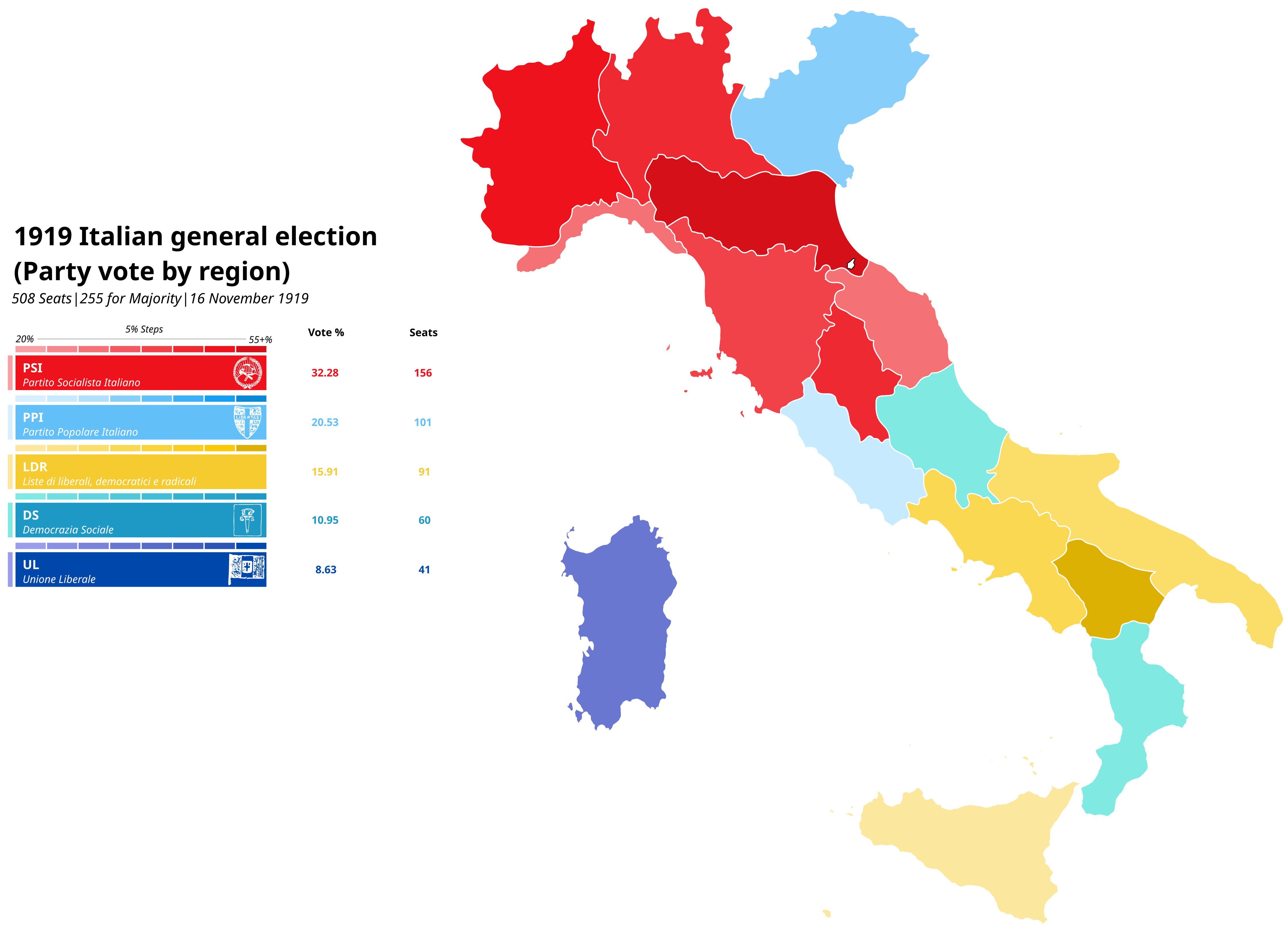
Map of the 1919 Italian General Election by Region

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The map titled "A Map of the 1919 Italian General Election by Region" provides a vivid snapshot of Italy's political landscape following World War I. It highlights the electoral outcomes across various regions, showcasing how different areas voted in that pivotal election. This visualization allows us to analyze the political affiliations and trends that emerged at a time of significant national transformation.
