Africa Size Comparison Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
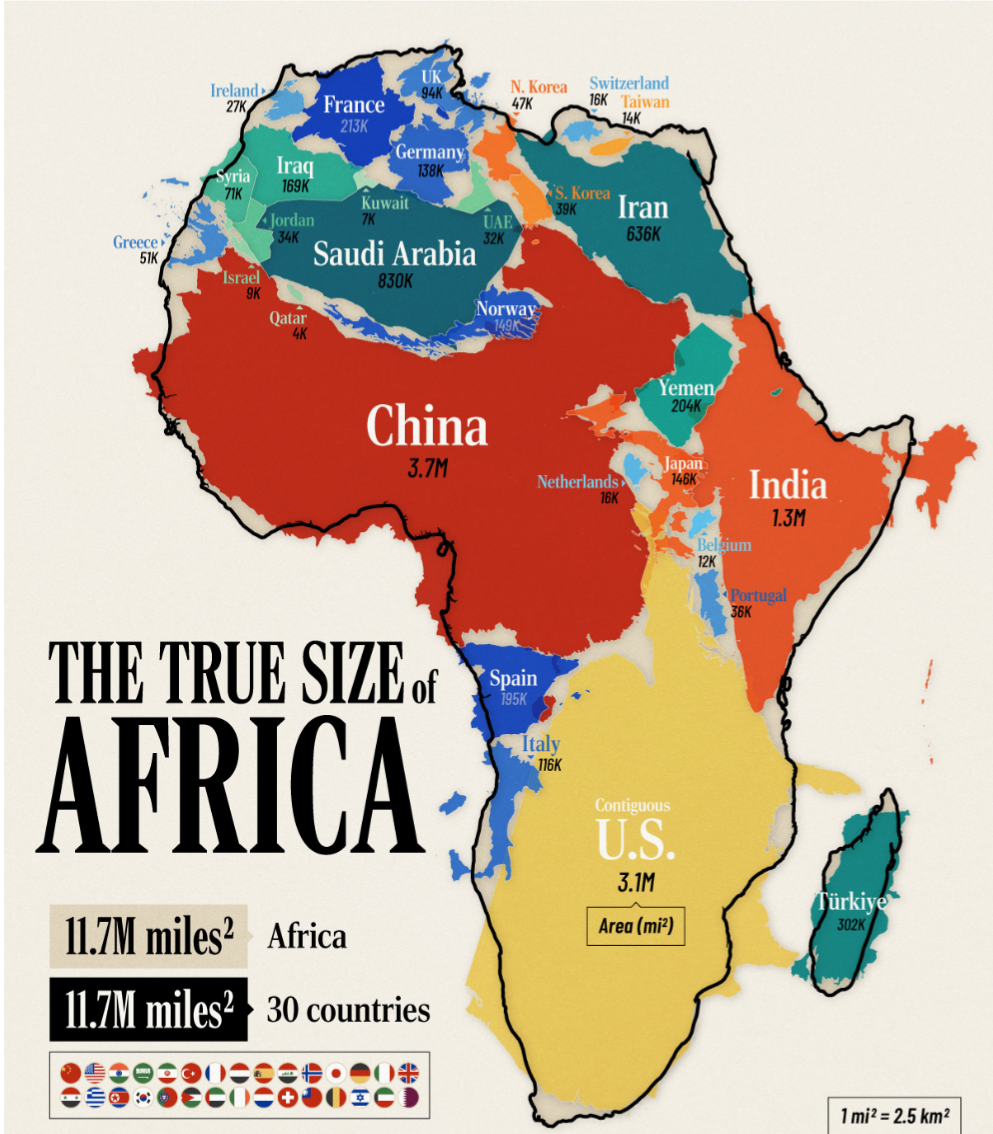
The "Africa is humongous" map offers a striking visual representation of Africa's vast land area compared to other continents and regions around the world. It's a powerful reminder of just how enormous Africa is, often underestimated due to its portrayal on smaller maps. The visualization highlights the continent's sheer size, showcasing how it can fit into other countries and continents multiple times over.
Deep Dive into Africa's Size
Africa is the second-largest continent, covering approximately 30.2 million square kilometers (about 11.7 million square miles). To put this in perspective, Africa is larger than the United States, China, India, and most of Europe combined. In fact, Africa is so large that it could encompass the entire land area of the United States and still have space for India and China. Ever wondered why Africa is often depicted as smaller than it is? This misrepresentation is largely due to the Mercator projection, which distorts size as it moves away from the equator.
Interestingly, Africa's size is not just about land area. It plays a significant role in geography, biodiversity, and climate. The continent is home to a myriad of ecosystems, from the Sahara Desert in the north, which is the largest hot desert in the world, to the rainforests of the Congo Basin in the central region, which are essential for global biodiversity.
Diving deeper into Africa's geography, the continent is divided into five major regions: North Africa, West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Each region has its own unique characteristics, topography, and climate, contributing to the incredible diversity of life found here. For example, the Ethiopian Highlands are often referred to as the “Roof of Africa,” while the Great Rift Valley cuts through East Africa, creating a unique geological landscape.
The size of Africa also affects its climate patterns. The continent stretches across the equator, leading to a variety of climate zones, from tropical climates in the central regions to arid deserts in the north and south. This diversity influences not only the natural environment but also human activity, agriculture, and settlement patterns.
Regional Analysis
When we examine the map closely, we can see how Africa’s size translates into diverse regional characteristics. North Africa, for instance, is predominantly desert, with countries like Egypt and Libya facing extreme heat and scarce water resources. In contrast, West Africa is characterized by a mix of coastal regions and savannahs, contributing to rich agricultural lands. Nigeria, for example, is the most populous country in Africa and showcases significant urban development in cities like Lagos.
Moving to East Africa, we find some of the continent's highest elevations, such as Mount Kilimanjaro in Tanzania, and expansive wildlife reserves that attract tourists from around the globe. The Great Lakes region, which includes Lake Victoria, is crucial for the biodiversity of the continent. It supports millions of people through fishing and agriculture while also being a vital water resource.
Southern Africa boasts a combination of deserts, savannahs, and coastal regions, with South Africa serving as a major economic hub. The diversity of landscapes here supports both wildlife and human populations, with cities like Cape Town and Johannesburg being key centers of commerce.
Central Africa is perhaps the least explored region, with dense rainforests and rich biodiversity, but it also faces challenges such as deforestation and climate change. Countries like the Democratic Republic of the Congo are vital for global ecological health but struggle with political and economic instability.
Significance and Impact
Understanding Africa's immense size and diversity is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it has significant implications for global biodiversity conservation efforts. The continent is home to countless species, many of which are endemic and face threats from habitat destruction and climate change. The scale of conservation efforts must match the scale of the continent to be effective.
Moreover, Africa's vastness impacts economic development. The continent is rich in natural resources, including minerals and oil, which are vital for global markets. However, the challenge lies in ensuring sustainable development that benefits local populations while preserving the environment.
Current trends show that Africa's population is on the rise, projected to reach over 2 billion by 2050. This growth will undoubtedly impact urbanization, resource management, and economic development strategies. Have you noticed that many countries are investing in infrastructure to support this growing population? This is crucial for enhancing connectivity and trade across the continent, unlocking Africa's potential as a global player.
In conclusion, the "Africa Size Comparison Map" is more than just a visual tool; it serves as a reminder of the continent's vastness, complexity, and the pressing issues it faces. By understanding Africa's geographical significance, we can better appreciate its role in global dynamics and work towards a sustainable future for its diverse populations and ecosystems.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 21, 2025
- Views
- 44
Comments
Loading comments...