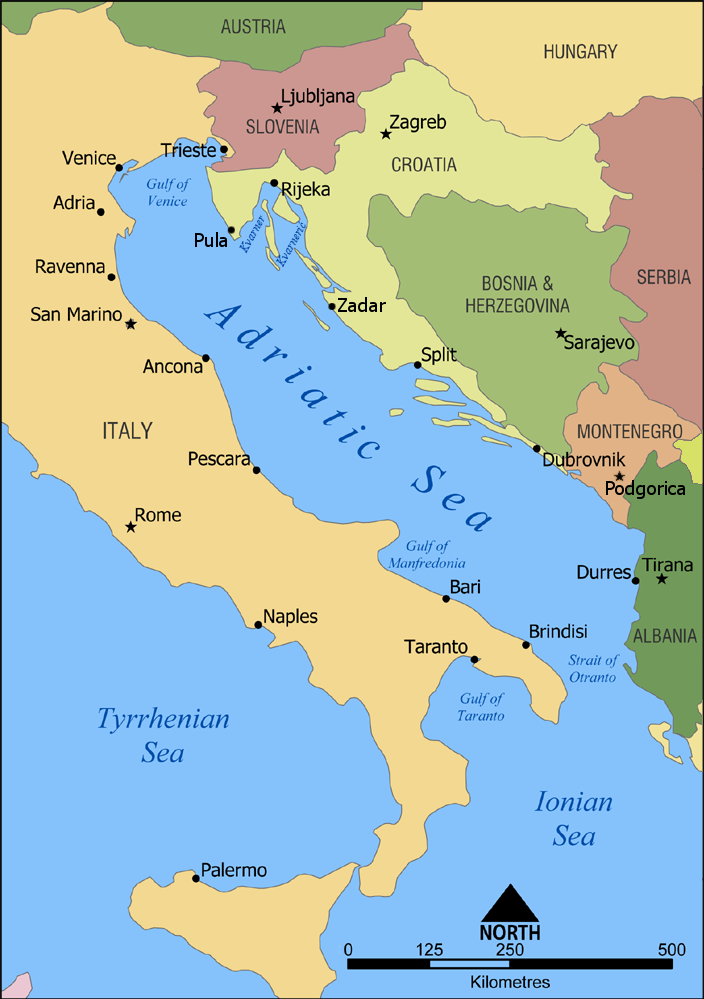
Geographic Orientation Map of Croatia and Bosnia

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The visualization titled 'Croatia is more North, West and South than Bosnia & Herzegovina, whilst Italy is more North, West, and South than Croatia' provides a clear geographic orientation of these countries in relation to one another. It highlights the unique positions of Croatia, Bosnia & Herzegovina, and Italy with respect to the cardinal directions: north, west, and south. By examining this map, it becomes evident how these three countries interact spatially, showcasing not just their geographical extents but also their relative positions on the European continent.
Deep Dive into Geographic Orientation
Geographic orientation refers to the position of a place on the Earth's surface, typically defined by its latitude and longitude. Latitude is crucial for understanding how far north or south a location is from the equator, while longitude indicates how far east or west a location is from the Prime Meridian. In this case, Croatia's geographical coordinates place it at a latitude that extends further north than that of Bosnia & Herzegovina, while also being more western and more southern than its neighboring country.
To understand why this matters, consider the implications of geographic orientation on climate, culture, and even economic activities. For example, Croatia, with its varied topography ranging from coastal areas along the Adriatic Sea to mountainous regions inland, experiences a Mediterranean climate in the coastal areas and a more continental climate further inland. This variation influences agricultural practices, tourism, and even lifestyle choices for residents and visitors alike.
Interestingly, Croatia’s more southern position compared to Bosnia & Herzegovina means it enjoys a longer tourism season, particularly along its stunning Dalmatian coast, which attracts millions of visitors each year. This not only boosts the local economy but also underscores Croatia’s strategic advantage in regional tourism.
Conversely, Bosnia & Herzegovina, which is positioned more centrally on the Balkan Peninsula, has a different climate profile that is characterized by more pronounced continental influences. This affects not only the weather patterns but also the types of crops grown and the industries that thrive there. The mountainous terrain of Bosnia & Herzegovina often results in cooler temperatures and heavier precipitation, shaping its unique ecological and agricultural landscape.
When we shift our focus to Italy, the map reveals that it is even more north, west, and south in relation to Croatia. Italy's geographic coordinates place it in a unique position that allows it to enjoy a diverse range of climates from the north’s alpine conditions to the Mediterranean climate in the south. This variety has led to Italy being a powerhouse in terms of cultural influence, agricultural output, and economic diversity. The northern regions, such as Lombardy and Veneto, are among the most economically productive areas in Europe, while the southern regions, like Sicily and Calabria, boast rich agricultural traditions and stunning coastal landscapes.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the geographic orientations presented in the map allows us to analyze how these positions influence various aspects of life in each country. For Croatia, being more southern than Bosnia & Herzegovina means it can cultivate a thriving tourism industry that capitalizes on its beautiful coastline. Coastal cities such as Dubrovnik and Split have become hotspots for European and global tourists, which significantly impacts local economies.
Bosnia & Herzegovina, while it may lack a coastline, has immense potential for eco-tourism due to its mountainous landscapes and national parks, such as Sutjeska National Park. This presents a contrast to Croatia's tourism model and highlights how geographic orientation can dictate economic opportunities.
Meanwhile, Italy’s vast geographical footprint means it can engage in multiple forms of tourism—ranging from cultural tourism in cities like Rome and Florence to adventure tourism in the Alps. The northern regions benefit from proximity to other European markets, enabling trade and economic exchanges that are less accessible to Croatia and Bosnia & Herzegovina.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the geographic orientations of Croatia, Bosnia & Herzegovina, and Italy is essential for grasping broader regional dynamics. These orientations not only define political borders but also shape economic interactions, cultural exchanges, and even environmental policies. As we move forward, the implications of geography will continue to play a vital role in how these countries approach challenges such as climate change, economic development, and social cohesion.
Have you noticed how important geography is in determining the fate of nations? As climate change reshapes the planet, countries that can effectively leverage their geographic advantages will be better positioned for growth and sustainability. Thus, the map serves as a crucial reminder of how vital geographic orientation is in our interconnected world.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 6, 2025
- Views
- 48
Comments
Loading comments...