Deep Dive into the 1919 Italian General Election
The 1919 Italian General Election was notable for its profound impact on the country's political trajectory. Coming just a year after the end of World War I, this election was the first in which universal male suffrage was implemented, allowing millions of Italians to participate in the democratic process. This dramatic expansion of the electorate marked a significant shift in Italy's political landscape, as prior elections had only included a limited number of voters.
The election results revealed a country deeply divided along regional lines. Interestingly, the results painted a picture of a nation grappling with the aftermath of war, economic challenges, and social change. In the north, particularly in industrial regions like Lombardy and Piedmont, the Socialist Party made substantial gains. This shift can be attributed to the growing discontent among workers and the desire for social reform amid rising unemployment and inflation. On the other hand, rural areas, especially in the south, showed stronger support for conservative parties, reflecting the more traditional values held by those communities.
One of the most fascinating aspects of the 1919 election is the emergence of the Italian People's Party (Partito Popolare Italiano) led by Luigi Sturzo. This party, which advocated for Christian democracy and social reform, captured the attention of many voters, particularly in regions like Lazio and Campania. The party’s focus on bridging the gap between the working class and the bourgeoisie resonated deeply with a populace looking for stability and hope in a post-war landscape.
The election also saw the rise of nationalist sentiments, as evidenced by the support for the nationalist parties in areas like Veneto and Friuli. This was a reaction not only to the territorial losses suffered by Italy in the war but also to the perceived betrayal felt by many Italians regarding the Treaty of Saint-Germain. The map thus serves as a historical document reflecting the complex political currents of the time.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map closely reveals stark contrasts in voting patterns across Italy's regions. In the industrialized north, cities such as Milan and Turin heavily favored the Socialist Party, where voter turnout was high among factory workers. For instance, in Lombardy, the Socialist Party received upwards of 40% of the vote, illustrating both the strength of labor movements and the push for social reforms.
Conversely, in the southern regions such as Calabria and Sicily, conservative parties dominated the electoral scene. Here, agrarian interests took precedence, and traditional values held sway over the more radical ideas gaining traction in the north. The map highlights how these contrasting ideologies created a clear political dichotomy between the north and south, a divide that would continue to influence Italian politics for decades to come.
What’s particularly interesting is the role of urbanization during this period. The rapid growth of urban centers in the north, fueled by industrialization, contrasted sharply with the more agrarian-based economies in the south. This demographic shift not only influenced voting patterns but also contributed to growing social tensions that would eventually lead to the rise of various political movements, including fascism.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the 1919 Italian General Election is crucial for comprehending Italy's subsequent political evolution. The election results laid the groundwork for future governmental structures and political parties, shaping the course of Italian democracy. The rise of the Socialist Party, for instance, signaled the beginning of a more pronounced leftist movement that would challenge the status quo.
Moreover, the election highlighted the importance of regional identities within Italy. The political and social disparities between the north and south have persisted throughout Italian history, affecting everything from economic policies to cultural perceptions. Today, these regional distinctions continue to manifest in various forms, influencing contemporary politics and discussions about national unity.
In conclusion, the map of the 1919 Italian General Election by region serves not only as a historical artifact but also as a lens through which we can examine the complexities of Italian society during a transformative era. As we reflect on this period, it’s essential to consider how the echoes of these electoral outcomes still resonate in modern Italy, making the study of this map not just an exploration of the past, but a relevant commentary on present-day political dynamics.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 4, 2025
- Views
- 76
Comments
Loading comments...