Mediterranean Biomes Around the World Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
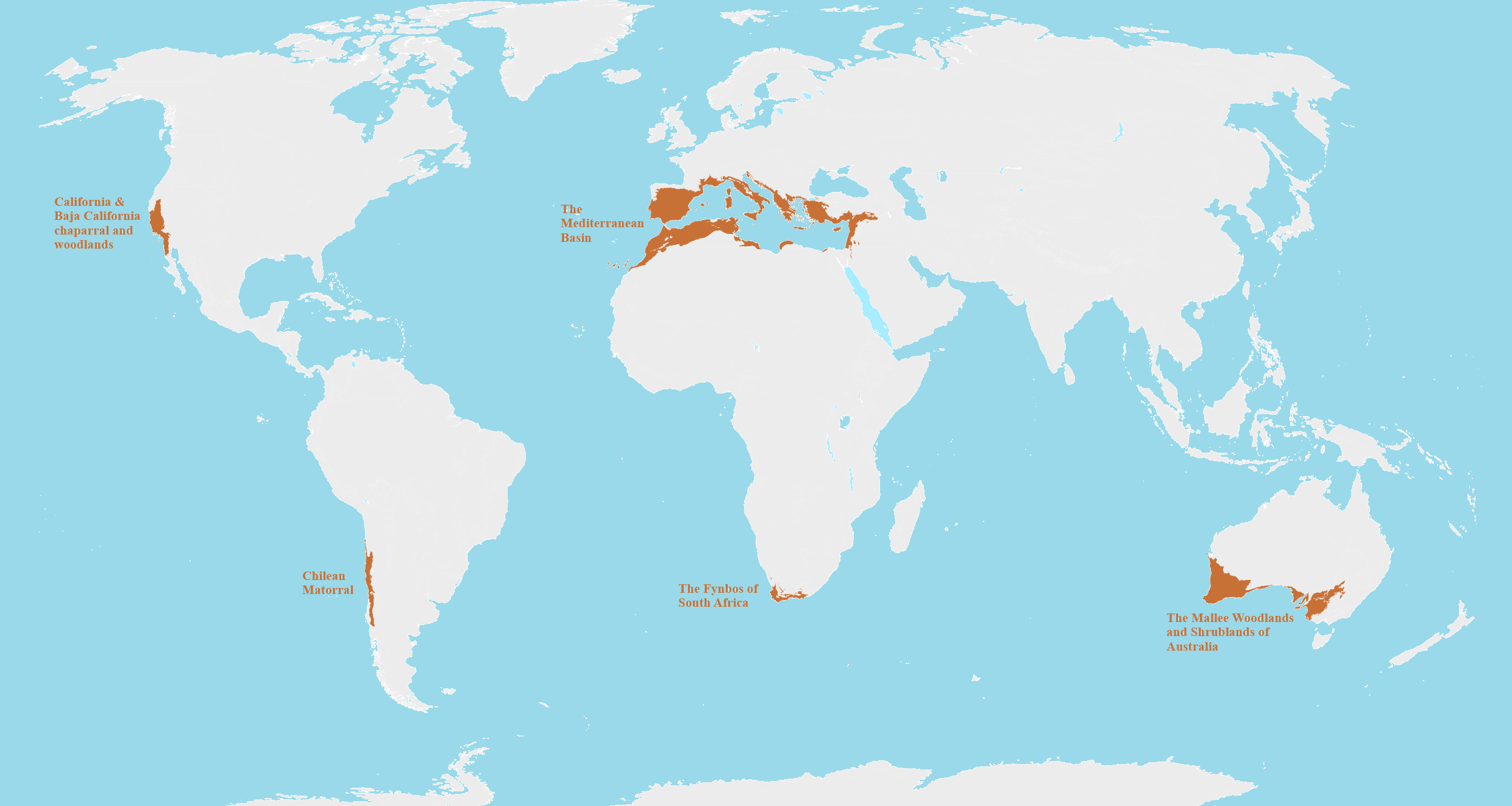
What This Map Shows
This map provides a detailed visualization of Mediterranean biomes across the globe, highlighting regions that share similar climatic conditions, flora, and fauna. The Mediterranean biome is characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, creating a unique environment for a variety of plant and animal species. This map not only delineates the traditional Mediterranean regions of Southern Europe, North Africa, and parts of the Middle East but also illustrates other areas around the world that exhibit similar climatic and ecological characteristics, such as parts of California, Australia, and Chile.
