World Population Distribution Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
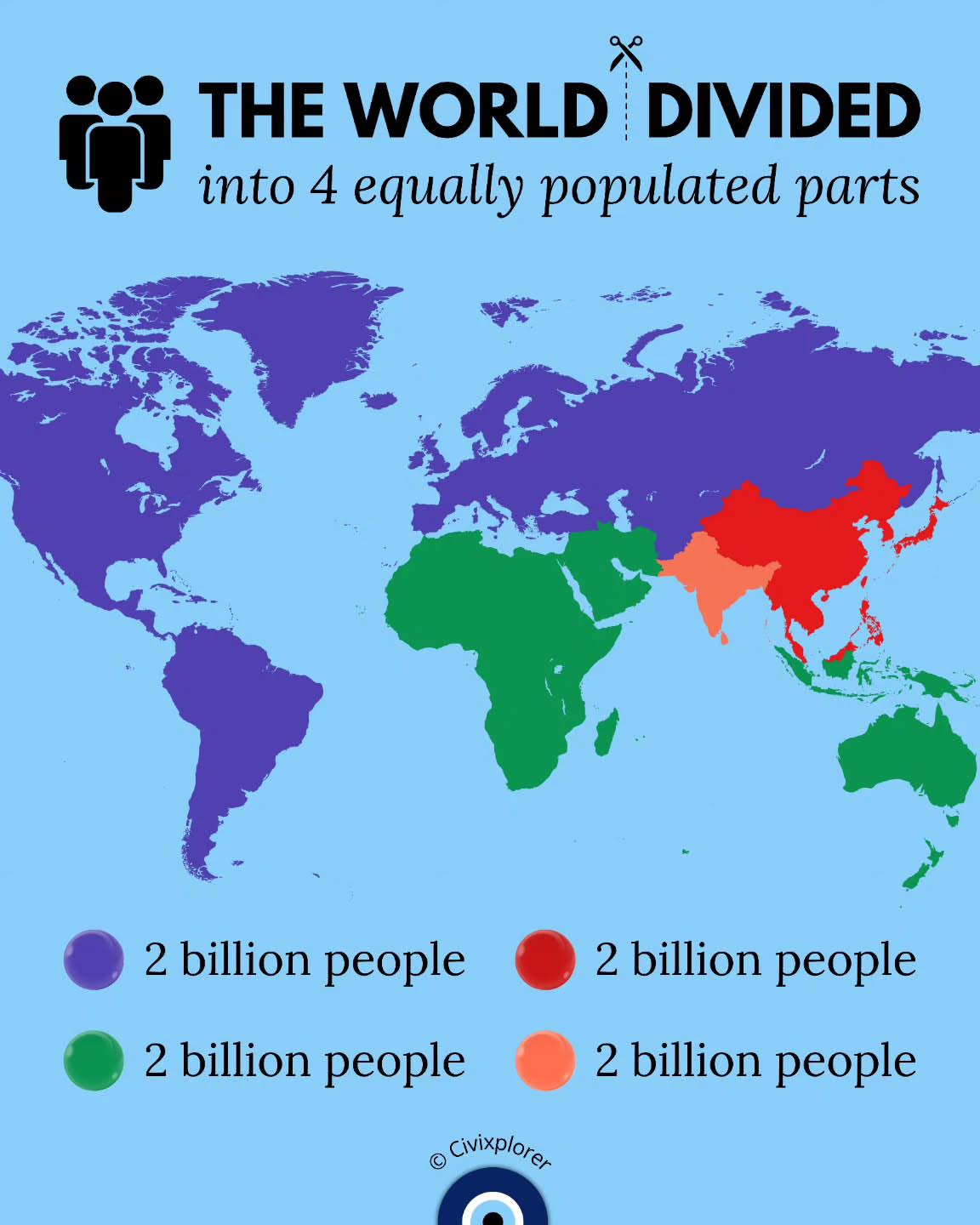
What This Map Shows
This map illustrates a fascinating concept: the world divided into four equally populated parts. It visualizes how Earth's population—currently over 8 billion—is allocated across different regions. By drawing boundaries that create four segments with roughly equal numbers of inhabitants, we gain insights into global population distribution, density, and urbanization patterns. These divisions provoke thought on how resources, cultures, and economies interact in various parts of the world, shaping our human experience.
Deep Dive into Global Population Distribution
Population distribution refers to the way in which people are spread across the Earth’s surface. This phenomenon is influenced by numerous factors, including geography, climate, economy, and social structures. Understanding where people live is crucial for planning infrastructure, services, and environmental management.
Interestingly, population densities can vary dramatically. For instance, urban areas tend to have much higher concentrations of people compared to rural regions. Cities like Tokyo, New York, and Mumbai are prime examples where millions reside in a relatively small area due to the economic opportunities and amenities available. In contrast, vast regions in countries like Canada, Russia, and Australia remain sparsely populated, often due to harsh climatic conditions or geographical barriers.
According to the latest estimates, the most densely populated areas on the planet are primarily found in Asia, particularly in countries such as India and China. These regions are characterized by a combination of high birth rates, migration, and urbanization, creating a robust demographic landscape. In India, for example, the population is projected to surpass that of China, making it the most populous country by the next few years.
Moreover, global population growth isn't uniform. Some regions, particularly in Africa, are experiencing rapid growth rates, with countries like Nigeria projected to double their population by 2050. Meanwhile, developed regions like Europe and parts of East Asia are seeing stagnant or declining populations. This uneven growth underscores significant challenges, such as resource allocation, education, and healthcare.
Regional Analysis
When we dissect the map’s four segments, we can observe distinct characteristics in each population cluster. For example:
1. **North America**: This region showcases a diverse population, with the United States and Canada having significant urban centers like New York City, Los Angeles, Toronto, and Vancouver. The population here enjoys high living standards and access to advanced healthcare and education.
2. **Europe**: Europe exhibits a unique demographic profile with aging populations and low birth rates in many countries. Nations like Germany and Italy are facing challenges related to sustainability and labor shortages due to their shrinking young populations. However, urban areas remain densely populated, with cities like London and Paris continuing to attract migrants.
3. **Asia**: Home to over half of the world’s population, Asia is marked by rapid urbanization and significant economic development. Mega-cities such as Shanghai and Delhi reflect the continent's dynamic demographic shifts. Interestingly, this region also faces challenges like pollution and overcrowding, which are exacerbated by the high population density.
4. **Africa**: Africa stands out with its youth-centric population profile. Countries like Ethiopia and Nigeria are experiencing some of the fastest growth rates globally. This demographic trend presents both opportunities, such as a potential economic boom, and challenges, including the need for jobs and education.
Significance and Impact
Understanding population distribution is not just an academic exercise; it carries real-world implications. From urban planning to environmental sustainability, the way populations are spread influences how societies function. For instance, cities must adapt to increasing populations through infrastructure improvements and resource management. Ever wondered why public transport systems are so critical in dense urban areas? It’s because efficient transport can mitigate traffic congestion and reduce pollution.
Furthermore, the disparity in population growth can lead to geopolitical tensions. Regions experiencing resource scarcity due to high population densities might find themselves in conflict with neighboring areas that have ample resources but lower populations. As we look toward the future, projecting population trends can help governments and organizations prepare for changes in resource demands, migration patterns, and economic shifts.
In conclusion, this map not only provides a snapshot of the current global population distribution but also raises important questions about how we manage our world’s resources and the implications of our growing numbers. As we continue to grow and shift, understanding these patterns will be vital for fostering a more sustainable and equitable future.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 26, 2025
- Views
- 140
Comments
Loading comments...