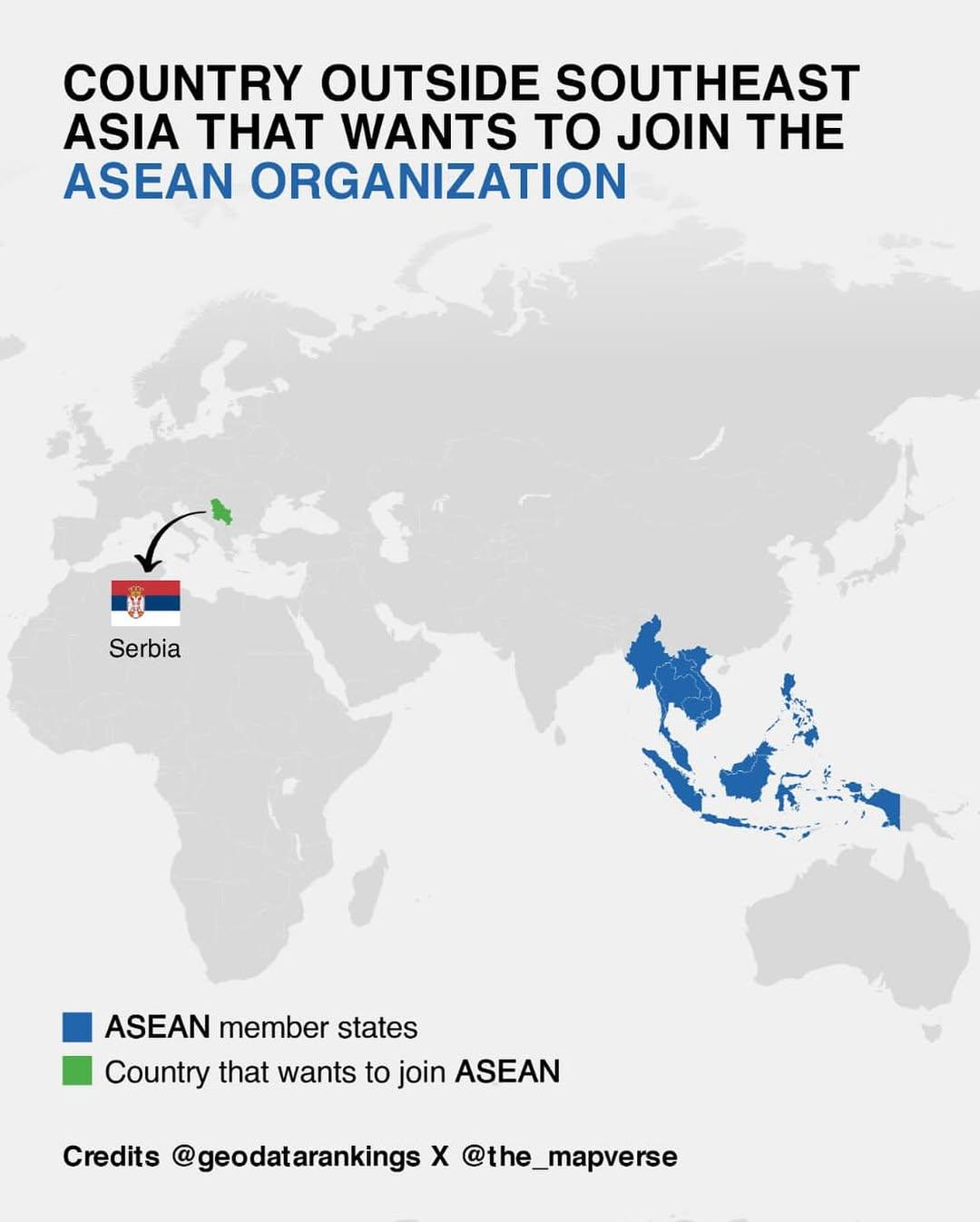
Map of Countries Outside Southeast Asia Wanting to Join ASEAN

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map illustrates the various countries outside of Southeast Asia that have expressed interest in joining the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). While ASEAN is primarily a regional grouping focused on promoting economic growth, political stability, and cultural exchange among its ten Southeast Asian member states, there is growing interest from other nations that see potential benefits in aligning with this influential bloc. Countries like India, Japan, and South Korea are highlighted on the map, each with unique reasons for wanting to engage more closely with ASEAN.
