West Eurasian Ancestry by Country Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
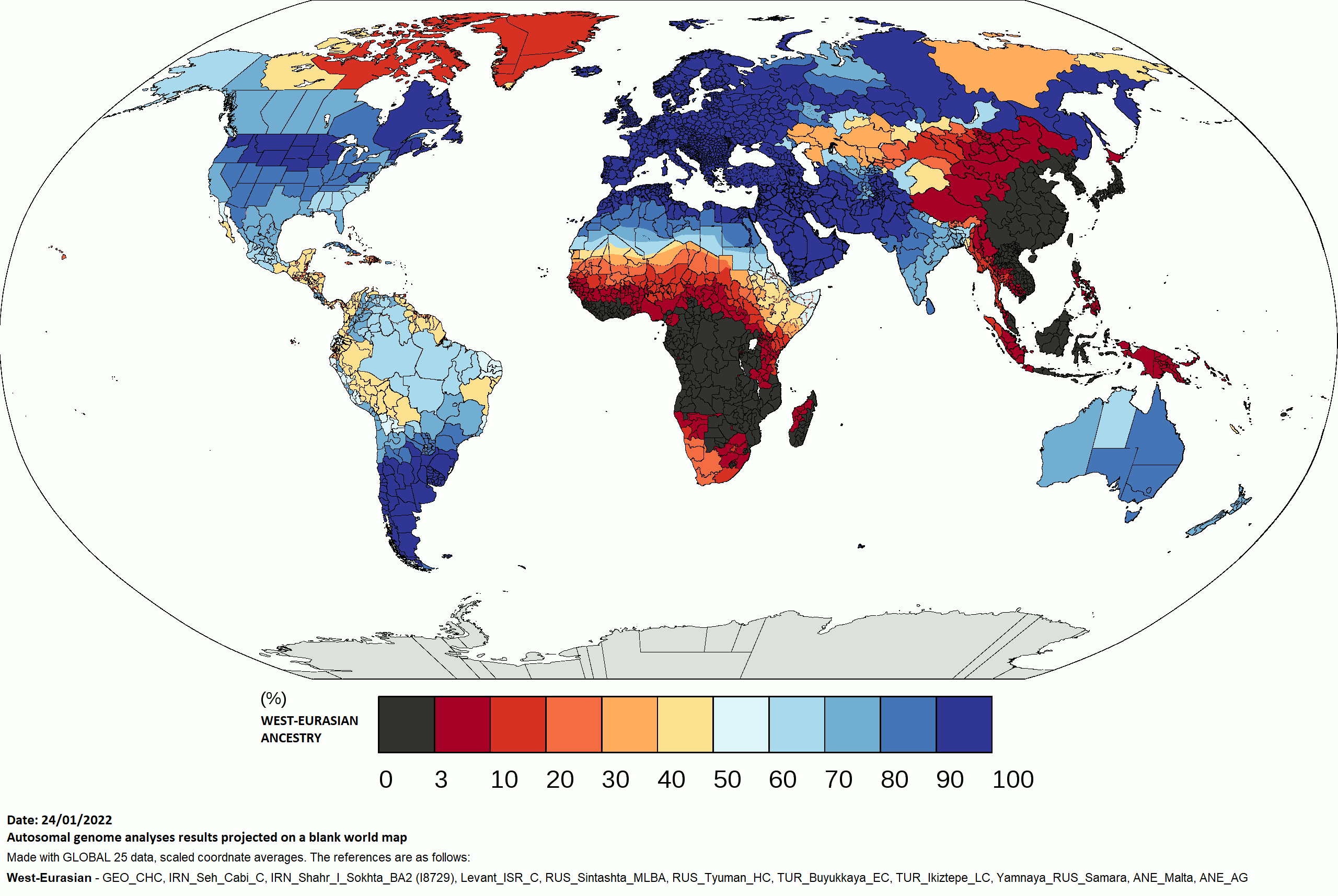
What This Map Shows
The "West Eurasian Ancestry by Country Map" provides a detailed visualization of the distribution of West Eurasian genetic ancestry across various countries. This map highlights the varying degrees of West Eurasian genetic contributions to the populations in these countries, showcasing a complex tapestry of human history and migration patterns. It serves as a visual representation of how ancestry can shape cultural and social identities in contemporary societies.
