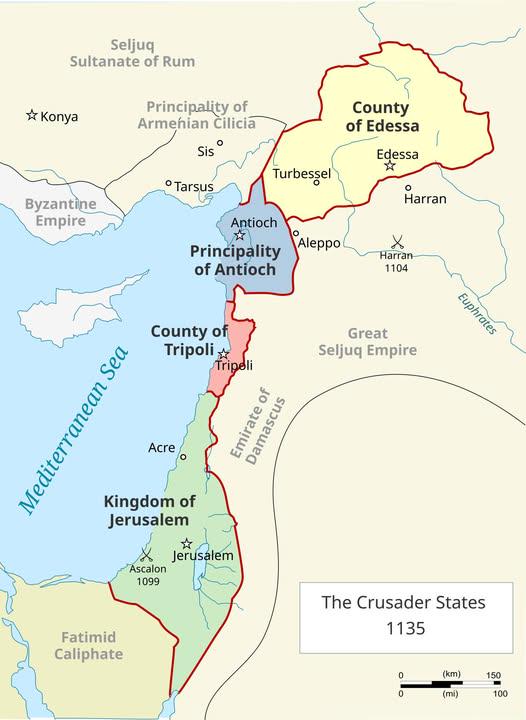
Map of the 4 Catholic Crusader States in 1135

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The "Map of the 4 Catholic Crusader States in 1135" provides a snapshot of a pivotal period in medieval history, highlighting the territorial extent of four key crusader states established during the First Crusade. These states—Jerusalem, Antioch, Tripoli, and Edessa—were critical in understanding the cultural and political landscape of the time. The map not only illustrates the geographical boundaries of these states but also serves as a testament to the complex interactions between European powers and the Islamic world during the 12th century.
Deep Dive into the Crusader States
The concept of crusader states emerged from the First Crusade (1096-1099), a military expedition initiated by European Christians aiming to reclaim Jerusalem and the Holy Land from Muslim control. By 1135, four prominent states had been firmly established, each with its own unique characteristics and challenges.
1. **Kingdom of Jerusalem**: Founded in 1099, the Kingdom of Jerusalem was the most significant of the crusader states, centered around the holy city itself. What’s fascinating is that Jerusalem became both a religious and political capital, attracting pilgrims and settlers from across Europe. Its strategic location allowed for control over key trade routes and religious sites, but it also made it a target for various Muslim leaders, including the formidable Saladin, who would later challenge its existence.
2. **County of Edessa**: Situated in the northern region, the County of Edessa was established in 1098. It was the first crusader state but faced challenges due to its isolation and proximity to hostile Muslim territories. Edessa's fall in 1144 to Zengi, the atabeg of Mosul, marked a significant turning point, leading to the Second Crusade. Interestingly, the loss of Edessa triggered a wave of new crusading fervor in Europe, showcasing the interconnectedness of these states and their impact on European politics.
3. **Principality of Antioch**: Established in 1098, the Principality of Antioch was a vital crusader state, strategically located near the Mediterranean coast. Its leadership was marked by rivalry and intrigue, especially between the Norman rulers and local Byzantine authorities. Antioch served as a crucial military and trade hub, linking the East and West, but it was also rife with internal conflicts, weakening its defenses against external threats.
4. **County of Tripoli**: The County of Tripoli, established in 1102, was the last of the four states to be founded. It played a pivotal role in trade, serving as a bridge between Europe and the Muslim world. The city's location along the coast allowed for robust maritime trade, but like its counterparts, it faced constant threat from Muslim forces. Tripoli's unique position enabled it to thrive economically, yet it struggled politically, often caught in the crossfire of conflicts between larger powers.
Regional Analysis
Analyzing these crusader states reveals a rich tapestry of cultural exchange and conflict. The Kingdom of Jerusalem, as the heart of crusader ambitions, had a diverse population comprising Christians, Jews, and Muslims. This diversity was not without its tensions, but it also fostered a unique fusion of cultures, influencing art, architecture, and commerce.
In contrast, the County of Edessa was marked by its isolation, making it particularly vulnerable to attacks. The fall of Edessa not only impacted its inhabitants but also sent shockwaves through the other crusader states, leading to a sense of urgency in Europe to mount a second crusade.
Antioch and Tripoli, with their coastal access, were better positioned for trade and military logistics. The Principality of Antioch, with its fortified walls and strategic alliances, managed to remain a significant player in the region, while Tripoli’s economic advantages allowed it to thrive, albeit with political fragility.
Significance and Impact
The establishment of these crusader states had lasting implications on both European and Middle Eastern history. The interactions between the crusaders and the local populations influenced trade routes, cultural exchanges, and even military tactics, setting a precedent for future interactions between these regions.
Today, historians and archaeologists continue to study these states to understand the complexities of medieval geopolitics. The legacy of the crusader states is still evident in modern discussions about religious and cultural identities in the region. Furthermore, the events following 1135—especially the subsequent Crusades—highlight the enduring impact of these early conflicts on contemporary global relations.
As we look back on this period, it’s essential to recognize not just the territorial gains made by the crusaders but also the profound changes they brought to the societies they encountered. The map serves as a reminder of a time when the lines between cultures were drawn not just by geography, but by faith, ambition, and the pursuit of power.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 7, 2025
- Views
- 36
Comments
Loading comments...