Modern Corrective Upside Down Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
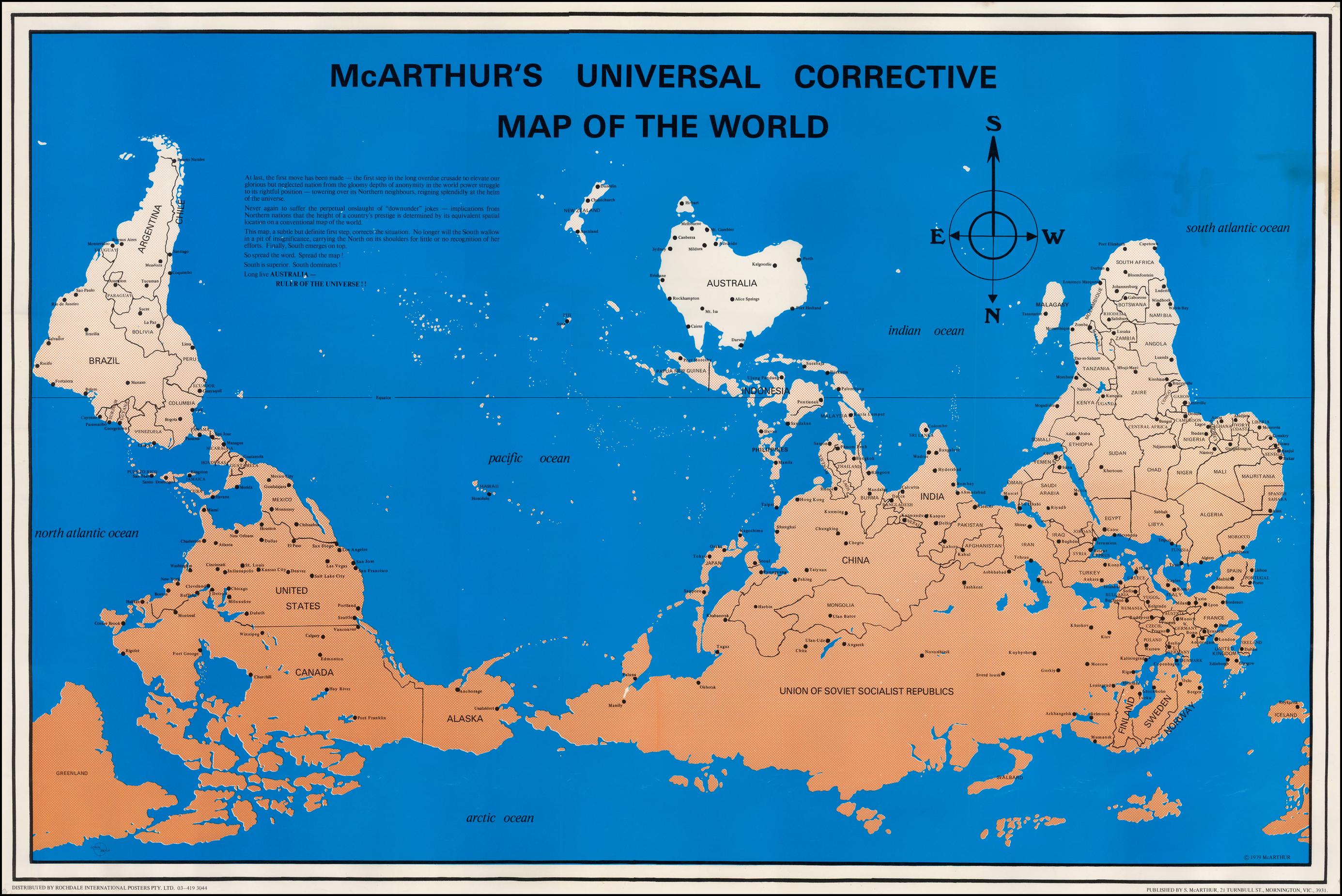
What This Map Shows
The modern corrective upside down map is a unique visualization that turns the traditional map orientation on its head, literally. Instead of placing the North at the top, this type of map positions the South in a prominent place, providing a fresh perspective on geography. This specific map focuses on current political borders, major cities, mountain ranges, and river systems, all while minimizing the distortions typically associated with projections like the Mercator.
