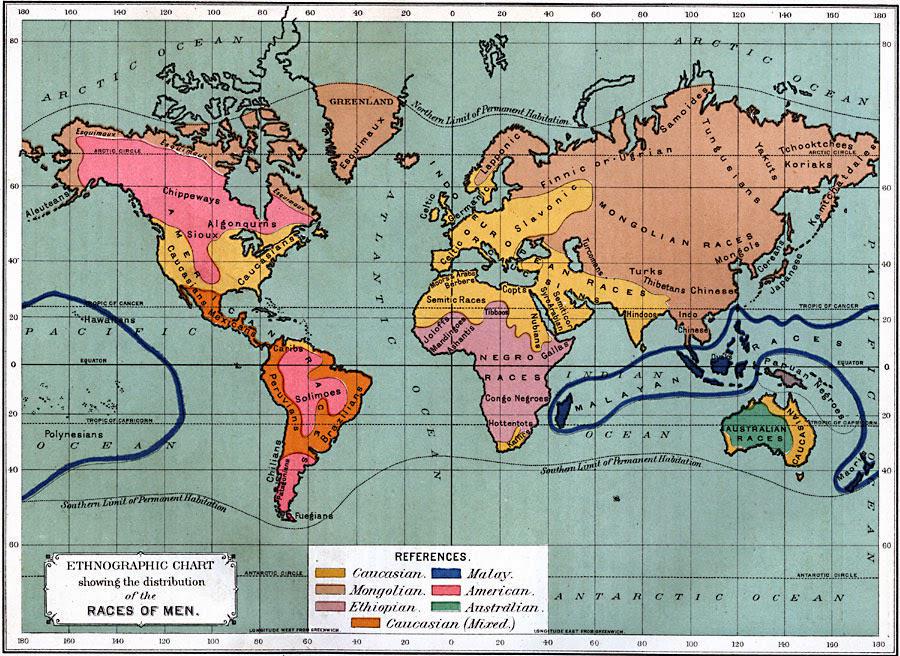
Races of Men Map 1891

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The "Races of Men" map from 1891 offers a fascinating insight into the ethnographic beliefs of the time, depicting human populations categorized by race across the globe. This map serves as a historical artifact, illustrating how different cultures and ethnic groups were perceived in the late 19th century, while also reflecting the scientific understanding and misconceptions of human diversity. The map is color-coded to represent various racial classifications, providing a snapshot of societal views on race during a period marked by colonial expansion and racial theories.
Deep Dive into Racial Classifications
The concept of race, as illustrated by this map, was influenced by social, political, and scientific factors of the time. In the late 1800s, ideas about race were often shaped by the prevailing theories of polygenism, which posited that different races had distinct origins. This contrasts starkly with modern understandings of race as a social construct rather than a biological one. Interestingly, the map delineates groups such as Caucasians, Mongolians, and Negroids, each displayed in unique shades, signaling a hierarchy of sorts that was pervasive in the scientific community of that era.
What's fascinating is that the map reflects European dominance and colonialism, as many regions depicted were under European control or influence. For example, Africa is largely represented as populated by those classified as Negroids, with little nuance to the vast diversity of ethnicities that exist on the continent. In Asia, the Mongolian classification encompasses a broad range of cultures and peoples, from Central Asia to the Far East, again oversimplifying complex identities.
Furthermore, this period saw the rise of anthropometry and other pseudo-scientific methods to classify humans based on physical characteristics. The map's creators believed they could categorize people into rigid groups, which inadvertently laid the groundwork for racial discrimination and segregation policies that would emerge in the 20th century.
Regional Analysis
Analyzing the map on a regional basis reveals stark contrasts in how different areas were portrayed. In Europe, for instance, the map predominantly features Caucasians, presenting them as the 'norm' against which other races were measured. Countries like Germany and France are often highlighted with a sense of pride in their so-called racial purity. However, this neglects the rich tapestry of ethnic diversity within Europe itself, where regions such as the Balkans and the Basque Country challenge simplistic categorizations.
In contrast, Africa's representation is highly generalized, with entire nations and ethnic groups lumped into a single category. This oversimplification ignores the thousands of tribes and languages that constitute the continent's cultural landscape. Notably, regions like West Africa, known for their diversity, are depicted in a monolithic manner, missing the opportunity to appreciate their unique histories and identities.
Asia, too, is broadly categorized, with the Mongolian classification overshadowing the nuanced identities of South Asians, Southeast Asians, and East Asians. For example, India, home to over 2,000 distinct ethnic groups and numerous languages, is reduced to a single racial label, undermining its rich cultural heritage.
Significance and Impact
The significance of the "Races of Men" map extends beyond geography; it delves into the very fabric of societal beliefs regarding race. The implications of such classifications were profound, influencing political policies, academic discourse, and public perception of different racial groups. The map represents a historical context where racial hierarchies justified colonialism and exploitation, perpetuating stereotypes that linger in various forms today.
In today's world, discussions around race are more nuanced, recognizing the social constructs that shape our understanding of identity. However, remnants of these outdated classifications can still be seen in societal attitudes and institutional practices. As we reflect on the past, it's essential to recognize how maps like these have influenced current views on race.
Interestingly, as we move towards a more inclusive understanding of human diversity, examining historical perspectives can illuminate the pathways that have led to modern debates on race, identity, and belonging. The "Races of Men" map serves as a reminder of the importance of critical engagement with historical narratives and the need to challenge oversimplified views of humanity. Through this lens, we can appreciate the complexity of cultures and the importance of treating every individual as part of a rich, interconnected global community.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 13, 2025
- Views
- 22
Comments
Loading comments...