European Indoor Radon Levels Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
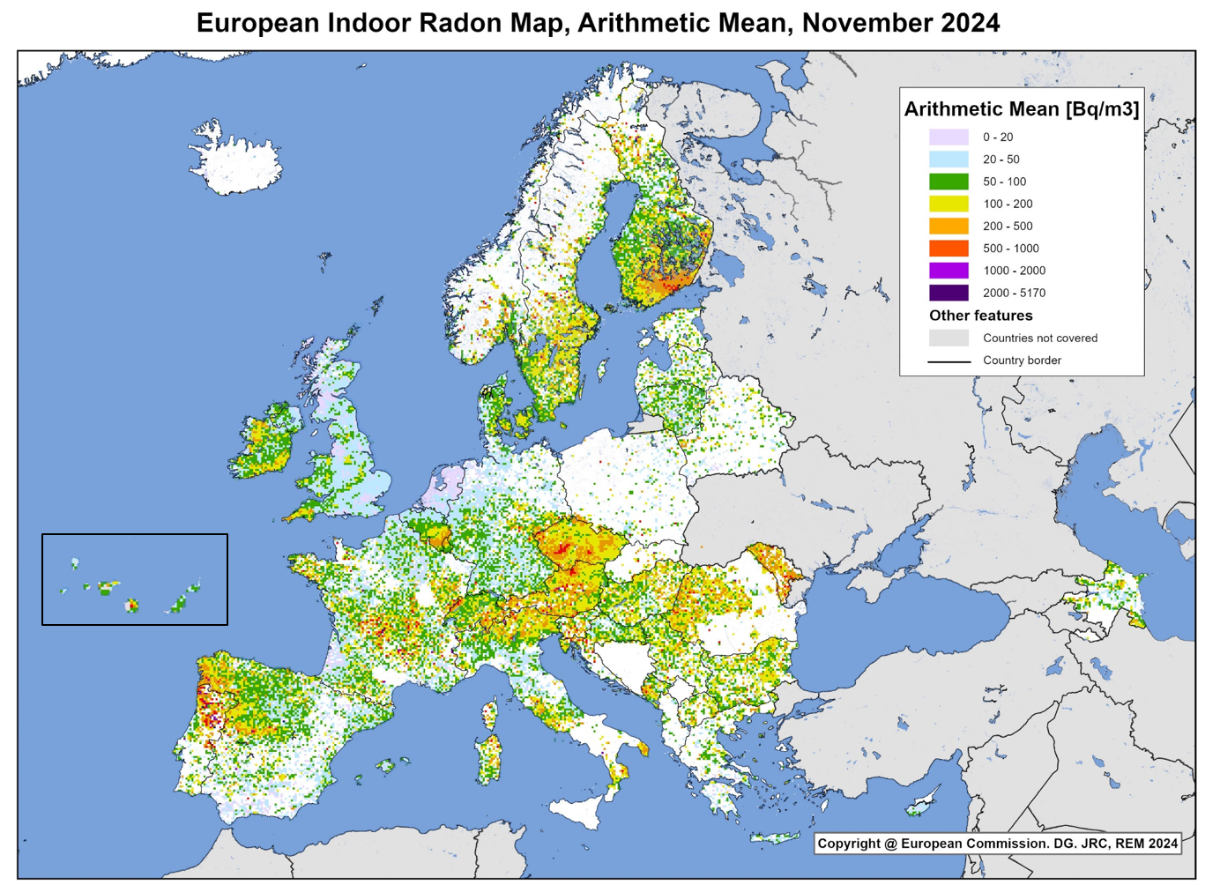
What This Map Shows
The European Indoor Radon Levels Map provides a comprehensive visualization of radon concentration levels across various regions in Europe. Radon, a naturally occurring radioactive gas, is produced by the decay of uranium found in soil and rock. This map highlights the average indoor radon levels, measured in becquerels per cubic meter (Bq/m³), across different countries and regions, allowing us to identify areas that may pose health risks due to elevated radon exposure.
Deep Dive into Radon Gas
Radon is an odorless, colorless gas that can seep into buildings from the ground, particularly in areas with high uranium content. Interestingly, while radon is part of our natural environment, it can become a serious health hazard in enclosed spaces, especially in poorly ventilated homes. Have you ever wondered why certain regions are more susceptible to high radon levels? The geology of an area plays a significant role. Regions with granite, shale, or phosphate rocks tend to have higher radon concentrations due to the natural uranium present in these formations.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has classified radon as a carcinogen, indicating that long-term exposure can lead to lung cancer. In fact, radon exposure is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking. According to the WHO, an estimated 3-14% of lung cancer cases in Europe are attributable to radon exposure. This statistic highlights the urgency for homeowners and policymakers alike to address indoor radon levels.
Interestingly, radon levels can fluctuate based on a variety of factors, including weather conditions and building construction. For instance, homes built on solid foundations or those with basements may have higher radon levels, as the gas can accumulate in these enclosed spaces. Proper ventilation and mitigation measures can significantly reduce radon levels, making it crucial for residents, especially in high-risk areas, to test their homes regularly.
Regional Analysis
Looking at the European Indoor Radon Levels Map, we can identify several key regions where radon levels are particularly concerning. For instance, areas in central and eastern Europe, such as the Czech Republic and Poland, report some of the highest radon concentrations. The Czech Republic has regions where average indoor radon levels exceed 400 Bq/m³, significantly higher than the WHO’s recommended action level of 100 Bq/m³.
In contrast, countries like Portugal and Spain generally report lower radon levels, with many regions falling below the recommended action level. However, it’s essential to note that even within these countries, localized geological variations can lead to hotspots of higher radon concentrations.
Nordic countries, such as Sweden and Finland, also show varied levels, with some areas experiencing significant radon issues due to the geological composition of the bedrock. Interestingly, in Norway, public awareness campaigns have helped increase testing rates, leading to more informed decisions regarding home safety and radon mitigation.
Significance and Impact
Understanding indoor radon levels is crucial not only for individual health but also for public health policy. The European Union and various national health authorities have initiated programs to raise awareness about radon exposure and promote regular testing in homes, particularly in high-risk areas.
The implications of radon exposure extend beyond health, influencing real estate markets and construction practices. Homebuyers are increasingly aware of radon risks, and properties with known radon issues may face decreased market value. Moreover, as climate change continues to impact weather patterns, the potential for increased radon levels due to changes in groundwater levels and soil moisture is a topic of ongoing research.
In conclusion, the European Indoor Radon Levels Map serves as a vital tool for understanding where radon poses a health risk. It emphasizes the need for ongoing education, testing, and mitigation strategies to protect public health across Europe. As we move forward, it is imperative to stay informed about radon levels in our living spaces and to advocate for necessary measures to ensure the safety and well-being of our communities.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 9, 2025
- Views
- 6
Comments
Loading comments...