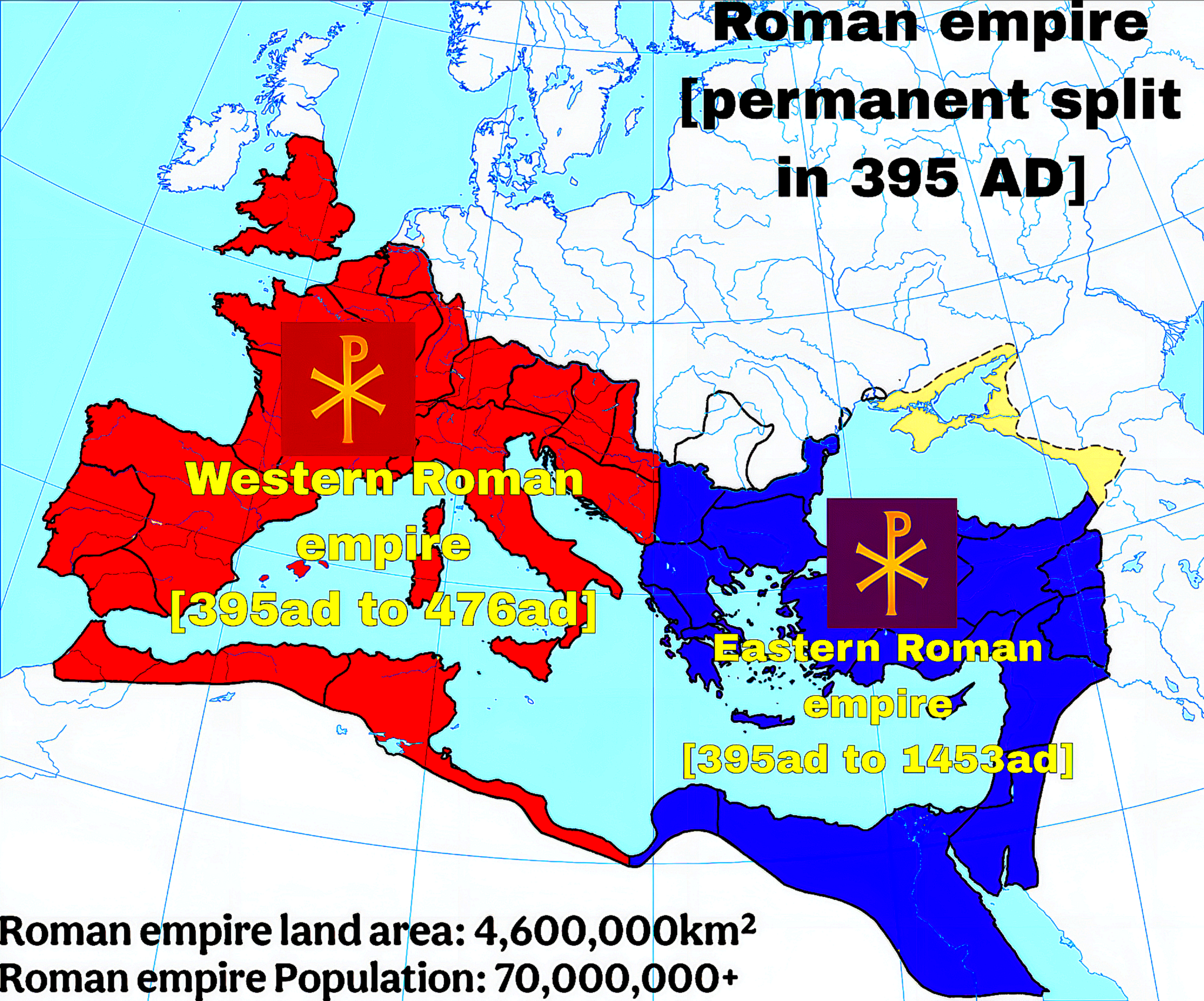
Map of the Permanent Split of the Roman Empire in 395 AD

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The map titled "The Permanent Split of the Roman Empire in 395 AD" visually delineates the division of the Roman Empire into the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. This split occurred during the reign of Emperor Theodosius I, marking a pivotal moment in history that would significantly influence the political, cultural, and social landscapes of Europe and the Mediterranean for centuries to come. The visualization highlights the geographical boundaries and key cities of each empire, providing a clear representation of the territories that fell under Roman control at this critical juncture.
