Water Used for Crop Irrigation Map by US States

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
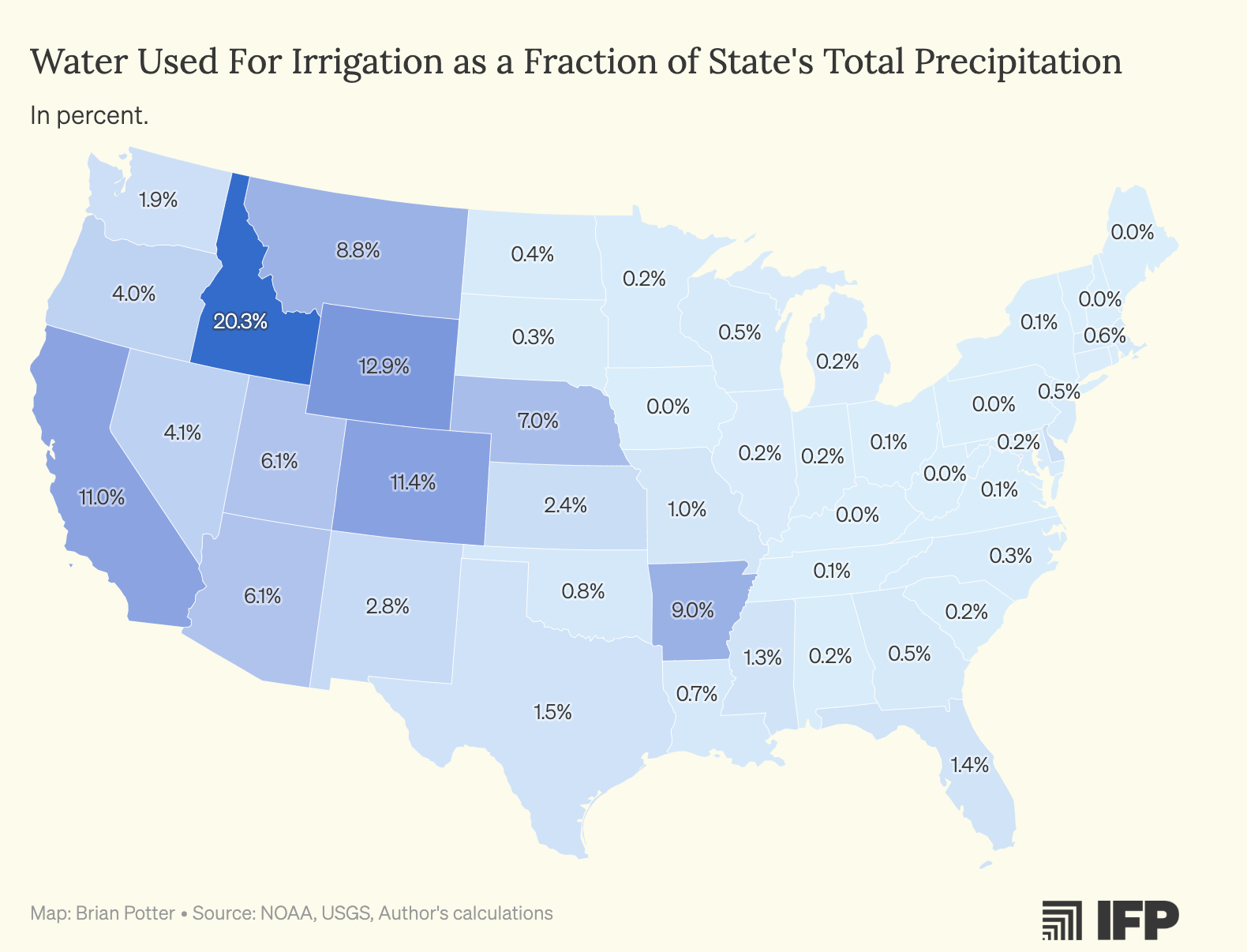
What This Map Shows
The map titled "Water Used for Crop Irrigation as a Percentage of US States' Total Precipitation" provides a compelling insight into the relationship between agricultural water use and precipitation across the United States. By illustrating the percentage of total precipitation allocated to crop irrigation, this visualization highlights how different states manage their water resources for agriculture, which is vital for food production and ecosystem health.
Deep Dive into Water Use for Irrigation
Water is an essential resource for agriculture, especially in a country like the United States, where farming plays a significant role in the economy. Interestingly, a considerable portion of the precipitation that falls across the country is not simply absorbed by the environment; rather, it is strategically utilized for crop irrigation. Crop irrigation is defined as the artificial application of water to soil or land to assist in the growing of agricultural crops.
It's fascinating to note that irrigation practices vary significantly from state to state, driven by climate, geography, and agricultural needs. For instance, states like California and Arizona, which experience a drier climate, rely heavily on irrigation to sustain their agricultural output. In contrast, states with higher precipitation levels, such as those in the Midwest, may use a lower percentage of their total precipitation for irrigation due to more favorable natural water availability.
Statistically, it's estimated that about 80% of the freshwater used in the United States is allocated for irrigation. This staggering figure underscores the importance of understanding how much of this water comes from precipitation. In regions where farming is intensive, such as the Central Valley in California, farmers often use irrigation to supplement the natural water supply, especially during dry spells.
Moreover, the type of crop grown also dictates irrigation needs. High-value crops like almonds and grapes require more water, thereby increasing the percentage of precipitation allocated for irrigation in those regions. Conversely, crops such as wheat or corn may require less irrigation due to their adaptability to local precipitation patterns.
As climates change and droughts become more frequent, the pressure on irrigation resources is likely to intensify. This brings into question how states will adapt their irrigation strategies to ensure food security while managing limited water supplies sustainably.
Regional Analysis
Looking at the map, we can discern distinct regional patterns in irrigation water usage. For example, in the Western United States, states like California, Nevada, and Utah show higher percentages of water used for crop irrigation relative to their total precipitation. California stands out, with a substantial portion of its precipitation diverted to support its vast agricultural sector, which produces nearly half of the country's fruits, vegetables, and nuts.
In contrast, states in the Midwest, such as Iowa and Illinois, typically have a lower percentage of irrigation relative to their precipitation levels. This is largely because the region enjoys a more stable rainfall pattern, which sufficiently supports crop growth without the need for extensive irrigation. Interestingly, while they may use less water for irrigation, these states are still major agricultural producers, showcasing how effective rainfall management can lead to successful farming even in less arid conditions.
The Southern states present a mixed picture. States like Texas and Florida utilize significant irrigation water, but also receive substantial rainfall. The balance between using natural precipitation and supplementary irrigation varies within the state, influenced by crop type and regional water policies.
Significance and Impact
Understanding water use for crop irrigation is crucial for several reasons. First, it informs water management policies and agricultural practices, which are essential as the country grapples with climate change and water scarcity. As populations grow and demand for food increases, the pressure on irrigation resources will only mount.
Moreover, the insights gained from this map can help policymakers and farmers alike make informed decisions about water conservation, crop selection, and irrigation methods. For instance, states that experience prolonged droughts may need to invest in more efficient irrigation technologies, such as drip irrigation, to maximize water use efficiency.
In conclusion, the percentage of water used for crop irrigation relative to total precipitation is not just a number; it reflects a broader narrative about resource management, agricultural practices, and environmental sustainability. As we move forward, it's vital for stakeholders at all levels to recognize the significance of this data in shaping a more sustainable agricultural future.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 27, 2025
- Views
- 78
Comments
Loading comments...