Infant Mortality Rate Map 2023

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
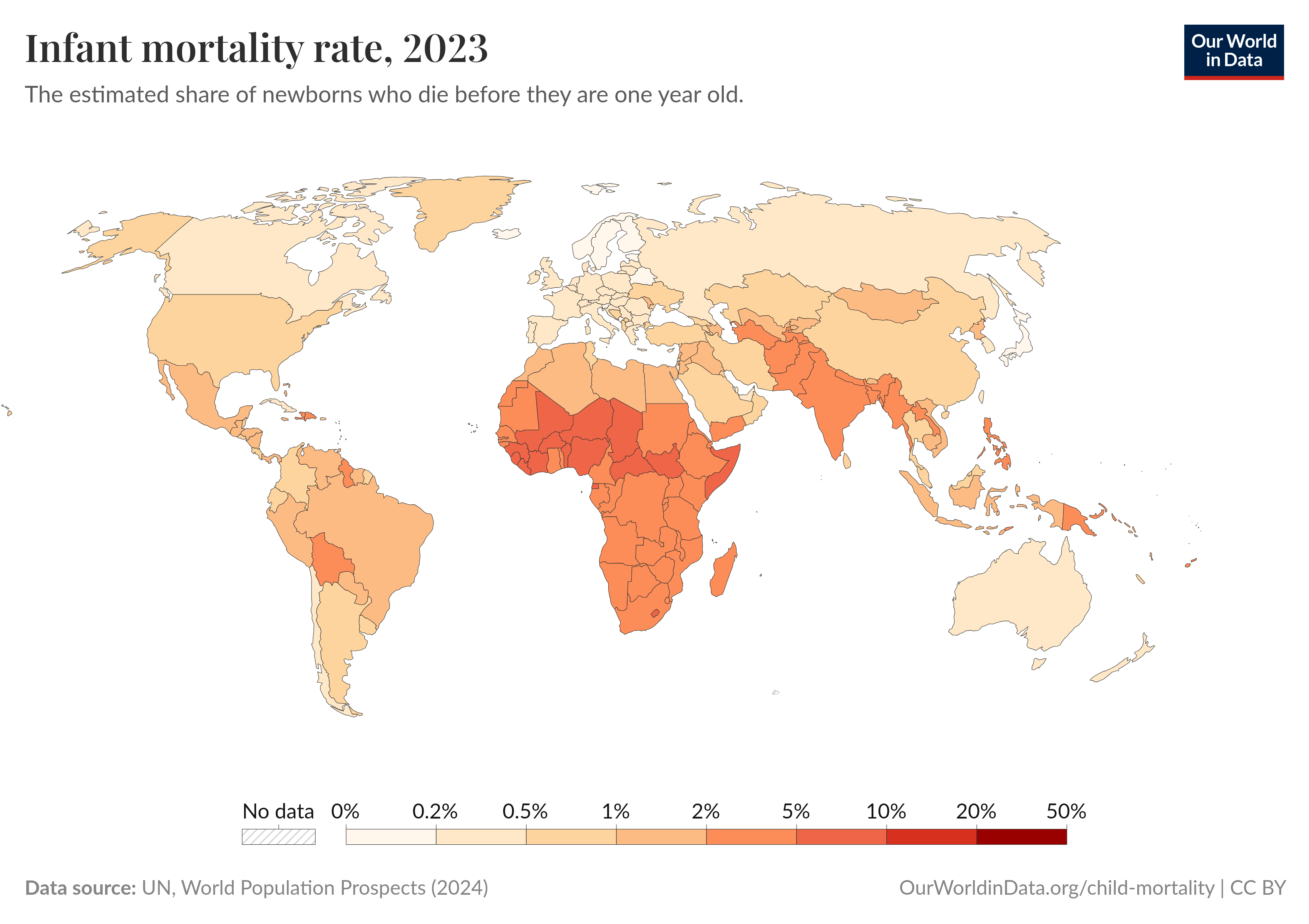
The "Infant Mortality Rate Map 2023" provides a comprehensive visual representation of the rates of infant deaths per 1,000 live births across the globe. This map highlights the stark disparities in infant mortality rates between different countries and regions, illustrating a crucial public health concern that often goes unnoticed. The visualization can be an eye-opener, revealing not just numbers, but the underlying issues affecting child health worldwide.
