium as a Nuclear Fuel
Thorium is a naturally occurring radioactive element that has garnered significant interest as an alternative to uranium and plutonium for use in nuclear reactors. One of the primary reasons for this shift in focus is thorium's abundance; it is estimated that thorium is about three to four times more plentiful in the Earth's crust than uranium. Interestingly, this shift could also address some of the major concerns associated with traditional nuclear power, such as safety and nuclear waste management.
When thorium is used in nuclear reactors, it undergoes a series of reactions that ultimately produce uranium-233, a fissile material that can sustain a nuclear chain reaction. This process is known as the thorium fuel cycle, and it has several advantages. For one, thorium reactors operate at higher temperatures and can be designed to be inherently safe, meaning that they are less likely to suffer from meltdowns compared to conventional uranium reactors. In fact, many thorium reactor designs incorporate passive safety features that automatically shut down the reactor in case of an emergency.
Moreover, thorium produces significantly less long-lived radioactive waste than uranium. The byproducts of thorium reactors are primarily short-lived isotopes, which decay to safe levels in a much shorter time frame. This characteristic could greatly reduce the challenges associated with nuclear waste disposal, a major issue that has plagued the nuclear industry for decades.
However, transitioning from uranium to thorium is not without its challenges. Current nuclear infrastructure is predominantly designed for uranium, requiring significant research and development to adapt existing reactors or to build new thorium-compatible ones. Additionally, while thorium's potential is widely recognized, there has been relatively little commercial investment in thorium technologies compared to uranium.
Regional Analysis
The map reveals significant regional disparities in thorium reserves. Countries like India, Australia, and the United States have some of the largest known thorium deposits. India, in particular, has made substantial investments in thorium research, aiming to leverage its vast reserves to meet its growing energy demands sustainably. With around 1 million metric tons of thorium, India is not only looking to enhance its energy security but also to reduce its reliance on coal.
Australia also stands out with over 300,000 metric tons of thorium reserves. Interestingly, while Australia is a major exporter of uranium, its thorium resources remain largely untapped. This raises questions about the future direction of the Australian energy sector and whether it will embrace thorium as a viable option.
In contrast, countries with less extensive thorium reserves, such as China and Russia, are investing heavily in research and development of thorium reactors. China, for example, has ambitious plans to integrate thorium-based nuclear power into its energy strategy, recognizing the need for cleaner energy sources amidst its rapid industrialization.
Significance and Impact
The significance of thorium as a nuclear fuel goes beyond just energy production; it has the potential to reshape global energy policies and strategies. As the world grapples with climate change and the urgent need for sustainable energy solutions, thorium offers a pathway to lower carbon emissions while providing a reliable power source.
Current trends indicate a growing interest in thorium research, especially as countries seek to diversify their energy sources and enhance energy security. Moreover, as public awareness of climate issues rises, there may be increased pressure on governments to invest in cleaner, safer nuclear technologies. In this context, thorium could emerge as a key player in the future energy landscape.
In conclusion, this map of the world's thorium reserves not only highlights the geographical distribution of this valuable resource but also opens up a discussion about the future of nuclear energy. As we look ahead, the potential of thorium may very well shape the next generation of sustainable energy solutions, paving the way for a cleaner and more secure energy future.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 22, 2025
- Views
- 10
Comments
Loading comments...