Deep Dive into West Eurasian Ancestry
West Eurasian ancestry primarily encompasses genetic lineages originating from Europe and parts of western Asia, including the Caucasus region. This area has seen a myriad of migrations, conquests, and cultural exchanges over millennia, contributing to the rich genetic diversity we observe today. Interestingly, the genetic makeup of modern populations is often a reflection of ancient migrations, such as those from the Indo-European expansions and the spread of agriculture.
The map reveals varying proportions of West Eurasian ancestry across countries. For instance, countries like Armenia and Georgia show a high percentage of West Eurasian ancestry due to their location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia. In contrast, nations such as Turkey exhibit a more varied genetic landscape, influenced by both European and Asian ancestries.
In addition to ancient migrations, more recent historical events have also shaped genetic profiles. The Ottoman Empire's expansion, for example, brought together diverse groups from the Balkans to the Middle East, resulting in a rich genetic mosaic that persists today. Furthermore, the impact of the Silk Road facilitated not only trade but also genetic exchange, intertwining the fates of distant populations.
What’s fascinating is that genetic studies often reveal that contemporary identities do not always align with genetic ancestry. For instance, while many Eastern Europeans exhibit significant West Eurasian ancestry, their cultural identities might be influenced by Slavic, Baltic, or Finno-Ugric heritages. This highlights the importance of understanding ancestry not just as a genetic blueprint but as a narrative of human experience.
Additionally, researchers have utilized advanced techniques, such as genome-wide association studies (GWAS), to explore how specific genes associated with West Eurasian ancestry can influence health and physical traits. For instance, certain genetic predispositions related to lactose tolerance are more prevalent in populations with significant West Eurasian ancestry, showcasing the adaptive nature of human genetics over time.
Regional Analysis
When we examine the map regionally, distinct patterns emerge. In Western Europe, countries like France, Germany, and the United Kingdom have high levels of West Eurasian ancestry, reflecting a long history of migrations and intermingling with adjacent populations. These nations often possess a blend of Celtic, Germanic, and Roman genetic influences.
Moving eastward, countries such as Poland and Hungary maintain significant West Eurasian genetic markers, influenced by historical movements and invasions, including the migrations of the Magyars and Slavs. Interestingly, the genetic landscape in Eastern Europe can be quite heterogeneous, with significant admixture from neighboring regions, such as the Middle East and Central Asia.
On the other hand, in the Caucasus region, countries like Azerbaijan and Georgia exhibit unique genetic characteristics due to their geographical positioning and historical interactions with both Europe and Asia. The genetic diversity here is particularly noteworthy, as it reflects ancient trade routes and migrations that have shaped the populations over thousands of years.
Significance and Impact
Understanding West Eurasian ancestry is vital for several reasons. Firstly, it sheds light on the historical movements of peoples and how these migrations have influenced cultural identities. In a globalized world, recognizing our shared ancestry can foster a sense of unity and understanding among diverse populations.
Moreover, genetic studies can inform public health initiatives. As we learn more about how ancestry influences health outcomes, we can tailor medical treatments and preventive measures to better suit different populations. This understanding is crucial in addressing health disparities that often exist along ethnic and geographic lines.
Looking forward, the implications of studying West Eurasian ancestry are profound. With advancements in genetic research, we can expect to uncover even more about our collective human story, providing insights into how migrations have shaped not just our genes, but our cultures, societies, and interactions. The future of genetic research holds the promise of connecting us to our ancestors, helping us understand the intricate web of human history that binds us all together.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 16, 2025
- Views
- 28
Comments
Loading comments...