Map of Arabic Language Expansion from 540 to 2022

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
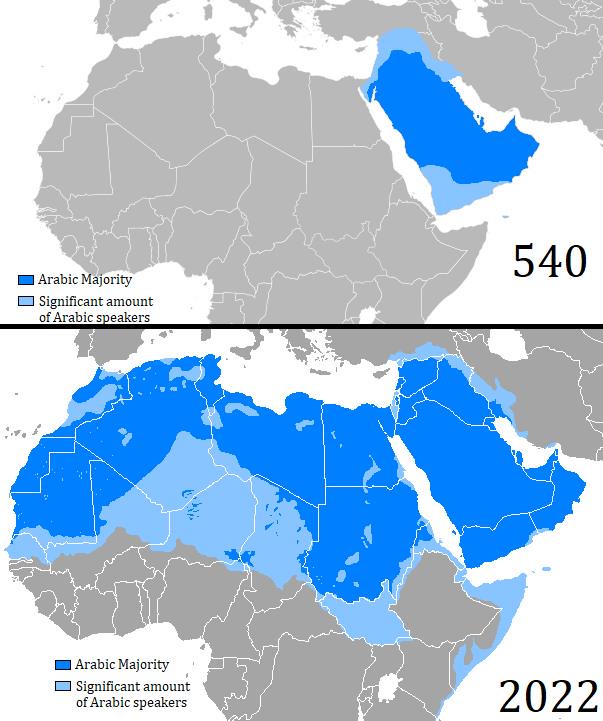
The map titled "Map of Arabic Language Expansion between 540 and 2022" visually illustrates the geographical spread of the Arabic language over nearly 1,500 years. This timeline highlights the regions where Arabic has become prominent, showcasing its growth from a local dialect to a global language. With its roots deeply embedded in the Arabian Peninsula, Arabic has expanded significantly through trade, conquest, and cultural exchange, influencing numerous regions worldwide.
Deep Dive into Arabic Language Expansion
Arabic is more than just a language; it's a rich tapestry that reflects the history, culture, and identity of millions of people. Initially, Arabic was confined to the Arabian Peninsula, but by the 7th century, following the rise of Islam, it began to spread rapidly across the Middle East and North Africa. The establishment of the Umayyad and Abbasid caliphates played a crucial role in this expansion, as Arabic became the language of administration, culture, and religion.
Interestingly, the spread of Arabic was not merely a linguistic phenomenon but also a cultural one. The Arabic script, with its unique calligraphy, became a symbol of Islamic art and education. During the Golden Age of Islam, from the 8th to the 14th centuries, Arabic emerged as a language of science, philosophy, and mathematics, facilitating a wealth of knowledge that would later influence the European Renaissance.
By the end of the medieval period, Arabic had established itself in regions far beyond its origins. North Africa, the Levant, and parts of the Arabian Peninsula became predominantly Arabic-speaking. However, the language's impact didn't stop there; it also reached sub-Saharan Africa, where it mingled with local languages and dialects, particularly in areas like Sudan and Chad.
In the contemporary era, Arabic has continued to thrive, with more than 310 million native speakers today, making it one of the most widely spoken languages globally. The language is not just limited to the Arab world; it also finds resonance in diaspora communities across Europe, North America, and Australia, where Arabic is a significant language due to immigration and globalization.
Moreover, the rise of digital communication has created new avenues for the Arabic language. Social media, blogs, and online platforms have facilitated the use of Arabic in various dialects, which sometimes diverge significantly from Modern Standard Arabic (MSA). This evolution is a testament to the language's adaptability and its connection to modern identity.
Regional Analysis
The map provides a fascinating overview of how Arabic has been adopted and adapted in different regions. In North Africa, for instance, countries like Egypt, Algeria, and Morocco boast a rich blend of Arabic with local Berber languages, creating unique dialects. This mixture is evident in everyday conversations and cultural expressions, showcasing the resilience and diversity of the Arabic language.
Conversely, in the Gulf states, Modern Standard Arabic predominates in formal contexts, while regional dialects are often used in casual conversations. Interestingly, the dialects in these areas can vary significantly, leading to a rich linguistic landscape. For example, the Arabic spoken in Qatar may be quite different from that in Saudi Arabia, yet they share a common foundation.
In the Levant, countries like Lebanon, Syria, and Jordan reflect a fascinating blend of Arabic and other languages due to historical influences, such as French and English colonization. This has resulted in Lebanese Arabic, for example, being peppered with words from French, making it distinct from its neighbors.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the expansion of the Arabic language is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it underscores the historical connections between regions, highlighting how language can be a bridge between different cultures. Moreover, Arabic is one of the six official languages of the United Nations, emphasizing its global importance.
In today's world, the Arabic language carries significant political, economic, and social implications. As the Middle East continues to play a pivotal role in global affairs, the ability to communicate in Arabic has become increasingly valuable. Businesses and governments recognize the necessity of understanding this language to engage effectively with Arabic-speaking populations.
Looking ahead, the future of the Arabic language appears promising. With the continued integration of technology and the rise of Arabic content online, the language is likely to evolve further, maintaining its relevance in an ever-changing world. Ever wondered how the rise of artificial intelligence might affect language learning? As tools become more sophisticated, we may see an increase in the accessibility of Arabic education, broadening its reach even further.
In conclusion, the map of Arabic language expansion from 540 to 2022 not only illustrates a fascinating linguistic journey but also serves as a reminder of the cultural richness and historical significance of Arabic across the globe.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 1, 2025
- Views
- 76
Comments
Loading comments...