Lead Paint Regulation Map by Country

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
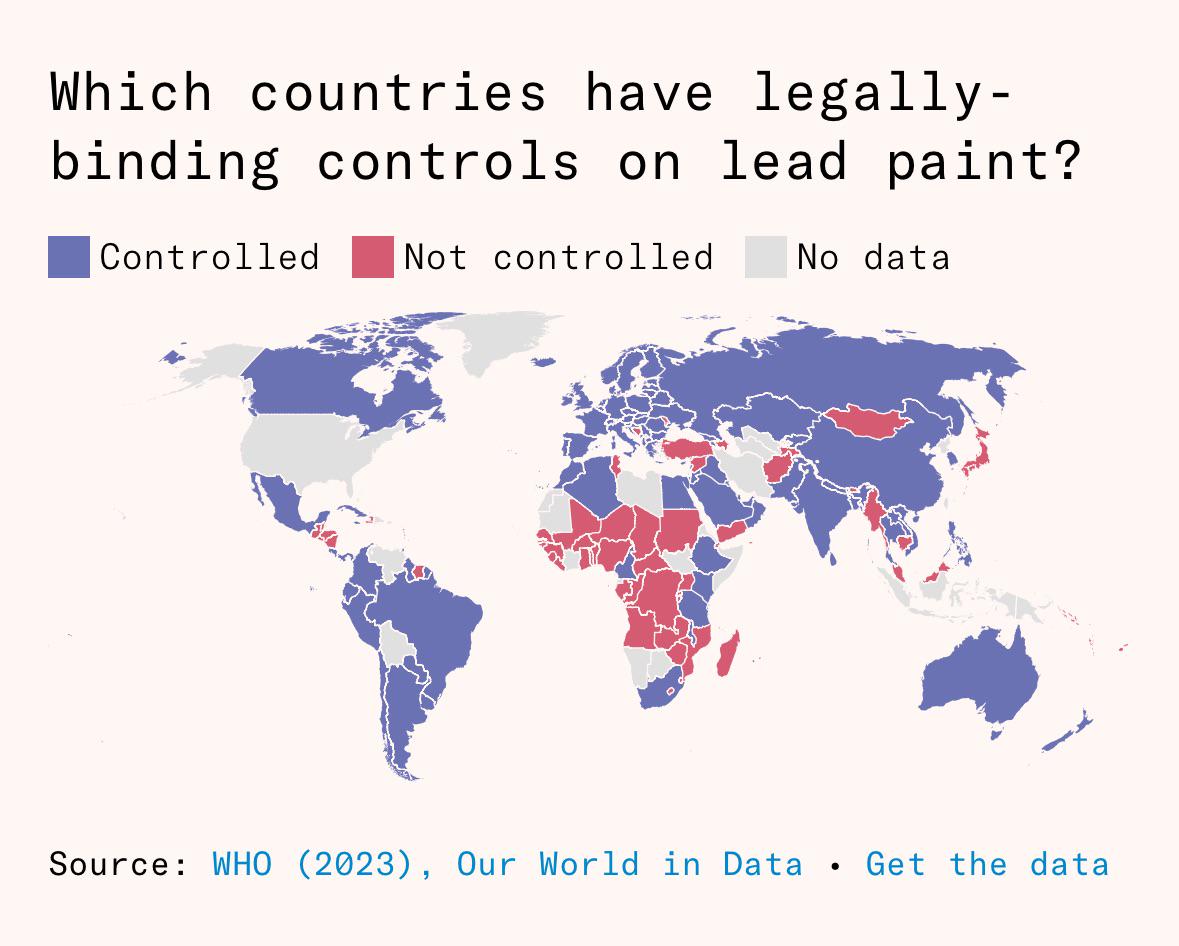
What This Map Shows
This visualization illustrates the global landscape of countries that have implemented legally-binding controls on lead paint. It highlights the significant strides made by some nations to mitigate the dangers of lead exposure, particularly in household paints, while underscoring the gaps that still exist in less regulated regions.
