Circumcision Rates by Country Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
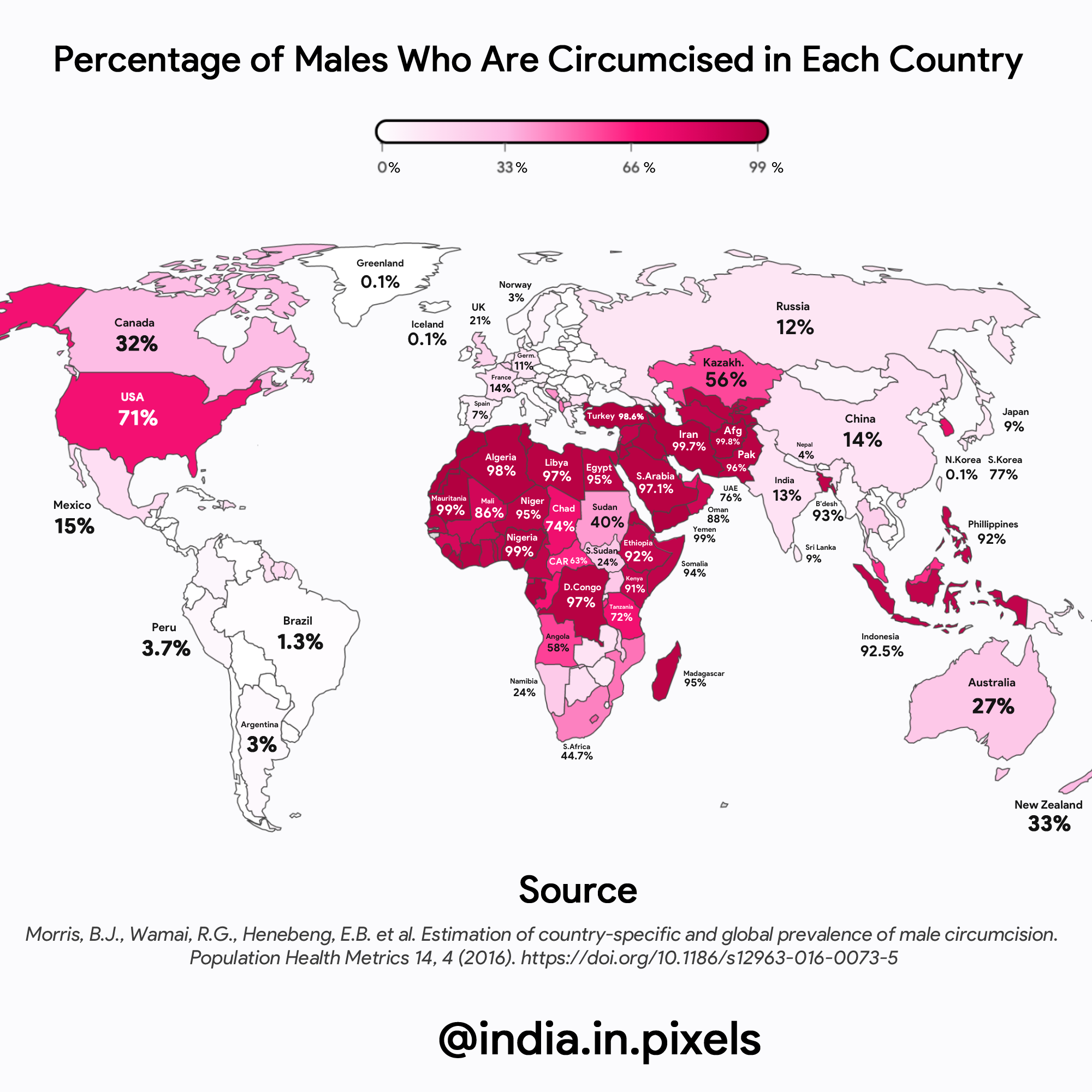
What This Map Shows\nThis map visualizes the percentage of males who are circumcised across various countries. Circumcision, a practice with deep cultural, religious, and medical roots, varies significantly from one region to another. The map highlights these differences, allowing us to see just how prevalent circumcision is in different parts of the world.
Deep Dive into Circumcision\nCircumcision, the surgical removal of the foreskin from the penis, is a practice that has been around for thousands of years. Its origins can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where it was often linked to religious beliefs and rites of passage. For instance, in Judaism, circumcision is a covenant between God and Abraham, practiced on the eighth day after birth. Similarly, in Islam, it is considered a Sunnah and is widely accepted among Muslim communities.
However, the prevalence of circumcision isn't solely tied to religious beliefs. In many parts of the world, it has become a common medical procedure often performed for health benefits. Research has shown that circumcision may reduce the risk of urinary tract infections in infants, sexually transmitted infections, and penile cancer in adult males. Interestingly, the medical community has debated its benefits and necessity, leading to varying practices from country to country.
In terms of statistics, the percentage of circumcised males can be quite telling. For example, in countries like Egypt and Turkey, the circumcision rates are nearly universal, often exceeding 90%. In contrast, many Western countries have much lower rates, with the United States reporting a rate of around 70%, while countries like Germany and Sweden hover around 10-20%.
The reasons for these disparities can be complex. In some regions, circumcision is viewed as a vital part of cultural identity or a rite of passage into adulthood. In others, it may be influenced by healthcare policies or the availability of medical services. For instance, in regions with high rates of HIV, such as parts of sub-Saharan Africa, circumcision is promoted as a preventive health measure, leading to increased circumcision rates.
Regional Analysis\nWhen we break down the map by regions, several trends emerge. In North America, circumcision is relatively common, especially in the United States, where cultural norms and medical recommendations have contributed to its prevalence. In contrast, Canada and Mexico show lower rates, reflecting different cultural attitudes and healthcare practices.
In Europe, the rates are markedly lower, with countries like Italy and Spain showing minimal circumcision practices. Interestingly, the variations within Europe can often be linked to historical and cultural contexts. For example, in the UK, circumcision is less common than in the US, reflecting differing views on the necessity of the procedure.
Moving to Africa and the Middle East, the map reveals high rates of circumcision. In countries such as Somalia and Sudan, circumcision is almost universally practiced, often tied to cultural identity and traditions. The practice is also prevalent in many Muslim-majority countries, where it is often performed shortly after birth or during childhood.
In Asia, the picture becomes more complex. Countries like the Philippines and Indonesia have high circumcision rates, often linked to Islamic practices, whereas in other regions like China and Japan, circumcision is relatively rare and often only performed for medical reasons.
Significance and Impact\nWhy does this topic matter? Understanding circumcision rates is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it provides insight into cultural practices and beliefs that shape health decisions. Secondly, it can inform public health policies, especially in regions where circumcision is promoted as a preventive health measure against sexually transmitted infections.
In recent years, the conversation around circumcision has evolved, especially in the context of HIV prevention efforts in sub-Saharan Africa. Organizations like the World Health Organization advocate for safe circumcision as part of broader health strategies to reduce the transmission of HIV and other infections. This initiative illustrates how cultural practices can intersect with public health, leading to significant implications for communities.
As we look to the future, it will be essential to monitor these trends. While some nations may continue to embrace circumcision for cultural or health-related reasons, others might move towards questioning its necessity, especially as global health perspectives shift and more information becomes available. Thus, the landscape of circumcision rates is likely to evolve, reflecting broader changes in societal attitudes and health policies.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 16, 2025
- Views
- 8
Comments
Loading comments...