Deep Dive into Infant Mortality Rates
Infant mortality, defined as the death of a child before their first birthday, is a significant indicator of health and well-being in a population. It reflects the overall health conditions of a society, the effectiveness of healthcare systems, and the socio-economic status of a region. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the global infant mortality rate was approximately 37 deaths per 1,000 live births in 2021. However, this average masks vast differences across continents and countries.
Interestingly, Sub-Saharan Africa continues to bear the highest burden, with countries like Nigeria and the Democratic Republic of the Congo reporting rates as high as 100 deaths per 1,000 live births. This tragic reality is often rooted in factors such as inadequate healthcare infrastructure, high rates of infectious diseases, and limited access to prenatal and postnatal care. Conversely, regions such as Europe and North America boast some of the lowest rates, with countries like Japan and Iceland recording rates below 2 deaths per 1,000 live births. These nations benefit from advanced healthcare systems, comprehensive maternal health programs, and socioeconomic stability.
What’s fascinating is that infant mortality rates are not only influenced by healthcare access but also by geographical factors, cultural practices, and public health policies. For instance, in many developing countries, malnutrition plays a critical role in infant mortality. According to UNICEF, malnutrition contributes to nearly half of all deaths in children under five. Addressing these issues requires a multifaceted approach that includes improving maternal education, enhancing healthcare access, and promoting nutrition and hygiene.
Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on global health systems, potentially reversing years of progress in reducing infant mortality rates. Disruptions in healthcare services, increased poverty levels, and heightened maternal stress during the pandemic have all contributed to this concerning trend. As we move forward, it is crucial to prioritize maternal and child health in our recovery efforts.
Regional Analysis
Looking at the map, we can see distinct patterns when breaking down infant mortality by region. For example, Southern Asia, which includes countries like India and Bangladesh, faces significant challenges, with mortality rates hovering around 30 deaths per 1,000 live births. This region’s struggles are compounded by high population density and poverty, which exacerbate health disparities.
In contrast, regions like Scandinavia consistently report some of the lowest infant mortality rates in the world. Norway, for example, has an impressive rate of just 2.5 deaths per 1,000 live births, attributable to universal healthcare, robust maternal support programs, and high living standards. However, it's essential to recognize that even within wealthier nations, disparities can exist. For instance, indigenous populations in Canada and the United States often experience higher infant mortality rates compared to their non-indigenous counterparts, underscoring the need for targeted health interventions.
The Middle East presents a mixed picture; some countries like Israel maintain low rates, while conflict-affected areas such as Syria face severe challenges, leading to higher infant mortality due to disrupted healthcare services and humanitarian crises.
Significance and Impact
The implications of infant mortality rates extend far beyond mere statistics; they reflect the health, economic stability, and social equity of nations. High infant mortality rates can hinder economic development, as a healthy population is crucial for a productive workforce. Furthermore, the loss of a child has profound emotional and psychological effects on families and communities, impacting societal structures and relationships.
As we look ahead, addressing the determinants of infant mortality is critical for achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, particularly Goal 3, which aims to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages. Policymakers, healthcare providers, and communities must work collaboratively to implement effective strategies that not only improve healthcare access but also address the social determinants of health.
In conclusion, the "Infant Mortality Rate Map 2023" serves as a reminder of the challenges that many countries face in safeguarding the health of their youngest citizens. By understanding these rates and their implications, we can work towards a future where every child has the opportunity to thrive, regardless of where they are born.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 24, 2025
- Views
- 122
Comments
Loading comments...