
Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
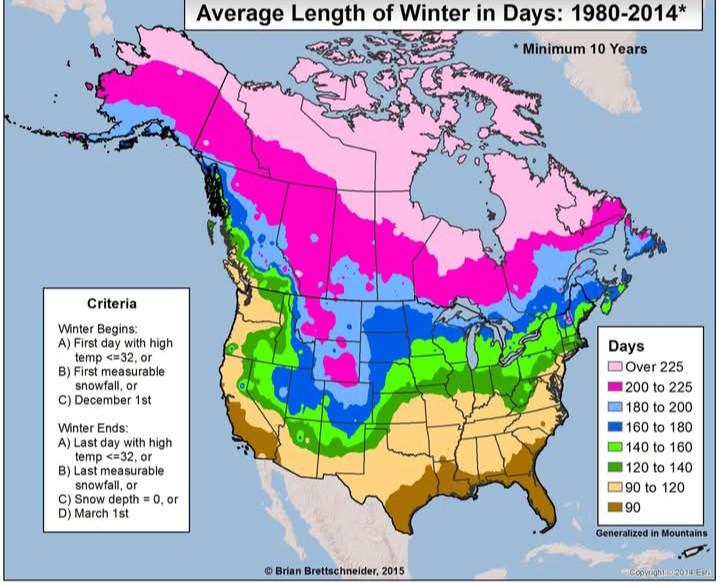
The map titled "Average Length of Winter Days between 1980-2014 by Region" provides a visual representation of the duration of daylight during the winter months across various global regions. It highlights how the length of winter days varies significantly depending on geographical location, reflecting factors such as latitude, climate, and seasonal changes.
The visualization serves as a powerful reminder of the relationship between geography and sunlight exposure. For instance, regions closer to the poles experience significantly shorter winter days compared to those near the equator. This phenomenon not only impacts the environment but also affects human activities, wildlife behaviors, and seasonal practices.
Deep Dive into Winter Day Length
The length of winter days is primarily influenced by the tilt of the Earth's axis and its orbit around the sun. During winter, the Northern Hemisphere tilts away from the sun, resulting in shorter days and longer nights. Conversely, the Southern Hemisphere experiences summer during this time, leading to longer days.
Interestingly, the variation in daylight length is not uniform; it can differ widely even within the same latitude due to local topography and atmospheric conditions. For example, mountainous regions may experience shorter daylight hours than adjacent lowlands due to shadows cast by peaks. Additionally, urban areas with tall buildings may have their daylight hours reduced further by obstructions.
From a scientific standpoint, sunlight is essential for maintaining ecosystems. It influences everything from plant growth to animal behavior. In many regions, the shorter days of winter can lead to a decrease in photosynthesis, affecting agricultural cycles and natural vegetation. In fact, studies have shown that areas with prolonged winters often see a decrease in plant biodiversity as many species struggle to adapt to the lack of light.
Moreover, human health can also be affected by the length of winter days. The phenomenon known as Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is linked to reduced sunlight exposure in winter months, leading to depression in some individuals. This highlights the importance of understanding daylight patterns and their broader implications on mental health and well-being.
Regional Analysis
When we delve into the specifics of the map, we can identify distinct patterns and variations across regions. For instance, the Arctic regions, such as northern Canada and parts of Scandinavia, experience extremely short winter days. In places like Barrow, Alaska, the winter sun barely rises above the horizon for weeks, leading to continuous darkness. Conversely, tropical regions near the equator, such as Kenya or Ecuador, maintain relatively consistent day lengths throughout the year, with only minor fluctuations.
European countries like Norway and Sweden exemplify the stark contrast in daylight hours. During the winter months, northern parts of these countries can experience as little as six hours of daylight, while southern regions may see up to eight or nine hours. Interestingly, this has cultural implications; for example, in Sweden, the concept of ‘fika’ (a coffee break) takes on a special significance during the darker months, providing social interaction that helps combat the effects of limited sunlight.
Furthermore, the map reveals variations within broader regions. In North America, the Great Lakes region experiences considerable snowfall and shorter days, impacting local agriculture and winter sports. In contrast, the Pacific Northwest has relatively mild winters, leading to longer days and diverse winter activities.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the average length of winter days is crucial for several reasons. It affects agriculture through planting and harvesting schedules, influencing food supply chains and local economies. Moreover, as climate change continues to alter weather patterns, these daylight variations may shift, impacting ecosystems and human lifestyles. For instance, changing winter day lengths could disrupt migratory patterns in birds, which rely on the length of daylight as a cue for movement.
Additionally, as urbanization increases, the phenomenon of urban heat islands can further complicate how local climates respond to winter day lengths. Cities may retain heat, leading to milder winters, which can confuse plant and animal life cycles.
In conclusion, the average length of winter days between 1980 and 2014 not only provides insights into geographical variations but also underscores the interconnectedness of natural systems and human activities. As we move forward, understanding these patterns will be vital for adapting to a changing world, ensuring both ecological and human resilience in the face of evolving climatic conditions.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 4, 2025
- Views
- 46
Comments
Loading comments...