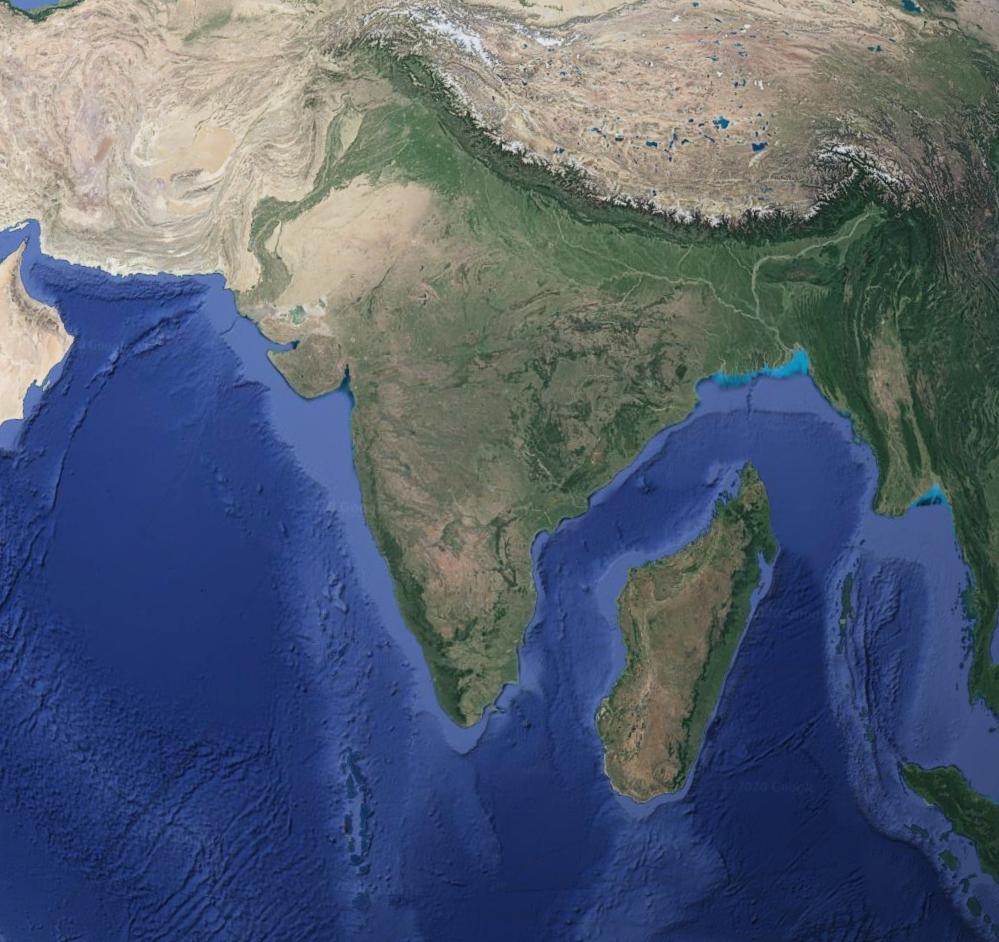
Geographical Comparison Map of Madagascar and India

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map provides a comparative geographical overview of Madagascar and India, two distinct nations that share a fascinating relationship through their diverse ecosystems and cultural histories. Situated in the Indian Ocean, Madagascar is often recognized for its unique biodiversity, while India, located to the north, is known for its vast population and cultural richness. By positioning Madagascar next to India on a map, we can better understand their geographical contexts, ecosystems, and the broader implications of their locations.
Deep Dive into Biodiversity and Ecosystems
Interestingly, Madagascar is home to an astonishing array of species that are found nowhere else on Earth. The island split from the African mainland around 160 million years ago, allowing for the evolution of a unique flora and fauna that includes lemurs, baobab trees, and diverse marine life. In fact, approximately 90% of the wildlife found in Madagascar is endemic, making it a biodiversity hotspot. The country's varied ecosystems range from rainforests to dry deciduous forests, and its geographic isolation has led to these remarkable biological divergences.
On the flip side, India boasts a rich tapestry of ecosystems, ranging from the towering Himalayas in the north to the coastal regions of the south. With its diverse climate zones, India supports a wide variety of wildlife, including Bengal tigers, Indian elephants, and countless bird species. The Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage site, is known for its exceptional biodiversity, similar to Madagascar's rainforests, and houses numerous endemic species.
What’s fascinating is how both countries face environmental challenges, yet their responses and results differ significantly. Madagascar struggles with deforestation and habitat loss due to agriculture and logging, impacting its unique wildlife. Meanwhile, India grapples with pollution and climate change, which affect its vast population and agricultural productivity. Understanding these environmental dynamics is crucial for conservation efforts in both regions.
Regional Analysis
When we analyze the regions depicted on the map, we can see distinct contrasts and similarities between Madagascar and India. For instance, Madagascar’s eastern coast is characterized by lush rainforests, while the western side features drier, spiny forests. In contrast, India’s geography varies widely: the northern regions experience heavy monsoons, while the southern areas enjoy a tropical climate.
In terms of population, India is one of the most densely populated countries in the world, with over 1.4 billion people. In stark contrast, Madagascar has a population of around 30 million, resulting in a much lower population density. This significant difference influences urban development, infrastructure, and resource management in both nations. For example, India's major cities like Mumbai and Delhi face challenges related to overpopulation, while Madagascar’s capital, Antananarivo, is expanding but remains less congested.
Moreover, the economic activities of the two countries reflect their geographical contexts. India, with its diverse economy, is a global leader in information technology and services, while Madagascar relies heavily on agriculture, fishing, and tourism, particularly eco-tourism, that showcases its unique wildlife. This geographic positioning plays a critical role in shaping each nation’s economic landscape.
Significance and Impact
The geographical relationship between Madagascar and India is significant not only for environmental studies but also for cultural exchanges and economic interactions. As our world becomes increasingly interconnected, understanding the geographical nuances of these two countries can inform global conversations about biodiversity, conservation, and sustainable practices.
Moreover, the situation in Madagascar highlights the urgent need for international cooperation in conservation efforts. With major industries in India contributing to climate change, there is potential for collaborative initiatives that protect the ecosystems unique to Madagascar while addressing broader environmental issues on a global scale.
Have you noticed how geographic locations influence cultural practices and economic strategies? The future of both Madagascar and India will depend on their ability to balance development with environmental stewardship, making the map not just a tool for navigation but a canvas for understanding our world's complex tapestry.
In conclusion, the geographical comparison of Madagascar and India reveals a rich interplay of unique ecosystems, population dynamics, and cultural histories. As we continue to explore and understand these regions, it is vital to promote conservation efforts and sustainable practices that honor their distinct environments.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 21, 2025
- Views
- 44
Comments
Loading comments...