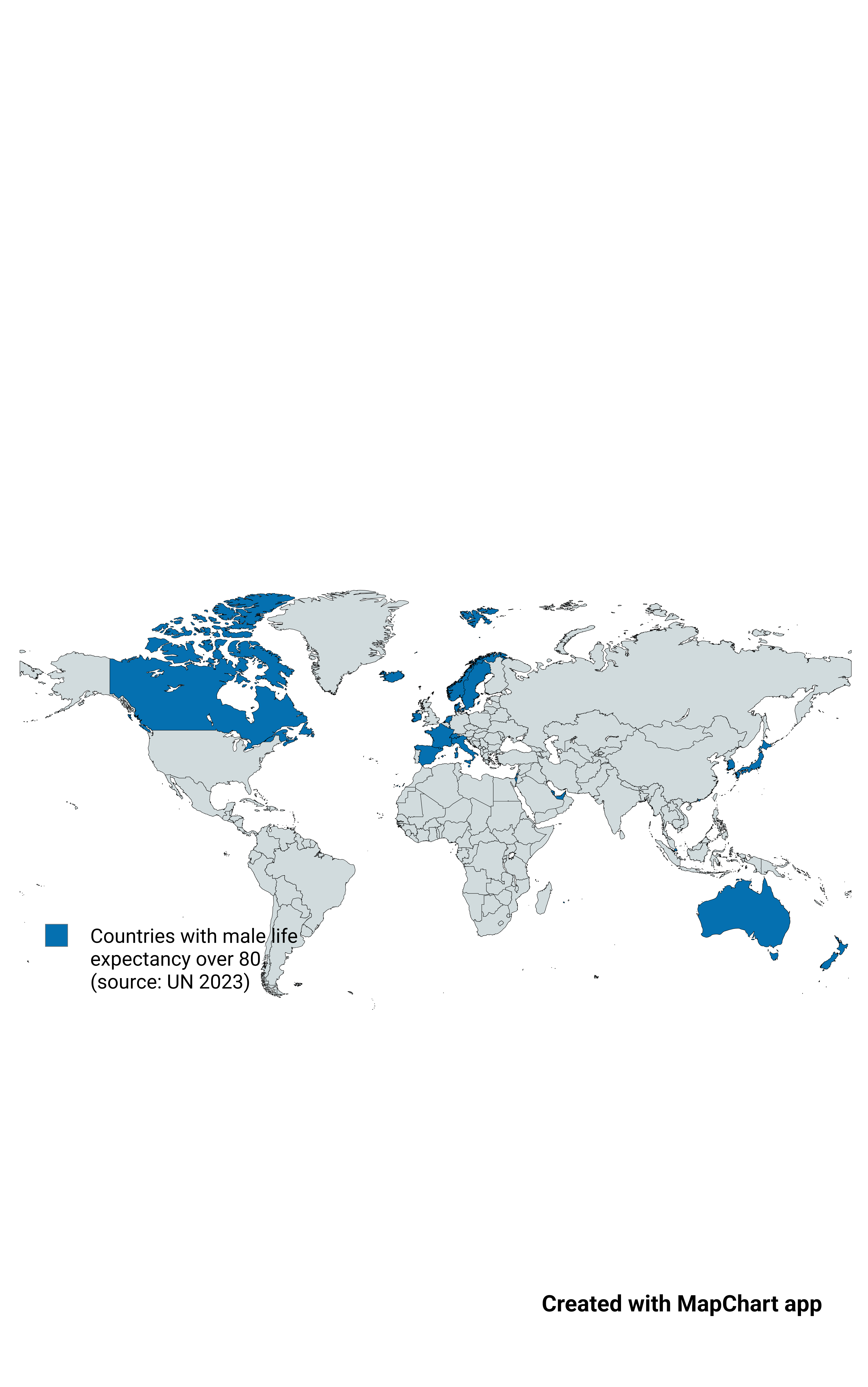
Map of Countries with Male Life Expectancy Over 80

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map highlights countries where male life expectancy exceeds 80 years, a more stringent criterion compared to the general life expectancy metrics typically showcased. While many countries boast an overall life expectancy surpassing 80 years when both genders are considered, this visualization zeroes in on the male demographic alone. This stricter threshold reveals a more selective group, as male life expectancy generally lags behind female life expectancy due to various biological, social, and lifestyle factors. As a result, countries like the UK, Belgium, and Germany, which have robust overall life expectancies, are notably absent from this map due to lower male averages.
