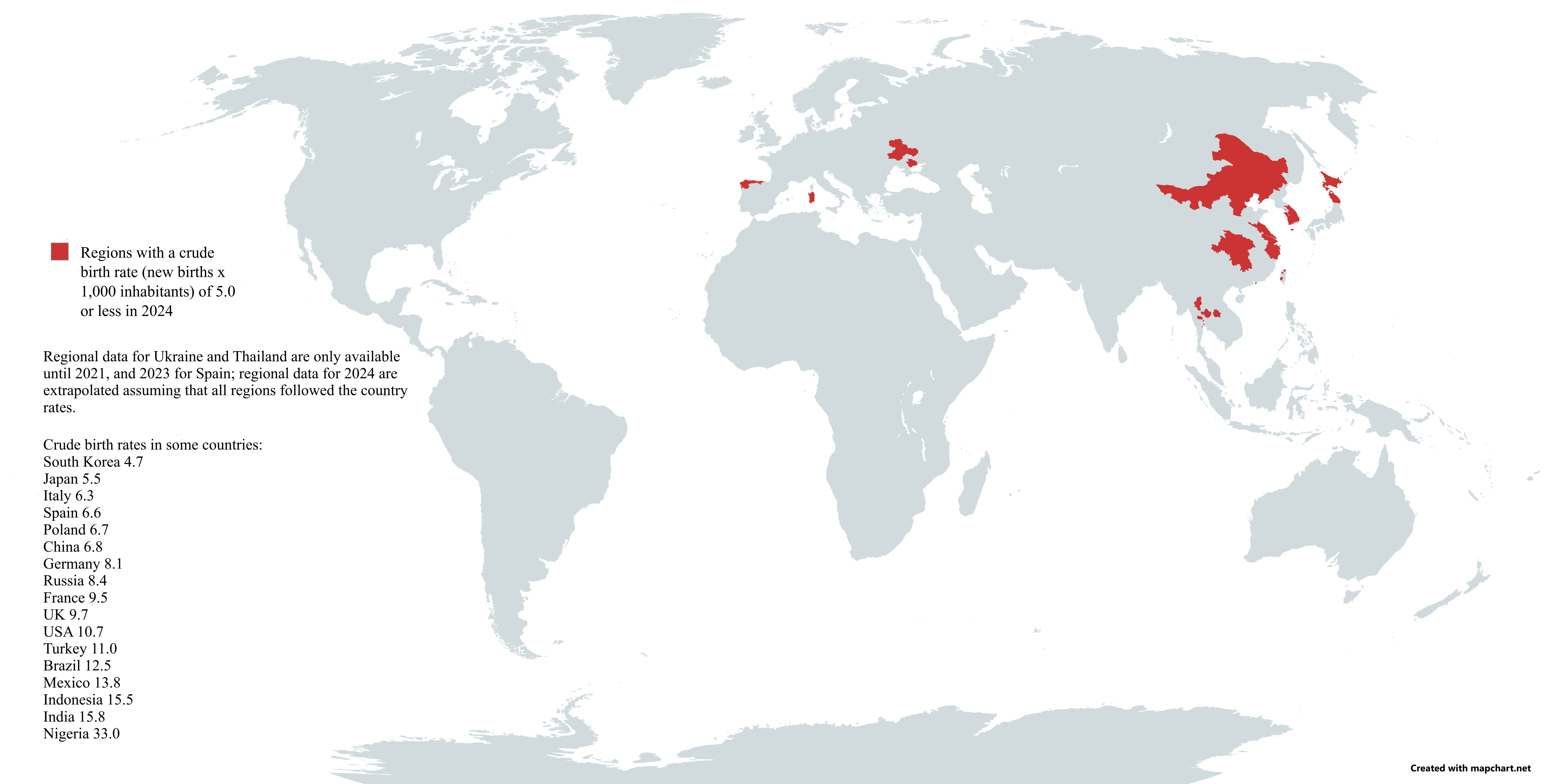
Map of Regions with Lowest Birth Rates

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map vividly illustrates the regions of the world that are grappling with the lowest birth rates. It highlights countries and areas where fewer births are occurring compared to global averages, emphasizing a significant demographic trend. As we dive into the topic of birth rates, we uncover not only the numbers but the implications behind these statistics. Birth rates serve as a vital indicator of a country’s health, development, and societal structure.
