Map of the Roman Empire at Its Peak 117 A.D.

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
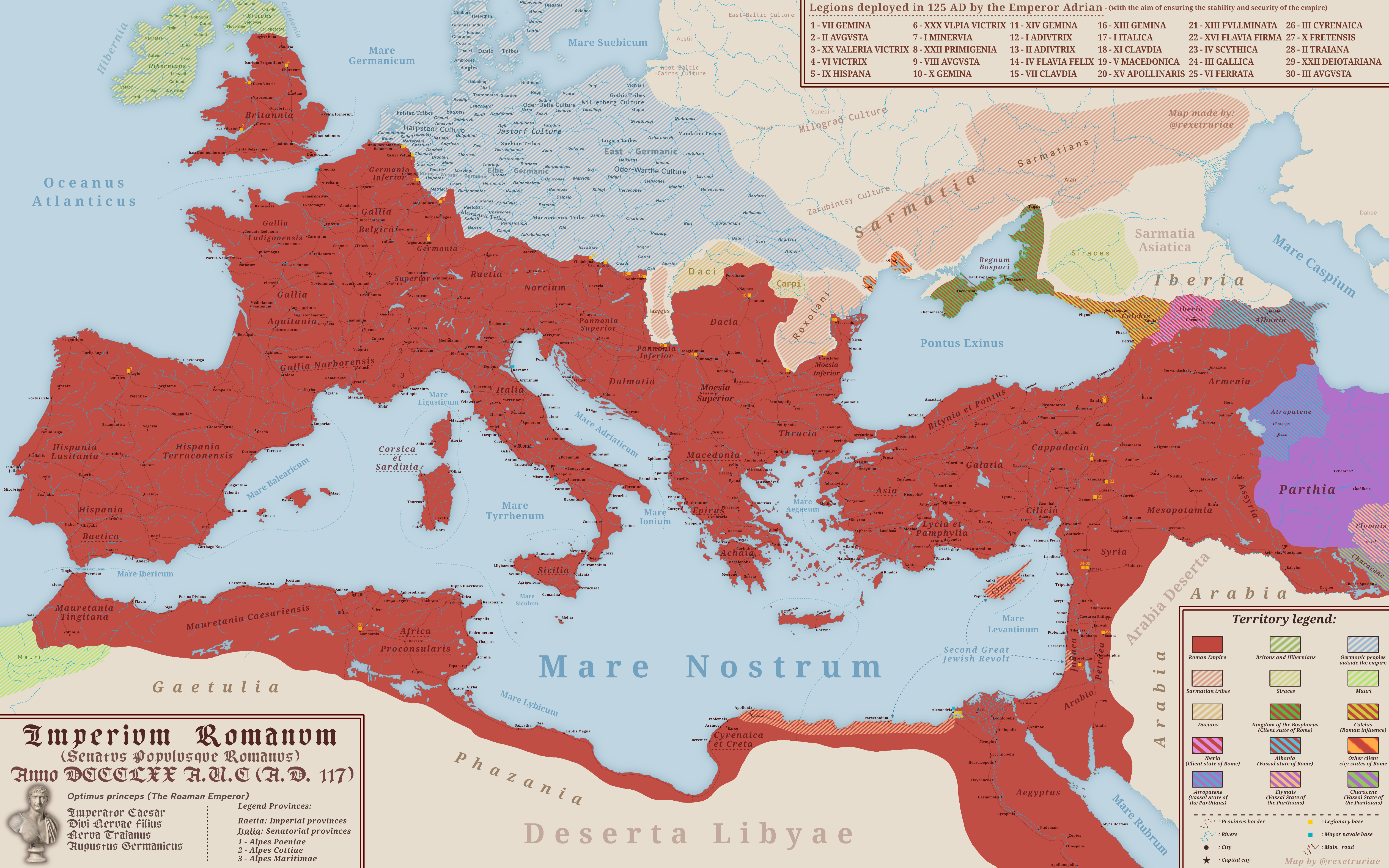
The map titled "The Roman Empire at Its Peak 117 A.D." illustrates the vast territorial expanse of one of history's most influential empires at its zenith. At this time, the Roman Empire reached its maximum size, stretching from the northern reaches of Britain down to the deserts of North Africa, and from the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the shores of the Black Sea in the east. This impressive visualization provides a clear representation of the boundaries of Roman territories, key cities, and important trade routes that defined the empire's economic and military prowess.
Deep Dive into the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was not just a political entity; it was a complex tapestry of cultures, economies, and societies. At its peak, the empire encompassed approximately 5 million square kilometers and is estimated to have had a population of around 60 million people. This diversity was one of the empire's strengths, allowing it to assimilate various cultural elements while maintaining a unified legal framework under Roman law.
Economically, the empire thrived due to its extensive network of roads and sea routes that facilitated trade. The famous Roman roads, such as the Via Appia, connected major cities and allowed for the efficient movement of goods, troops, and information. Have you ever wondered how these roads contributed to the empire's expansion? By enabling quick military deployment and promoting trade, they played a crucial role in maintaining control over distant provinces.
Moreover, the Mediterranean Sea acted as a vital trade artery, linking various regions through commerce. Goods like olive oil, wine, and grain were traded extensively, and the empire's wealth was reflected in the luxurious lifestyles of its elite. Interestingly, the Roman economy was also bolstered by the vast agricultural production from its provinces, particularly in regions such as Egypt and North Africa, which were known as the empire's breadbasket.
The military might of Rome was another cornerstone of its dominance. The Roman legions, renowned for their discipline and training, were crucial in both expanding and defending the empire's borders. The strategic placement of forts and garrisons throughout the territories ensured that Rome could respond to threats swiftly, maintaining stability and order.
Regional Analysis
When we dissect the Roman Empire's regions, we can observe significant variations in culture, economy, and governance. For instance, in the western provinces, such as Gaul (modern-day France), Romanization took on unique characteristics, blending local customs with Roman traditions. The Gallic Wars led by Julius Caesar facilitated the integration of these regions into the empire, showcasing the adaptability of Roman culture.
Conversely, in the eastern provinces, such as Asia Minor and the Levant, the influence of Hellenistic culture was profound. Cities like Antioch and Ephesus became important centers of trade and culture, where Greek art and philosophy flourished alongside Roman engineering and architecture. Interestingly, these eastern regions contributed significantly to the empire's intellectual life, serving as hubs of learning and innovation.
Another stark contrast can be observed in the governance of provinces. The provinces in the west were often governed directly by Roman officials, while those in the east were frequently allowed a degree of autonomy, particularly in local governance. This difference can be attributed to the varying levels of resistance and acceptance of Roman rule, highlighting the empire's flexibility in administration.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the Roman Empire at its peak is crucial for grasping the foundation of modern Western civilization. The legal systems, architectural innovations, and military strategies developed during this period have had lasting impacts on later societies. For example, the concept of citizenship and legal rights, which originated in Rome, laid the groundwork for contemporary ideas of democracy and governance.
Moreover, the cultural exchanges facilitated by the empire helped shape languages, religions, and customs that are still evident today. The spread of Christianity, for instance, was significantly influenced by the infrastructure established by the Romans. As we analyze current trends, we can see echoes of Roman influence in modern legal systems and urban planning.
As we move forward, the study of the Roman Empire offers vital lessons on governance, cultural integration, and economic management that remain relevant in today’s globalized world. The empire's rise and fall also remind us of the impermanence of power and the importance of adaptability in an ever-changing landscape. The lessons learned from this extensive history continue to resonate, prompting us to reflect on our own societal structures and cultural identities.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 8, 2025
- Views
- 62
Comments
Loading comments...