Deep Dive into Male Life Expectancy
Life expectancy is a crucial indicator of the health and well-being of a population. It reflects the average number of years a person can expect to live based on current mortality rates. Male life expectancy often trails behind that of females due to several reasons, including biological differences, risk behaviors, occupational hazards, and healthcare access.
Interestingly, the countries that do meet the criteria for male life expectancy over 80 years predominantly fall into specific regions, such as East Asia and parts of the Mediterranean. For instance, countries like Japan and Switzerland are often highlighted for their exceptional healthcare systems, healthy diets, and active lifestyles that contribute to longevity. Japan, with its rich tradition of healthy eating, low obesity rates, and a strong emphasis on community and family, boasts one of the highest male life expectancies in the world.
Moreover, the Nordic countries, including Sweden and Norway, have made significant strides in public health policies that promote wellness and preventive care. These nations invest heavily in healthcare and social welfare, resulting in lower mortality rates among men, which directly impacts life expectancy. The emphasis on work-life balance and mental health also plays a critical role in these high figures.
On the other hand, countries that struggle with lower male life expectancies often face issues such as high rates of smoking, poor diet, and limited access to healthcare services. Countries in Sub-Saharan Africa, for example, often see lower averages due to various factors, including the prevalence of diseases like HIV/AIDS and malaria, along with economic instability.
Interestingly, cultural factors cannot be overlooked. In many societies, traditional gender roles may result in men taking on riskier jobs or engaging in harmful behaviors, impacting their health outcomes. These cultural aspects can significantly shape life expectancy figures in different regions, demonstrating the complex interplay between health, environment, and societal norms.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing the regions represented on the map, it's clear that East Asia stands out with countries like Japan and South Korea leading the charge. Both nations have made substantial investments in healthcare and education, which have contributed to healthier lifestyles and longevity among males. Japan's traditional diet, rich in fish and vegetables, combined with its stress on community health practices, has led to remarkable life expectancy figures.
In Europe, countries such as Switzerland and Iceland also lead with male life expectancies over 80 years. Switzerland's strong public health system, paired with a high standard of living, ensures that men have access to quality healthcare and support services. Comparatively, Nordic countries, known for their robust social welfare systems, also present high male life expectancies, showcasing how effective policies can lead to better health outcomes.
Conversely, regions like Africa and parts of South Asia face significant challenges. Countries like Nigeria and India struggle with a variety of health issues that lower male life expectancy, including infectious diseases, malnutrition, and inadequate healthcare infrastructure. These disparities highlight the importance of addressing health inequities to improve outcomes.
Significance and Impact
Understanding male life expectancy is crucial, not just for demographics but for shaping public policy and health initiatives. As life expectancy rates rise, it brings attention to the quality of life for older populations and the need for systems that support aging men. Improved longevity can place strain on healthcare systems, necessitating robust frameworks to accommodate an aging demographic.
Additionally, the trends observed in this map can help inform global health initiatives aimed at reducing disparities. By identifying regions with lower male life expectancy, targeted interventions can be implemented to address specific health risks and improve overall quality of life. This data can also provide insights for countries striving to enhance their health systems and promote healthier lifestyles among men.
In conclusion, while the map of countries with male life expectancy over 80 years presents a selective view, it underscores the importance of addressing the factors that contribute to health disparities. By focusing on the male demographic, we can better understand the broader implications for public health and societal well-being, paving the way for future improvements in health outcomes worldwide.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 7, 2025
- Views
- 78
Comments
Loading comments...