Deep Dive into Mediterranean Biomes
Mediterranean biomes are one of the most biodiverse ecosystems on the planet. They cover about 2% of the Earth’s surface, yet they are home to approximately 20% of the world's plant species. This remarkable biodiversity is largely due to the unique climate and the geological history of these regions.
Interestingly, the Mediterranean biome is primarily defined by its seasonal climatic patterns. During the summer months, these regions experience intense heat and minimal rainfall, which can lead to drought conditions. In contrast, the winter months bring cooler temperatures and significant precipitation. This climate supports a variety of plant life known as sclerophyllous vegetation, which includes hardy shrubs and small trees adapted to conserve water.
Notably, the flora includes iconic species like olive trees, cork oaks, and various types of aromatic herbs like rosemary and thyme. These plants not only thrive in the Mediterranean climate but have also become integral to the local culture and economies, especially in regions like Southern Europe where agriculture is prominent.
From an ecological perspective, Mediterranean biomes are home to countless animal species. Birds, reptiles, and mammals find refuge in these regions, often exhibiting unique adaptations that allow them to survive in an environment where water is scarce during the summer. For example, the endangered California condor and the Mediterranean monk seal both rely on the Mediterranean ecosystem for their survival, showcasing the importance of these biomes in global biodiversity.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing the Mediterranean biomes around the world, it is essential to consider the particular characteristics of each region. In the classic Mediterranean region, such as Southern Spain and Italy, the landscape is often dominated by agricultural terraces and vineyards, reflecting human adaptation to the environment. Here, the climate supports the cultivation of olives and grapes, key components of Mediterranean cuisine.
Contrastingly, in California, the Mediterranean biome is represented in the chaparral ecosystems, which feature dense shrubs and a variety of wildlife, including the California quail and various species of lizards. The state's Mediterranean climate has led to significant urban development, particularly in places like Los Angeles, where the population density impacts the natural habitat.
In Australia, the Mediterranean climate is found in regions like the southwestern corner. This area supports unique flora and fauna, including the critically endangered Western Australian black cockatoo. The impact of climate change poses a significant threat to these ecosystems, highlighting the urgent need for conservation efforts.
Finally, in South America, areas like central Chile display Mediterranean characteristics with their own unique ecosystems, such as the sclerophyll forests that are home to diverse wildlife, including the endangered Chilean flamingo.
Significance and Impact
Understanding Mediterranean biomes is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, they are essential for maintaining global biodiversity, acting as refuges for numerous species. However, these biomes are increasingly threatened by climate change, urbanization, and agricultural expansion. The Mediterranean region is already experiencing shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns, raising concerns about the future viability of these ecosystems.
Moreover, the economic implications of Mediterranean biomes cannot be overstated. They are vital for agriculture, tourism, and even pharmaceuticals, as many medicinal plants originate from these regions. The preservation of these biomes is essential not only for environmental health but also for sustaining local economies and cultures.
In conclusion, the Mediterranean biomes map provides a valuable insight into the distribution and significance of these unique ecological regions. As climate change continues to challenge these areas, understanding their dynamics becomes increasingly important for conservation efforts and sustainable development strategies. By raising awareness and addressing the threats they face, we can work towards preserving these vital ecosystems for future generations.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 19, 2025
- Views
- 70
Comments
Loading comments...