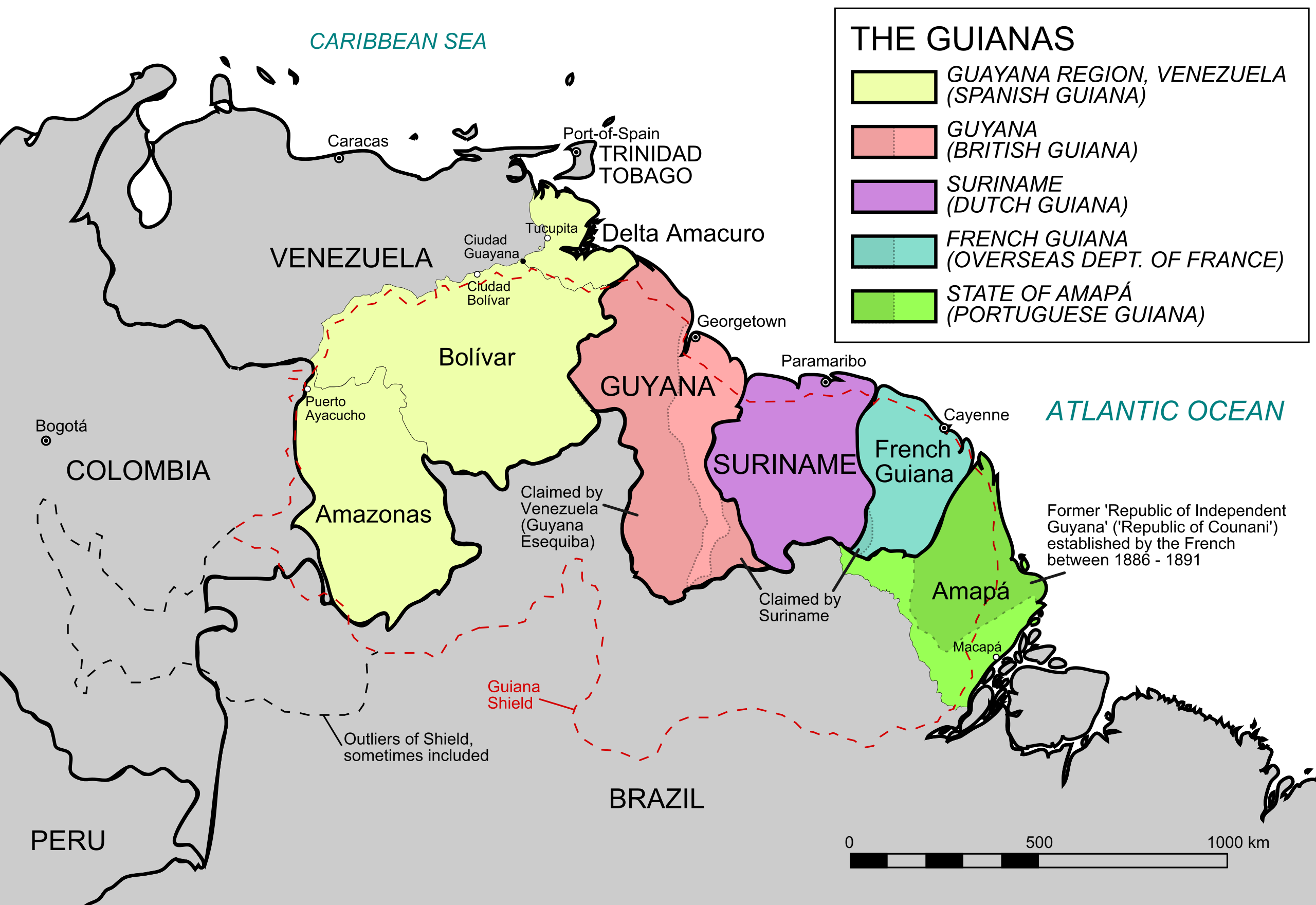
Geography Map of the Five Guianas

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The map titled "The Five Guianas" highlights the unique geographical features and political borders of a region in northeastern South America, comprising five distinct territories: Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, Venezuela, and Brazil. This visualization provides insights into their locations, sizes, and the diverse landscapes that characterize this captivating area. It serves as an excellent starting point to explore the rich cultural and natural diversity of the Guianas.
Deep Dive into the Guianas
The Guianas are a remarkable geographical region that includes several countries and territories, each with its own distinct characteristics. This area is known for its stunning biodiversity, unique ecosystems, and rich cultural heritage. Guyana, for instance, is home to one of the largest rainforests in the world, the Amazon rainforest, which stretches into its territory. With an area of approximately 214,970 square kilometers, Guyana's varied landscapes range from coastal plains to mountainous regions.
Suriname, occupying an area of about 163,820 square kilometers, is another vital player in this region. Interestingly, over 90% of Suriname is covered in pristine tropical rainforest, making it one of the most forested countries in the world. This abundance of forest not only supports a rich array of wildlife but also plays a crucial role in global carbon sequestration.
On the eastern flank lies French Guiana, an overseas department of France. Covering approximately 83,534 square kilometers, it is unique in that it is the only territory in the Guianas that is part of the European Union. The territory is characterized by its lush rainforests and diverse wildlife, including species like the giant river otter and the Guiana dolphin. Additionally, French Guiana is known for its spaceport, the Guiana Space Centre, which is a significant hub for space exploration.
Venezuela borders the Guianas to the west, presenting a stark contrast in landscape and development. The Gran Sabana region, with its table-top mountains or tepuis, is notable for its unique geological formations and is home to many endemic species. Brazil to the south also contributes to the biodiversity of the region, with parts of the Amazon rainforest extending into its territory.
Regional Analysis
Analyzing the Guianas individually reveals significant variations in population density, economic activities, and environmental challenges. For instance, Guyana has a population density of just about 4 people per square kilometer, reflecting its vast uninhabited areas. The capital, Georgetown, serves as a cultural and economic hub, drawing urban migration despite the country’s overall low population.
In contrast, Suriname has a more concentrated population in its capital, Paramaribo, which is home to over 240,000 people. The country’s economy is heavily reliant on mining, particularly bauxite and gold, which has implications for both environmental sustainability and economic stability.
French Guiana presents a different demographic dynamic, with a population of around 300,000, influenced by migration from France and neighboring countries. Its economy, while bolstered by the space industry, also faces challenges related to illegal gold mining, which poses threats to its delicate ecosystems.
Venezuela, although not officially part of the Guianas, influences the region’s dynamics through its border with Guyana. The political and economic crises in Venezuela have led to an influx of refugees into Guyana, altering the social fabric and posing challenges for resource management.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the Guianas is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, the region is a biodiversity hotspot, harboring numerous species that are vital for ecological balance. However, it also faces environmental threats from deforestation, mining, and climate change, which could jeopardize these natural resources.
Moreover, the geopolitical dynamics of the Guianas affect regional stability. With borders that have been contested in the past, particularly between Guyana and Venezuela, the importance of diplomatic relations cannot be overstated. The ongoing issues surrounding resource exploitation, land use, and indigenous rights further complicate this delicate balance.
As we move forward, the Guianas will likely continue to encounter challenges related to climate change, particularly as rising sea levels threaten coastal areas. However, there is also an opportunity for sustainable development practices to be implemented, leveraging the rich natural resources in a way that benefits local communities while preserving the environment. Ever wondered how these countries might adapt in the coming years? Their response to these pressing issues will shape not only their futures but also the ecological health of the entire region.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 4, 2025
- Views
- 46
Comments
Loading comments...