By flipping our conventional understanding of maps, this visualization encourages us to rethink our perceptions of the world. It highlights how geographical orientation impacts our view of global dynamics, from political relations to economic influences. But let's delve deeper into the geographical aspects represented in this map.
Deep Dive into Current Geographical Features
The core of any map is the representation of physical and human geography. In the case of the modern corrective upside down map, we see a fascinating interplay of natural and man-made features. Major mountain ranges such as the Andes in South America, the Rockies in North America, and the Himalayas in Asia stand out prominently. These mountain ranges not only define the physical landscape but also influence climate, biodiversity, and human settlement patterns.
Interestingly, rivers also play a crucial role in this map. The Amazon River, which flows primarily through Brazil, is one of the most significant waterways in the world, supporting a vast ecosystem and providing essential resources for millions of people. Similarly, the Nile River, which flows through northeastern Africa, is often hailed as the lifeblood of Egypt, showcasing the importance of watercourses in shaping civilizations.
What’s fascinating is how this upside down perspective might alter our understanding of these features. For instance, the perception of the Amazon rainforest may shift when viewed from the South, emphasizing its connection to the Southern Hemisphere's biodiversity and climate patterns.
Moreover, contemporary maps can now integrate information about urbanization and population density, providing a snapshot of human geography. Cities like Cape Town, Sydney, and Buenos Aires take on new significance in this flipped orientation, prompting us to consider their roles within global networks of trade, culture, and political influence.
Regional Analysis
In analyzing the regions highlighted on the modern corrective upside down map, we can observe distinct geographic features and socio-economic conditions.
- **South America**: The Andes mountains create a formidable barrier that affects climate and settlement. Countries like Chile and Argentina often have contrasting climates and ecosystems due to this range, with the western side being lush and the eastern side more arid. The Amazon basin is crucial for biodiversity and climate regulation, making it a focal point for environmental discussions.
- **Africa**: The Nile River's importance cannot be overstated. As it runs through multiple countries, its management is a critical issue for political stability and agricultural productivity. The diverse climates from the Mediterranean in the north to the arid deserts in the south highlight the continent's varied geography.
- **Oceania**: Australia, when viewed in this orientation, presents unique features such as the Great Barrier Reef and vast deserts. The coastal cities like Sydney and Melbourne are vital economic hubs, contributing significantly to the nation’s GDP.
- **Asia**: The Himalayas, serving as the highest mountain range, not only influence the climate of surrounding areas but also act as a natural barrier between countries like India and China. The economic powerhouses in this region, such as Tokyo and Seoul, drive technological and cultural trends worldwide.
Significance and Impact
Understanding geography through the lens of a modern corrective upside down map is not merely an exercise in cartography; it has real-world implications. By challenging the conventional North-centric view, we can foster a more inclusive understanding of global dynamics. This shift in perspective can lead to a greater appreciation of the Southern Hemisphere's contributions to global culture, economy, and ecology.
Moreover, with contemporary issues like climate change and globalization, recognizing the interconnectedness of regions becomes paramount. For instance, the Amazon rainforest’s role in carbon sequestration is critical in the fight against climate change, affecting not just South America but the entire planet.
As we continue to confront global challenges, this modern corrective upside down map serves as a reminder that our understanding of geography shapes our actions and policies. It encourages us to think critically about how we perceive the world and the implications of those perceptions on our interactions with one another and the environment. By embracing varied perspectives, we open the door to a more comprehensive understanding of our shared planet.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 3, 2025
- Views
- 68
Comments
Loading comments...