Google Maps Fixed Borders by Country Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
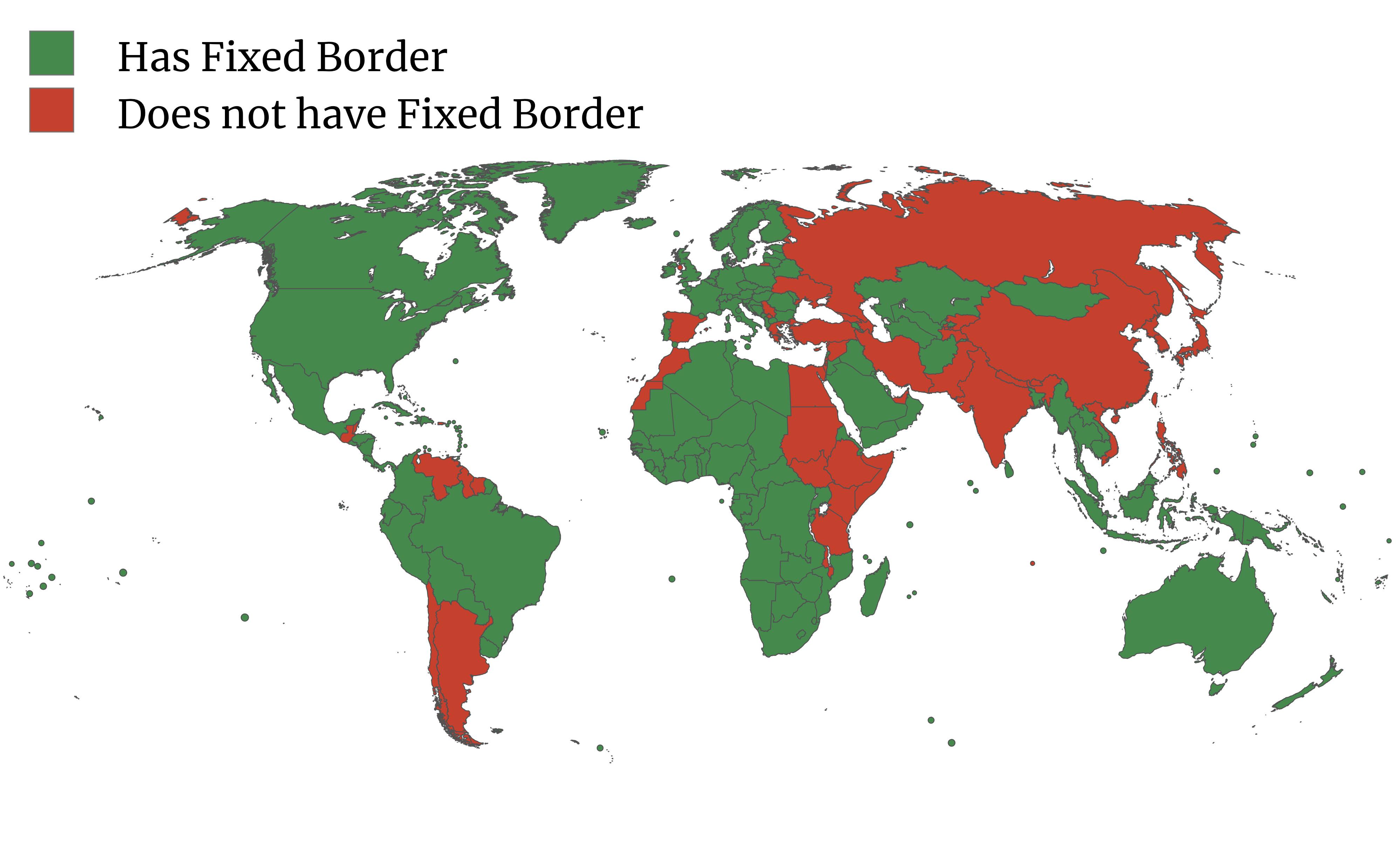
What This Map Shows
The map titled "Does Google Maps consider your country to have a fixed border?" highlights an interesting aspect of international geography: the concept of fixed borders as visualized on Google Maps. When you click on a country, you may either see it outlined with a red dotted line or presented without any borders at all. This visual representation indicates whether or not Google Maps recognizes the country as having a 'fixed' border. Countries marked with a red dotted line typically experience border disputes or have regions with contested sovereignty.
