Indian States Literacy Rate Compared to Countries Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
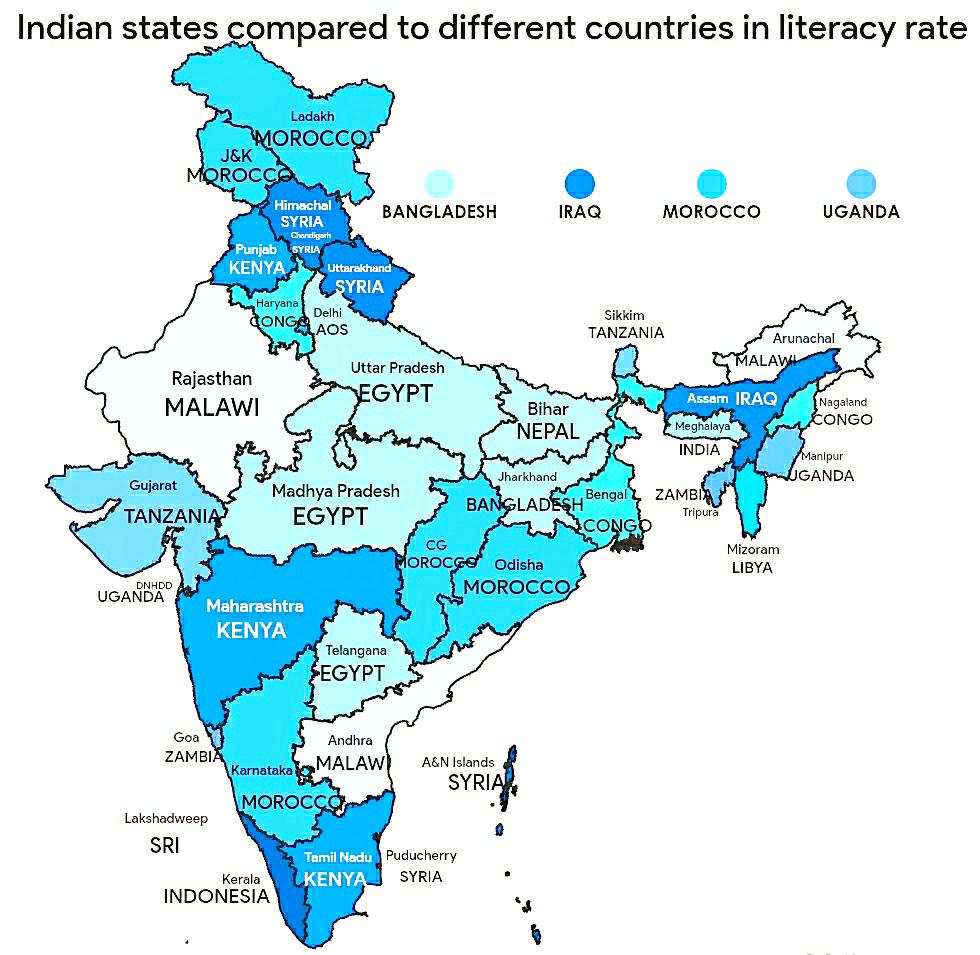
What This Map Shows
This map presents a fascinating comparison of the literacy rates across various Indian states, juxtaposing them with those of different countries. By visualizing such data, we can instantly grasp where India stands in relation to the global literacy landscape. Literacy is a vital indicator of development, reflecting not only education levels but also economic prospects and social health in a given area. The map effectively highlights disparities, showcasing which Indian states are on par with other countries in terms of literacy, and which ones have room for improvement.
Deep Dive into Literacy Rates
Literacy rates are critical benchmarks for assessing a country's education system and overall human development. In India, literacy is defined as the ability of individuals aged seven and above to read and write. According to the latest census data, India's national literacy rate stands at approximately 77.7%. However, this figure masks significant regional variations. For instance, states like Kerala boast a literacy rate of over 96%, comparable to some of the most developed countries. In contrast, states like Bihar and Uttar Pradesh lag behind, with literacy rates hovering around 70% and 73% respectively.
Interestingly, the literacy rates in Indian states can be compared to those of various countries. For example, Kerala's literacy rate is akin to that of Japan, a nation renowned for its educational excellence. Meanwhile, states like Meghalaya show literacy rates similar to those of countries in Sub-Saharan Africa. The stark contrasts among states reflect historical, socio-economic, and cultural factors that influence educational attainment.
The role of government initiatives, such as the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan and the Right to Education Act, has been pivotal in improving literacy rates in recent years. However, challenges remain, particularly in rural areas where access to quality education is still a significant barrier. The urban-rural divide is notable, with cities like Mumbai and Delhi achieving higher literacy rates compared to their rural counterparts.
Additionally, the medium of instruction plays a crucial role in literacy. Many states have adopted regional languages for education, which can either aid in comprehension or create barriers, depending on the context. The effectiveness of educational policies and the quality of teaching also contribute significantly to these disparities.
Regional Analysis
When we break down the map by region, we can see distinct patterns emerge. In southern India, states like Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh also show literacy rates that are comparable to several middle-income countries, reflecting strong investment in education since the late 20th century. Conversely, northern states like Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh are still grappling with lower literacy levels, influenced by socio-economic factors such as poverty and gender inequality in education.
In the east, states like West Bengal display literacy rates that rival nations such as Sri Lanka, while Odisha is still catching up, reflecting the impact of historical neglect in educational infrastructure. In the northeast, states like Nagaland and Mizoram have achieved impressive literacy rates, often surpassing those of several ASEAN countries, showcasing the region's unique educational strategies and community involvement.
Significance and Impact
Understanding literacy rates is more than a statistical exercise; it has profound implications for development policy and economic growth. High literacy rates correlate with improved health outcomes, reduced poverty levels, and greater participation in civic life. As India aims to become a global economic powerhouse, enhancing literacy is crucial. The National Education Policy 2020 aims to address these disparities by promoting holistic and inclusive education that caters to diverse needs.
Moreover, as globalization continues to shape the economy, a well-educated workforce will be essential for fostering innovation and competitiveness. Have you noticed how countries with high literacy rates often lead in technological advancements? This trend is evident in the case of India, where states with better literacy are also witnessing rapid economic development.
In conclusion, this map serves not only as a visualization of literacy rates but as a call to action. Improving literacy across all Indian states is not just a goal; it’s a necessity for national progress and social equality. As we look to the future, addressing educational disparities will be key in shaping a well-informed and empowered citizenry, ready to tackle global challenges head-on.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 12, 2025
- Views
- 88
Comments
Loading comments...