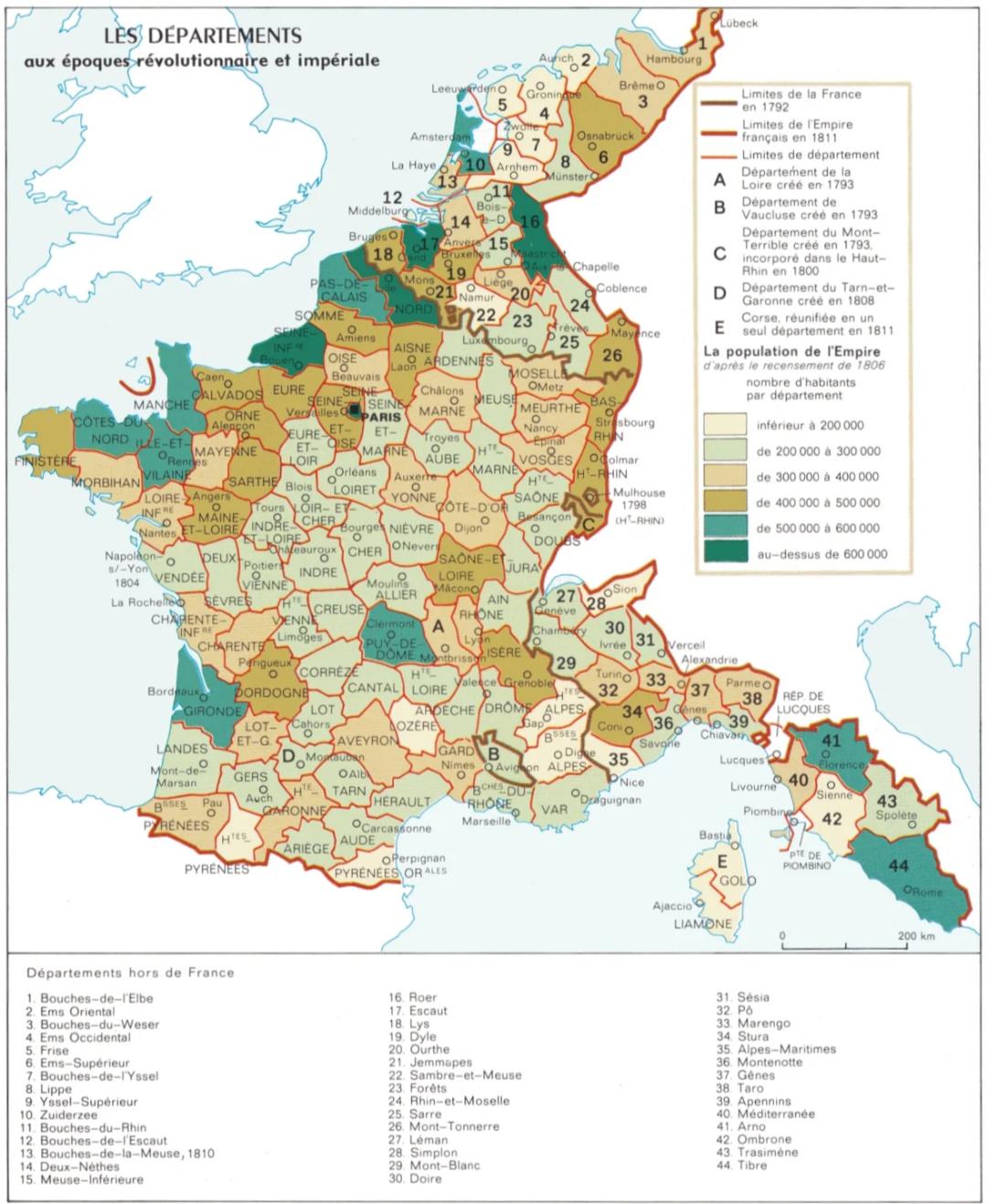
Population Map of French Empire Departements 1806

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The map titled "Population of the Departements of the First French Empire (1806 Census)" illustrates the population distribution across the various administrative regions (or departements) established during Napoleon Bonaparte's rule. This historical visualization is not just a representation of numbers; it provides a snapshot of demographic trends, urbanization, and social structures in early 19th-century France. The census data captured on this map showcases how populations were concentrated in certain areas, reflecting economic activities, geography, and historical significance.
Deep Dive into Population Dynamics in the First French Empire
The early 1800s were a transformative period for France, especially under the ambitious reign of Napoleon. The census of 1806 revealed significant insights into the population distribution throughout the empire, which at that time included parts of present-day Belgium, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and Italy. What's fascinating is that this map serves as a historical document that illustrates not only the sheer number of inhabitants but also their urban versus rural distribution, economic activities, and social organization.
In 1806, the total population of the French Empire was approximately 27 million. Paris, as the capital, was the most populous department, boasting over 600,000 residents. This concentration of people indicates the city's role as a political, cultural, and economic hub. In contrast, many rural areas, particularly in the less developed regions of Brittany or the mountainous territories of the Alps, had significantly lower population densities.
The disparities in population density across the map can be attributed to various factors. Urban areas typically attracted people due to economic opportunities, access to resources, and better living conditions. The industrial revolution was beginning to take root, and cities were becoming centers of commerce and industry. Interestingly, the coastal areas of Normandy and the Mediterranean regions also showed higher populations, possibly due to trade and agriculture.
The map also reflects the effects of the Napoleonic Wars and territorial changes, as the empire expanded and contracted throughout Europe. Understanding these population dynamics not only highlights the demographic landscape of the time but also foreshadows future urban development and migration patterns that would emerge in the decades to follow. For instance, the growth of cities like Lyon and Marseille would continue well into the 19th century, driven by industrialization and trade.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the population data by region reveals significant variations across the First French Empire. For example, the northern regions, particularly areas like Picardy and Champagne, had a higher concentration of agriculture and thus a larger rural workforce. The densely populated regions of Île-de-France, which included Paris, contrasted sharply with the sparsely populated mountainous regions of Auvergne and the Massif Central.
Interestingly, the southeast regions, such as Provence, not only had agricultural bases but also benefitted from tourism and trade, leading to higher population figures. In the northwest, Brittany struggled with a declining population due to emigration and economic hardships during this period. The demographic trends depicted in the map provide insights into the geographical and economic factors that influenced where people lived and how they interacted with their environment.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the population distribution in the First French Empire is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it allows us to grasp the socio-economic fabric of early 19th-century France and how these patterns set the stage for future developments. The disparities in population density influenced infrastructure projects, social policies, and even military strategies during the Napoleonic Wars.
Moreover, the impact of urbanization seen in this map can be correlated with contemporary issues such as urban planning, migration, and demographic changes. Today, France continues to grapple with population distribution challenges, especially as urban centers expand and rural areas decline. The historical context provided by the 1806 census offers a reflective lens through which we can examine current trends, such as the movement towards urbanization and the socio-economic dynamics that accompany it. As we navigate these changes, understanding our past remains essential.
In conclusion, the population map of the First French Empire not only serves as a historical artifact but also as a reminder of how demographic changes shape societies over time. It encourages us to ponder: how will the population dynamics of today influence the France of tomorrow?
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 9, 2025
- Views
- 82
Comments
Loading comments...