Population Distribution Map of Finland

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
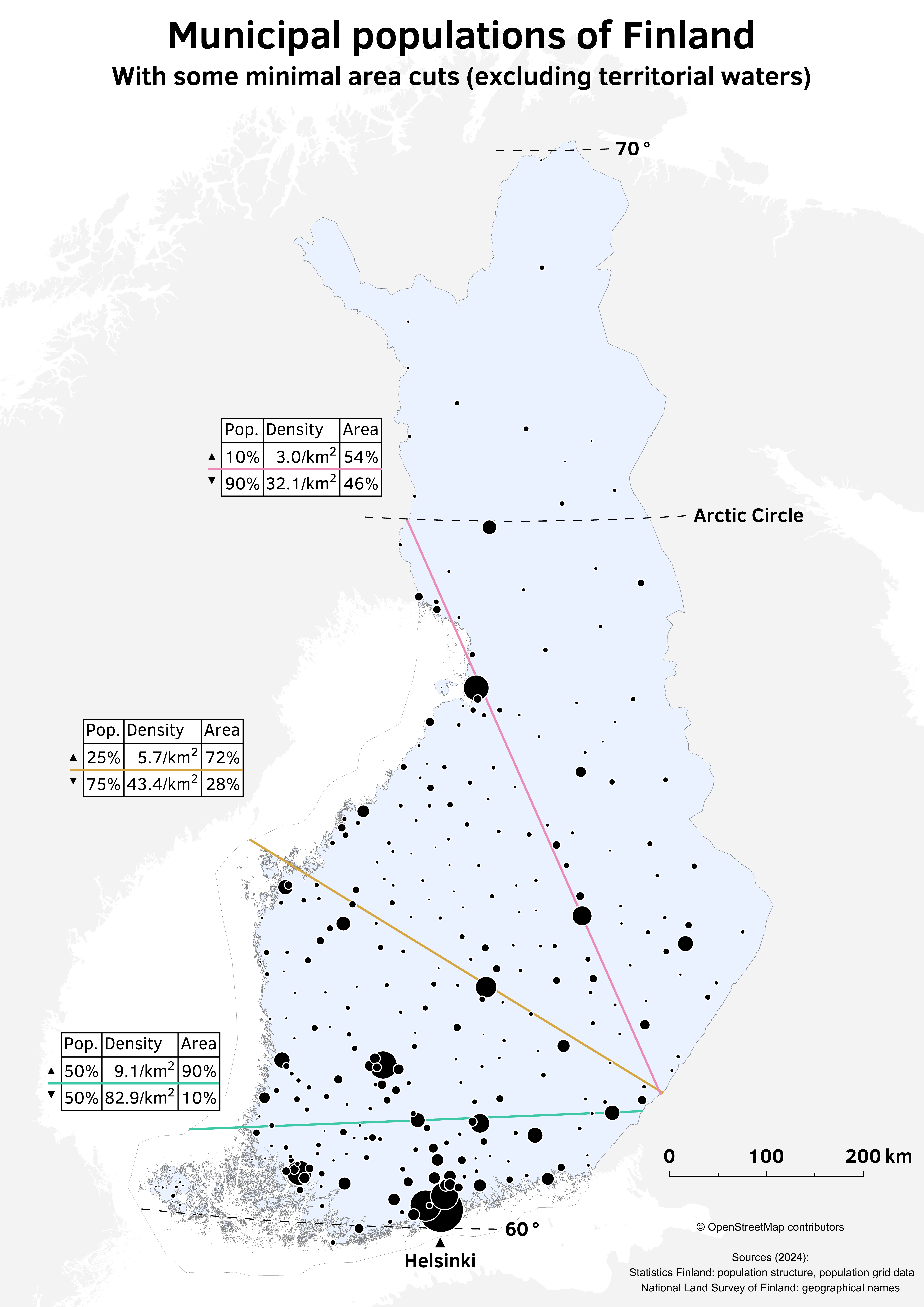
What This Map Shows
The "Population Distribution Map of Finland" offers a clear visual representation of where people live across this Nordic country. It highlights the density of population in various regions, showcasing urban areas, rural communities, and the vast uninhabited expanses of wilderness. In Finland, the population density is unevenly distributed, with urban centers like Helsinki and Tampere standing out amid the largely rural backdrop.
Deep Dive into Population Distribution in Finland
Finland's population distribution is a fascinating topic that reflects both historical and contemporary factors influencing settlement patterns. As of the latest data, Finland has a population of approximately 5.5 million people, concentrated heavily in the southern region. This concentration is largely driven by economic opportunities, climate, and historical migration patterns.
Interestingly, urbanization has surged in Finland over the last few decades. The capital city, Helsinki, is home to about 1.5 million residents and serves as the country's political, cultural, and economic hub. Following Helsinki closely are cities like Espoo and Vantaa, which are part of the greater Helsinki metropolitan area. These urban centers provide not only jobs but also educational institutions, healthcare, and vibrant social communities.
However, as you move north, the population density diminishes dramatically. The northernmost regions, such as Lapland, are characterized by vast stretches of wilderness with very few inhabitants. This is primarily due to the harsh climate—long, cold winters and short summers—which makes living and farming challenging. These areas are home to the indigenous Sámi people, who have adapted their lifestyles to the unique conditions of the Arctic.
The population distribution also reflects historical migration trends. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, many Finns migrated from rural areas to cities in search of better economic prospects. This trend has slowed in recent years, but urbanization continues to be a significant factor, especially among younger populations who seek education and employment in cities.
Regional Analysis
The map distinctly illustrates several notable regions within Finland. For instance, the Uusimaa region, where Helsinki is located, boasts the highest population density in the country, with many suburbs contributing to its overall numbers. In contrast, the Kainuu region, located in central Finland, shows a sparse population, primarily consisting of small towns and rural communities.
Moreover, the North Karelia region, known for its beautiful lakes and forests, presents an interesting case of population distribution. While its natural beauty attracts tourists, the population has been declining, which is a trend seen in many rural areas across Finland. Interestingly, the government has implemented various strategies to revitalize these regions, including promoting local industries and enhancing infrastructure.
The Ostrobothnia region is another area worth discussing. It has a relatively higher population density compared to other rural areas due to its agricultural activities and proximity to the coast, leading to economic opportunities in fishing and shipping.
Significance and Impact
Understanding population distribution in Finland is crucial for several reasons. From a governmental perspective, it informs infrastructure development, resource allocation, and public service provision. For example, urban areas require more healthcare facilities, schools, and transportation systems to accommodate growing populations. Conversely, rural areas need support to prevent depopulation and to sustain local economies.
Moreover, population distribution has significant environmental implications. Urbanization contributes to land use changes that can affect local ecosystems. As cities expand, there is a growing need for sustainable development practices to mitigate environmental impacts. A balance must be struck between growth and preservation, especially in areas rich in natural resources and biodiversity.
Looking to the future, Finland faces challenges related to its aging population. With a declining birth rate, the country must consider immigration policies to maintain its workforce and economic stability. Moreover, climate change may further influence population distribution, as areas previously deemed inhospitable could become more livable, while urban centers may face increased pressure from rising sea levels and extreme weather events.
In conclusion, the population distribution map of Finland not only illustrates where people live but also tells a story of economic opportunity, cultural heritage, and environmental sustainability. As we move forward, understanding these dynamics will be essential in shaping Finland's future.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 26, 2025
- Views
- 156
Comments
Loading comments...