Deep Dive into Birth Rates
Birth rates, typically expressed as the number of live births per 1,000 people in a year, tell us a lot about a population's growth potential. Over the past few decades, many regions have witnessed a marked decline in these rates. Interestingly, the global average birth rate has decreased significantly since the 1960s, from about 25 births per 1,000 people to around 18 in recent years. This decline can be attributed to various factors, including increased access to education, particularly for women, economic changes, and shifts in cultural attitudes toward family and childbearing.
Have you noticed how urbanization influences birth rates? In urban areas, families often tend to have fewer children due to higher living costs, professional aspirations, and lifestyle choices. This phenomenon is evident in countries like Japan and South Korea, where cultural expectations of success and economic pressures have led to some of the lowest birth rates in the world. For instance, South Korea’s birth rate has plummeted to around 0.84 children per woman, far below the replacement level of 2.1.
Moreover, birth rates are closely linked to healthcare access and reproductive rights. Countries with comprehensive healthcare systems and family planning resources generally experience lower birth rates. On the contrary, nations with limited access to such services often see higher rates due to unintended pregnancies. For example, in many African nations, despite having high birth rates, there is a growing recognition of the need for improved reproductive health services.
What’s fascinating is that lower birth rates can lead to an aging population, which poses its own set of challenges. Countries like Italy and Germany are facing significant demographic shifts, resulting in labor shortages and increased pressure on social security systems. The balance between the working-age population and retirees becomes increasingly skewed, raising concerns about sustainability in these societies.
Regional Analysis
As we examine the regions highlighted on the map, we can see distinct patterns emerge. In Europe, countries like Italy, Spain, and Greece are struggling with low birth rates, often attributed to economic uncertainties and changing social norms. Italy, for instance, has one of the lowest rates in the region, sitting at about 1.24 children per woman. The Italian government has attempted various incentives to encourage families to have more children, but the cultural shift has proven difficult to reverse.
In East Asia, Japan and South Korea exhibit strikingly low birth rates. Japan’s rate hovers around 1.34, while South Korea is even lower. Both countries face unique societal pressures that discourage larger families, including long working hours and high costs associated with child-rearing. Interestingly, both nations are also experiencing significant immigration, which could alter demographic trends in the future.
Conversely, regions such as Sub-Saharan Africa still exhibit high birth rates, largely due to cultural values that favor large families. However, even in these regions, there are signs of change. Countries like Nigeria and Kenya are beginning to see declines in birth rates as urbanization and education levels rise. The contrasts between these regions showcase the multifaceted nature of demographic trends across the globe.
Significance and Impact
The implications of low birth rates are profound and far-reaching. On one hand, they can signal progress in gender equality, education, and economic development. On the other hand, they pose challenges related to workforce sustainability, economic growth, and social support systems. As populations age, countries may need to rethink their immigration policies and workforce strategies to maintain economic stability.
Furthermore, this demographic shift impacts global trends, such as migration patterns. Countries with low birth rates may see increased immigration as they seek to fill gaps in the labor market. In contrast, nations with high birth rates may experience significant outflows as young people seek opportunities elsewhere. This interplay of demographics shapes not only individual nations but also international relations and global economics.
In conclusion, the regions with the lowest birth rates present a complex tapestry of societal changes, economic realities, and cultural shifts. Understanding these patterns is crucial for policymakers and communities as they navigate the future challenges and opportunities posed by demographic changes.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 27, 2025
- Views
- 28
Comments
Loading comments...