Greener Areas Near India-Pakistan Border Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
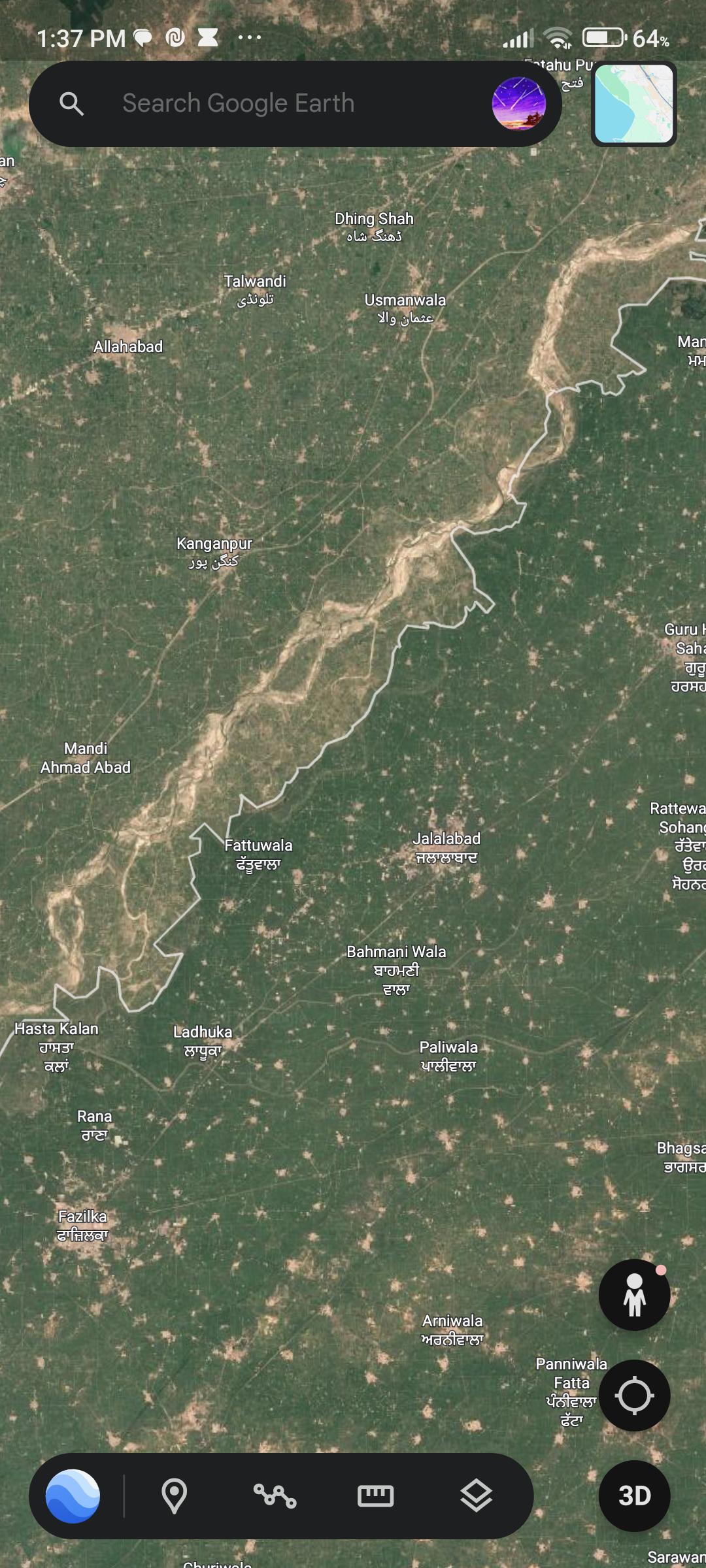
What This Map Shows
The visualization titled "Why is the grass greener on this side?" illustrates the stark contrast in vegetation along the India-Pakistan border. On the right side of the border, which represents India, the map shows a significantly greener landscape compared to the drier, more arid regions on the left, which denote Pakistan. This striking difference raises questions about the underlying factors contributing to this discrepancy in vegetation, soil quality, and agricultural practices.
Deep Dive into Vegetation and Agriculture
The lush green areas in India can be largely attributed to several key factors: agricultural practices, irrigation systems, and climatic conditions. India’s diverse climate ranges from tropical in the south to temperate in the north, allowing for a wide variety of crops and vegetation. However, what’s particularly interesting is the role of irrigation, especially in states like Punjab and Haryana, which are located close to the border.
Punjab, often referred to as the "Granary of India," boasts one of the most intensive agricultural systems in the country. The region benefits from the extensive canal irrigation system derived from the Indus River, which has long been a lifeline for its agriculture. The Green Revolution of the 1960s further propelled India’s agricultural output, introducing high-yield crop varieties and modern farming techniques that have transformed the landscape into a vibrant agricultural hub. This has resulted in not just greener fields, but also a robust economy centered around agriculture.
On the other hand, Pakistan faces challenges in agricultural productivity due to a combination of factors. The region has experienced significant water management issues. The Indus River, which is also crucial for Pakistan's agriculture, has been subject to over-extraction and inefficient irrigation practices, leading to a decline in soil fertility and crop yields. Additionally, the impacts of climate change have resulted in more frequent droughts and irregular rainfall patterns, exacerbating the difficulties farmers face.
Interestingly, the soil composition and land management practices further differentiate the two sides of the border. While Indian farmers have increasingly adopted sustainable farming practices, such as crop rotation and organic farming, many areas in Pakistan still rely heavily on traditional methods, which may not be as effective in maintaining soil health and productivity. This difference in agricultural approaches contributes significantly to the disparities observed in vegetation along the border.
Regional Analysis
When we break down the vegetation patterns regionally, we find varying degrees of greenery along the border. In India’s Punjab region, for instance, the extensive irrigation systems allow for the cultivation of wheat, rice, and sugarcane, which thrive in these conditions. The contrast becomes stark when you look at the adjacent areas in Pakistan, where the Thal Desert and arid regions dominate the landscape, leading to limited agricultural output and sparse vegetation.
In the Sindh province of Pakistan, the situation is somewhat better due to the presence of the Indus River. However, the over-reliance on this single water source has led to significant challenges, including salinity issues in the soil, which further diminishes agricultural productivity. The contrast between the lush fields of Indian Punjab and the dry, cracked soil of Sindh illustrates the impact of water management practices and agricultural policies.
Interestingly, as you move towards the Rajasthan border in India, the vegetation becomes sparser due to the Thar Desert, yet the agricultural techniques employed have allowed for the cultivation of drought-resistant crops, showcasing adaptability in farming practices.
Significance and Impact
Understanding why one side of the border is greener than the other is not just a matter of curiosity; it has real-world implications. The disparities in vegetation directly impact food security, economic stability, and even geopolitical relations between India and Pakistan. For instance, as climate change continues to affect weather patterns, the reliance on sustainable agricultural practices becomes paramount. Countries need to collaborate on water management and agricultural strategies to ensure mutual benefits.
Furthermore, these differences in agricultural productivity could influence migration patterns, economic opportunities, and long-term regional stability. As such, addressing these issues could pave the way for improved relations and cooperative efforts in resource management.
In conclusion, the greener pastures of India, juxtaposed against the drier landscapes of Pakistan, tell a story of agricultural practices, water management, and climatic influences that shape the daily lives of people on both sides of the border. As we move forward, recognizing these geographical disparities will be crucial for fostering a sustainable future for the region.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 7, 2025
- Views
- 96
Comments
Loading comments...