Deep Dive into the Roman Empire's Division
The Roman Empire, at its height, was one of the most expansive and influential empires in history. However, by the late 4th century AD, several factors contributed to its division. Internal strife, economic difficulties, and external pressures from invading tribes led to an administrative restructuring that ultimately resulted in the formal split in 395 AD. This division was not merely administrative; it reflected growing cultural and political divergences between the two halves of the empire.
The Western Roman Empire, with its capital in Rome and later Ravenna, faced increasing challenges from Germanic tribes. This region experienced significant upheaval, culminating in the eventual fall of Rome in 476 AD. Interestingly, the Western Empire struggled with urban decay, a declining economy, and a series of ineffective leaderships, which hastened its downfall.
On the other hand, the Eastern Roman Empire, often referred to as the Byzantine Empire, thrived. With its capital at Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul), the Eastern Empire managed to maintain relative stability and prosperity for nearly a thousand years after the split. This region benefitted from a strategic location that facilitated trade between Europe and Asia, allowing for a flourishing economy. Additionally, the Eastern Empire preserved much of the Roman law and governance structures, which would later inform European legal traditions.
What’s fascinating is how the cultural and religious dynamics of the two empires diverged. The Eastern Roman Empire became a center of Christianity, with the Orthodox Church playing a significant role in its governance and culture. In contrast, the Western Empire struggled with the rise of various barbarian kingdoms and the establishment of the Papacy as a significant political force. This led to a distinct development of Western Christianity, which would evolve differently from its Eastern counterpart.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map reveals significant differences between the Western and Eastern Roman Empires. The Western Empire included territories like Gaul (modern France), Hispania (Spain), and parts of North Africa, which were often in turmoil due to invasions and internal revolts. For example, the Visigoths, Vandals, and Huns frequently tested the defenses of the Western provinces, leading to a fragmented political landscape.
In contrast, the Eastern Empire encompassed regions such as the Balkans, Asia Minor, and the Levant. These areas were relatively stable and culturally rich. The cities of Antioch, Alexandria, and Constantinople became hubs of learning, commerce, and culture. The Eastern Empire's ability to engage in trade along the Silk Road and its strategic maritime routes contributed to its economic strength. Interestingly, this economic prosperity allowed the Eastern Empire to invest in impressive architectural projects, including the Hagia Sophia, which remains a symbol of Byzantine architectural achievement.
Significance and Impact
The permanent split of the Roman Empire in 395 AD is not merely a historical event; it laid the groundwork for the development of modern Europe and the Mediterranean region. The division created two distinct cultural and political spheres that would influence global history for centuries. The Eastern Roman Empire continued the legacy of Roman governance, contributing to the development of Byzantine culture, which would later influence the Renaissance in Western Europe.
Furthermore, the split set the stage for the rise of nation-states in Europe. The fall of the Western Empire led to the emergence of various kingdoms and the eventual rise of feudalism, changing the sociopolitical landscape permanently. Today, the impact of this division can still be felt in the cultural and religious differences that exist between Eastern and Western societies.
In conclusion, the map of the Permanent Split of the Roman Empire in 395 AD serves as a reminder of a transformative period in history. Understanding this division helps us appreciate the complexities of cultural and political evolution in Europe and the Mediterranean, shaping the identities and histories of nations that exist today. As we reflect on this pivotal moment, it prompts us to consider how historical divisions continue to shape our world in the present day.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 6, 2025
- Views
- 118
Comments
Loading comments...