Population Concentration Map of Finland

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
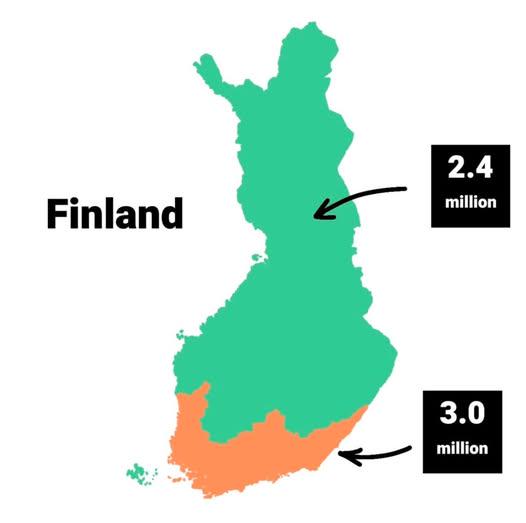
What This Map Shows
The "Population Concentration of Finland" map provides a visual representation of where the majority of Finland's inhabitants are located. It highlights the urban centers, rural areas, and the varying population densities across different regions. This visualization is crucial for understanding demographic patterns, urbanization trends, and regional development in Finland.
Transitioning from the map, let's delve deeper into Finland's population dynamics.
Deep Dive into Population Distribution in Finland
Finland is known for its unique demographics, where a relatively small population of approximately 5.5 million people is spread over a vast area of approximately 338,455 square kilometers. The population density varies significantly across the country, creating striking contrasts between urban and rural areas.
A significant majority of Finns live in urban settings, particularly in the southern regions. Cities like Helsinki, Vantaa, and Espoo form a metropolitan area that houses over a million residents. Helsinki, as the capital, is not just the political heart; it’s also the economic and cultural hub of Finland. Interestingly, about 1.5 million people reside in the greater Helsinki region, accounting for nearly a quarter of the nation's total population.
However, venture north or east, and you enter sparsely populated areas. For instance, Lapland, known for its stunning natural beauty and vibrant indigenous Sámi culture, has a population density of less than 2 people per square kilometer. This stark contrast raises questions about urbanization and the migration patterns that drive people towards cities while others choose to remain in rural settings.
Moreover, Finland's population is aging, with projections indicating that by 2030, almost 25% of the population will be over 65. This demographic shift poses challenges for healthcare, social services, and the economy. Interestingly, while the overall population is aging, urban areas tend to attract younger residents, leading to a vibrant, multicultural urban life, while rural areas face the risk of depopulation.
Another important aspect of the population distribution is the role of immigration. Finland has seen an increase in immigrants over the past decade, contributing to the diversity of its population. Many immigrants settle in urban areas, particularly in Helsinki and its surroundings, adding layers to the cultural fabric of these cities.
Regional Analysis
When we break down the map regionally, we can see distinct population patterns. In southern Finland, cities like Turku and Tampere also boast significant populations, serving as important economic and cultural centers. Each of these cities has developed unique identities, drawing people for education, employment, and lifestyle opportunities.
Conversely, as we shift towards central and northern regions, the population density decreases. Areas like Kainuu and North Karelia, while rich in natural resources and beauty, are experiencing population decline due to youth migration to urban centers for better job prospects.
Interestingly, the coastal regions, particularly the archipelago, show a mixed pattern. While some islands are densely populated during the summer months due to tourism, they are quite empty in winter. This seasonal fluctuation highlights how geography and climate influence residency patterns in Finland.
Significance and Impact
Understanding population concentration in Finland is essential for various reasons. It affects economic planning, infrastructure development, and the provision of public services. Urbanization trends indicate a need for sustainable development practices to address the growing populations in cities while rejuvenating rural areas.
Moreover, as Finland grapples with an aging population and declining birth rates, the government is faced with the challenge of supporting an economy that relies on a shrinking workforce. This creates a pressing need for policies that not only attract and retain young people in rural areas but also effectively integrate immigrants into society.
Looking ahead, the interplay between urban growth and rural decline will likely shape Finland's future. As cities expand, they must also account for environmental sustainability and quality of life. Will Finland find a way to balance these challenges while preserving its unique cultural and geographical identity? This is a question worth pondering, as the answers could define the nation’s trajectory in the coming decades.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 14, 2025
- Views
- 80
Comments
Loading comments...