Ethnic Map of Nepal Showing Indo-European and Sino-Tibetan Divide

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
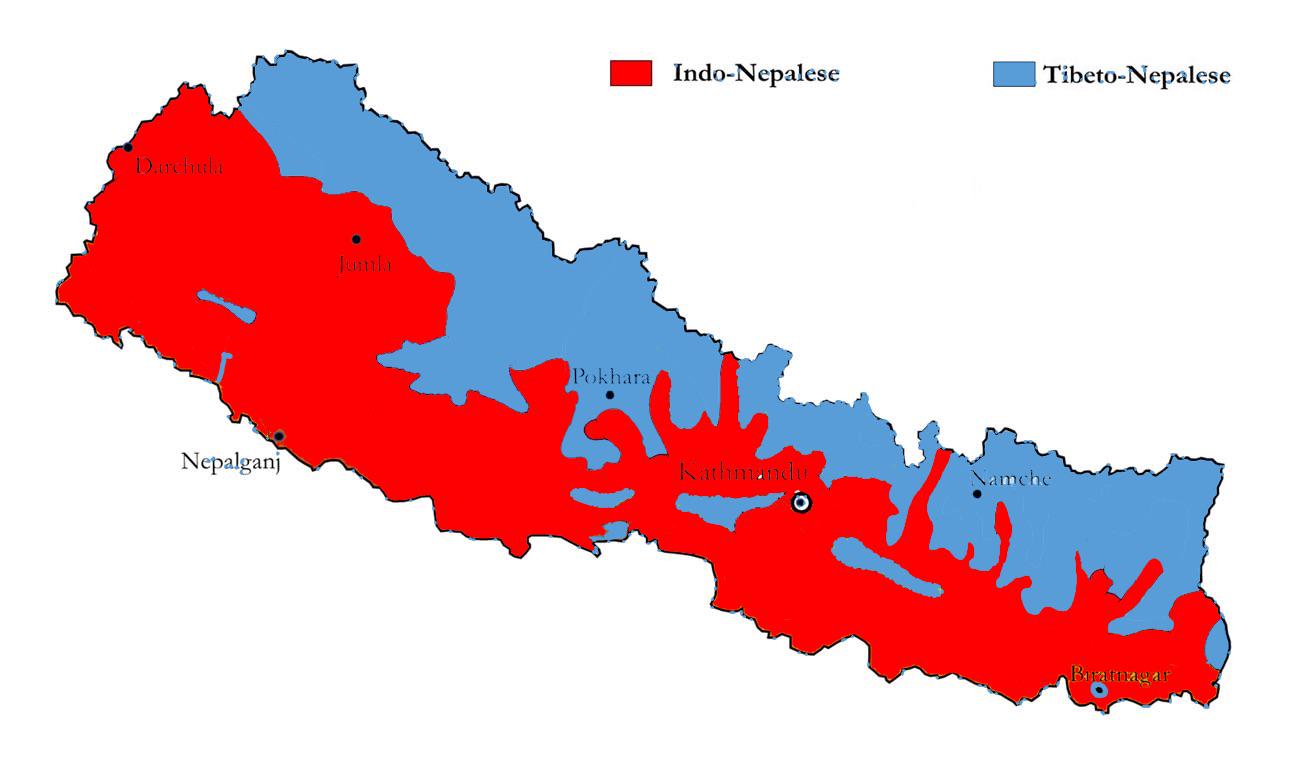
What This Map Shows
This ethnic map of Nepal provides a detailed visualization of the demographic divide between Indo-European Nepalese and Sino-Tibetan Nepalese populations. By employing color gradients and boundary delineations, the map effectively highlights the geographical distribution of these two significant ethnic groups within the country. While the Indo-European Nepalese are primarily concentrated in the lowland Terai region and central hilly areas, the Sino-Tibetan Nepalese predominantly inhabit the mountainous regions of the north. This geographical differentiation is not just a matter of physical space; it reflects centuries of migration, cultural evolution, and socio-political dynamics that have shaped Nepal’s identity.
Deep Dive into Ethnic Diversity in Nepal
Nepal is often celebrated for its rich tapestry of ethnic diversity, with over 120 distinct ethnic groups recognized by the government. The two largest groups represented on this map, the Indo-European and Sino-Tibetan Nepalese, highlight the complexities of the country's cultural landscape. The Indo-European population, which includes ethnic groups such as the Brahmins, Chhetris, and Tharus, is primarily of Aryan descent and has roots tracing back to migrations from northern India several millennia ago. In contrast, the Sino-Tibetan communities, which include the Sherpas, Tamangs, and Limbus, are believed to have ancestral ties to the Tibetan plateau and migrated southward into Nepal's highlands.
Interestingly, the cultural practices, languages, and lifestyles of these two groups differ markedly. Indo-European Nepalese generally speak languages from the Indo-Aryan family, such as Nepali and Maithili, while Sino-Tibetan groups communicate in various Tibeto-Burman languages, including Sherpa and Tamang. This linguistic diversity is not just a reflection of communication; it plays a significant role in the preservation of unique cultural identities and traditions.
Furthermore, the socio-economic conditions of these populations show stark contrasts. The Indo-European communities in the Terai region are often engaged in agriculture, with fertile plains facilitating the cultivation of rice, maize, and sugarcane. Meanwhile, the Sino-Tibetan populations, primarily residing in the rugged Himalayan terrain, rely on pastoralism and trade, especially with Tibetan communities across the border. This economic divide has implications for access to resources, education, and healthcare, highlighting the need for targeted development policies to address inequalities.
Regional Analysis
The ethnic segmentation visible on the map can be further analyzed by region. Starting with the Terai region, which forms Nepal’s southern border with India, Indo-European populations dominate, particularly in districts like Bara and Parsa. This area is characterized by a relatively higher population density and urbanization compared to other regions, which can be attributed to its agricultural productivity and proximity to major trade routes.
In contrast, the northern hilly and mountainous regions, such as Solukhumbu and Dolakha, are home to the Sino-Tibetan groups. These areas are less densely populated and present a rugged landscape that poses challenges for infrastructure development. The Sherpas, for instance, have adapted to the harsh conditions of the Himalayas, developing unique skills in mountaineering and tourism, which significantly contribute to Nepal’s economy through trekking and expedition activities. However, globalization and climate change pose threats to their traditional lifestyles and economic sustainability.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the ethnic divide in Nepal is crucial for comprehending the nation’s socio-political landscape. Ethnic identity plays a vital role in politics, influencing party affiliations, representation, and policies. The federal structure established in the 2015 Constitution aimed to address ethnic inclusion, but challenges remain in achieving equitable representation across diverse groups.
Moreover, this ethnic mapping has significant implications for conflict resolution and social cohesion. Historically, tensions have arisen between different ethnic groups, particularly in terms of resource allocation and cultural recognition. By acknowledging and respecting these ethnic differences, Nepal can work towards a more harmonious society that values diversity as a strength rather than a source of division.
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, have you ever wondered how these ethnic dynamics in Nepal might influence its future? The impacts of climate change, migration, and globalization are reshaping ethnic identities and relationships, making it imperative for policymakers, scholars, and citizens alike to engage in conversations about inclusivity and representation. With the right focus on sustainable development and cultural preservation, Nepal can navigate these challenges, ensuring that its rich ethnic diversity continues to thrive for generations to come.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 5, 2025
- Views
- 42
Comments
Loading comments...