Deep Dive into International Borders
International borders are much more than just lines on a map; they represent the legal boundaries between nations and are often the result of historical agreements, wars, or negotiations. However, not all borders are universally recognized, and this can lead to complex geopolitical situations. For instance, let’s consider the case of Italy, which is fully recognized as having fixed borders, displayed clearly on Google Maps.
Interestingly, Italy’s borders have been influenced by various historical factors, including its unification in the 19th century and subsequent treaties post-World War I and II. The country's borders are stable, stretching from the Alps in the north to the Mediterranean Sea in the south. However, it’s worth noting that even established borders like Italy's can be subject to changes in international law or territorial disputes stemming from colonial history, such as with the territories of South Tyrol or the ongoing discussions regarding the maritime boundaries in the Adriatic Sea.
Globally, there are numerous examples of countries with non-fixed borders, such as Cyprus, where the island is divided into the Republic of Cyprus and the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus— the latter of which is recognized only by Turkey. This division has resulted in a red dotted line on Google Maps, signifying the lack of consensus regarding its borders.
The phenomenon of fixed versus non-fixed borders highlights the importance of diplomacy and international law in resolving disputes. The United Nations plays a significant role in mediating these discussions, yet many regions remain contentious. In Africa, for example, the borders drawn during colonial times often ignored ethnic and cultural divisions, leading to conflicts that persist today.
Regional Analysis
When we analyze borders regionally, the variations in how borders are perceived and recognized become even more pronounced. Take the example of Eastern Europe and the Caucasus region, where borders often reflect historical grievances and ethnic tensions. Countries like Ukraine and Georgia have borders marked by international disputes, leading to their depiction on Google Maps with dotted lines. In contrast, countries such as Poland or Hungary boast fixed borders, recognized by their neighbors and the international community.
In Africa, the situation is equally complex. The map of Africa is marked by many countries that have fixed borders, but there are also numerous regions where boundaries are disputed or unclear. Countries like Somalia and Somaliland provide a stark example of this, where the self-declared Republic of Somaliland has a disputed status despite functioning as an independent entity. The representation of these regions on Google Maps with dotted lines emphasizes the ongoing struggles for recognition and stability.
Furthermore, in South America, the borders between countries such as Peru and Ecuador have seen historical disputes, yet they currently hold fixed status. This stability is vital for trade and international relations, allowing countries to engage more effectively in economic development and cooperation.
Significance and Impact
Understanding fixed versus non-fixed borders is crucial for several reasons. First, it affects international relations and diplomacy. Countries with disputed borders may face challenges in trade, security, and international recognition. This can lead to tensions that have broader implications, including humanitarian crises and migration patterns. For instance, ongoing conflicts in border regions like the India-Pakistan border have led to significant geopolitical ramifications, impacting millions of lives.
Moreover, as globalization continues to reshape the world, the significance of borders is evolving. With increased movement of people and goods, the rigidity of borders is often challenged. Countries with fixed borders may find themselves navigating new challenges that arise from economic interdependence and global issues like climate change or pandemics. Addressing these issues collaboratively can lead to more stable relationships and a more peaceful international community.
In conclusion, the representation of fixed and non-fixed borders on Google Maps serves as a reminder of the complexities of international relations and the ongoing need for dialogue and negotiation. As we continue to explore these dynamics, it’s essential to recognize the importance of diplomacy in fostering stability and peace in our increasingly interconnected world.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 27, 2025
- Views
- 76
Comments
Loading comments...