Lead paint has long been recognized as a severe health hazard, especially for children. The map serves as a crucial reference point for understanding which countries are actively protecting their populations from this toxic substance.
Deep Dive into Lead Paint Regulation
Lead, when ingested or inhaled, can cause serious health problems, especially in young children. The dangers of lead exposure have been well-documented, linking it to developmental delays, cognitive impairments, and various physical health issues. As a result, many countries have taken steps to regulate or ban lead in household paints, recognizing the dire need for public health protection.
Interestingly, the regulation of lead paint varies significantly across the globe. Some countries, such as the United States and Canada, have stringent laws that limit the amount of lead permissible in residential paint to nearly zero. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established strict standards to ensure that residential and commercial paints contain no more than 90 parts per million (ppm) of lead, a measure that reflects a robust public health approach to this issue.
However, not all nations have adopted such rigorous controls. In many developing countries, lead paint remains a significant risk. According to recent data, over 50 countries still allow lead levels in paints that vastly exceed safe limits, often reaching thousands of ppm. This discrepancy is concerning, especially when considering that children's exposure can occur through ordinary activities, like playing with toys painted with lead-based paint or living in homes where such paint was used.
International organizations, including the World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), have made concerted efforts to promote the elimination of lead in paints worldwide. Their advocacy has led to legislative changes in several countries, showcasing how global collaboration can effect change. The Global Alliance to Eliminate Lead Paint, launched in 2011, aims to provide technical support to countries seeking to establish and enforce lead paint regulations.
The importance of regulating lead paint cannot be overstated. The economic costs associated with lead exposure, including healthcare expenses and lost productivity, can be staggering. Studies have estimated that the cost of lead exposure in the U.S. alone could exceed hundreds of billions of dollars annually. Therefore, investing in lead paint regulation is not only a public health imperative but also an economically sound decision.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map, we see stark contrasts between regions. For instance, countries in North America and Europe generally show strong regulatory frameworks, reflecting a high level of awareness and proactive measures to eliminate lead hazards. In contrast, regions in Africa and Southeast Asia exhibit a worrying prevalence of lead paint usage. Countries like India and Nigeria have made some progress by enacting regulations, but enforcement remains a significant challenge.
In Latin America, nations such as Brazil and Argentina are in varying stages of addressing lead paint regulations. Brazil has implemented measures to limit lead in paints, but compliance and monitoring are ongoing concerns. The Caribbean also faces challenges, with some islands lacking comprehensive regulations, which raises questions about the safety of imported products.
Interestingly, the variability in legislation often correlates with the level of industrialization and economic development. Wealthier nations tend to have more resources to enforce regulations effectively, while developing nations may struggle with both the capacity to regulate and the prioritization of public health issues amid other pressing concerns.
Significance and Impact
Why does the regulation of lead paint matter? The implications of these regulations extend beyond mere compliance. They resonate deeply in public health, economic productivity, and even social equity. Children are particularly vulnerable to lead exposure, and protecting them is vital for fostering healthy future generations. Ensuring that all children, regardless of where they live, grow up in safe environments is a shared responsibility.
Current trends indicate a growing awareness of the dangers of lead and a push towards comprehensive regulations globally. As nations become more interconnected, the spread of information and advocacy for health standards has gained momentum. Future projections suggest that with continued international collaboration and pressure from health organizations, more countries will adopt stringent controls, ultimately leading to a significant reduction in lead exposure.
In conclusion, the journey toward eliminating lead paint is ongoing, and while strides have been made, there is still much work to be done. Understanding where countries stand in this critical issue allows us to advocate for change and support those who are still at risk. The map serves as a vital tool in this endeavor, highlighting both progress and the need for continued vigilance.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 5, 2025
- Views
- 104
Comments
Loading comments...