Deep Dive into ASEAN Membership Aspirations
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations was founded in 1967, originally comprising Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand. Over the years, it has expanded to include Brunei, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar, and Cambodia. The primary goals of ASEAN include fostering economic growth, ensuring regional peace and security, and promoting cultural exchanges.
Interestingly, the interest from outside nations stems from several factors. For instance, India views ASEAN as a strategic partner in its “Act East” policy, intending to enhance trade and investment ties with Southeast Asia. With a population of over 1.3 billion, India's involvement could significantly impact ASEAN's economic dynamics, especially in sectors like information technology and manufacturing.
Similarly, Japan has maintained a long-standing economic relationship with ASEAN countries, investing heavily in infrastructure, technology, and education. The Japanese government has been actively seeking to strengthen its ties with ASEAN as a counterbalance to China's growing influence in the region. Japan's technological advancements and economic prowess position it as a vital partner for ASEAN in terms of innovation and sustainable development.
South Korea is another key player looking to deepen its engagement with ASEAN. With its dynamic economy and cultural influence through the Korean Wave (Hallyu), South Korea aims to tap into ASEAN's burgeoning markets. The Free Trade Agreement (FTA) between South Korea and ASEAN is a testament to this growing relationship, enhancing trade flow and economic collaboration.
In addition to these countries, there are emerging interests from nations like Australia, which seeks to bolster its political and economic presence in Southeast Asia. Australia's involvement in ASEAN dialogues and initiatives underscores its commitment to regional cooperation, especially in areas like security and climate change.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing the countries outside of Southeast Asia that wish to join or engage with ASEAN, it's essential to look at how different regions approach this desire. For example, India’s interest can be contrasted with that of Japan. India focuses on enhancing trade and cultural ties, while Japan emphasizes technological investment and strategic partnerships. This difference highlights how geography influences each country's approach to ASEAN.
Australia, while geographically distant, leverages its historical ties and political relationships to seek deeper integration with ASEAN. Interestingly, the motivations of these countries vary based on their economic needs and geopolitical strategies. For instance, while India's population and workforce could significantly contribute to ASEAN's labor market, Japan's focus is on high-tech industries and innovation.
On the other hand, South Korea's cultural diplomacy through entertainment and technology presents a unique avenue for engaging with ASEAN's youthful demographic. By analyzing these regional approaches, we can see a multifaceted picture of international relations that transcends mere geography and delves into the realm of economic strategy and cultural exchange.
Significance and Impact
The aspirations of countries outside Southeast Asia to join ASEAN carry significant implications for regional stability and economic growth. As these nations seek closer ties, the potential for economic collaboration increases, presenting opportunities for trade, investment, and shared development goals. Moreover, the inclusion of new members could reshape ASEAN’s dynamics, bringing fresh perspectives and challenges.
Additionally, as global economic power shifts towards Asia, the relevance of ASEAN continues to grow. Countries looking to integrate with ASEAN can leverage the bloc's collective bargaining power on the global stage. This is particularly significant in the context of ongoing trade tensions and geopolitical rivalries, where a united ASEAN could serve as a stabilizing force.
In conclusion, the interest from countries outside of Southeast Asia to join ASEAN is indicative of a rapidly changing geopolitical landscape. As ASEAN continues to evolve, the engagement of these nations will not only enhance economic ties but also contribute to a more interconnected and cooperative regional framework. The future of ASEAN could very well hinge on how effectively it manages these external interests and integrates them into its existing structure, thus fostering a more comprehensive approach to regional cooperation.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 12, 2025
- Views
- 72
Comments
Loading comments...