
Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
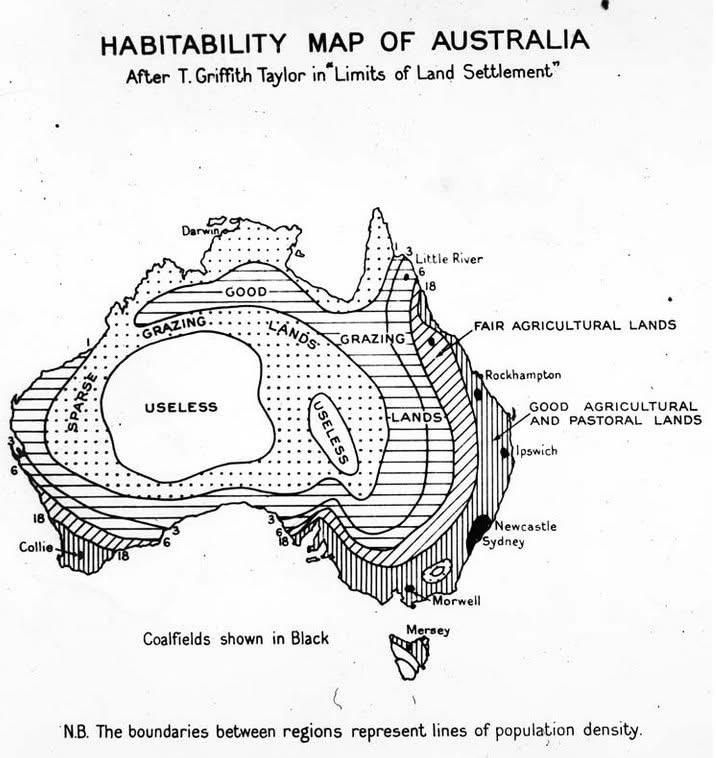
The 1946 Map of Australia that coded the "habitability" of the land presents a fascinating visual representation of the country's varying degrees of livability. On this map, areas are color-coded based on their capacity to support human habitation, indicating where populations might thrive and where the harsh environment poses challenges. This visualization is not just a display of geography; it encapsulates the relationship between humans and their environment, revealing how natural features, resources, and climate influence where people can live.
Deep Dive into Habitability in Australia
Habitability is a multi-faceted concept that takes into account a variety of factors including climate, water availability, soil fertility, and natural resources. In Australia, the interplay of these elements paints a complex picture of livability. The continent is renowned for its diverse landscapes—ranging from arid deserts and tropical rainforests to temperate coastal regions—all of which significantly impact habitability.
Interestingly, Australia's interior, often referred to as the Outback, is marked by extreme aridity and harsh climates, making it largely uninhabitable. The 1946 map highlights these regions in muted tones, signaling their low habitability. Here, temperatures can soar above 40 degrees Celsius (104 degrees Fahrenheit) in summer, while winter nights can be frigid. Water scarcity is a significant issue, with rivers like the Diamantina and the Georgina often drying up during the dry season. It's no surprise that only a small fraction of Australia’s population lives in these areas.
Conversely, the more hospitable coastal areas, particularly in the southeast and southwest, are depicted in vibrant colors, indicating their higher habitability. Cities such as Sydney, Melbourne, and Perth thrive in these regions, benefiting from milder climates, ample water supply, and fertile lands. The Great Dividing Range, which runs along the eastern coast, also plays a crucial role. This mountain range captures moisture-laden winds, leading to more rainfall and supporting lush vegetation in the adjacent coastal areas. Such geographical advantages have led to increased urban development and population density.
Moreover, the availability of natural resources, including minerals and fertile land for agriculture, significantly influences habitability. Areas like the Murray-Darling Basin, shown prominently on the map, are not just vital for agriculture but also serve as key water sources for millions of Australians. The basin is a critical agricultural region, producing significant portions of the nation’s food supply. This further enhances the habitability of the surrounding areas, attracting more residents and fostering economic growth.
Regional Analysis
Looking at the map more closely, we can discern distinct regional variations in habitability. For example, the northern regions of Queensland and the Northern Territory are characterized by tropical climates, which can be both a blessing and a curse. While these areas benefit from rich biodiversity and agricultural potential, they are also prone to cyclones and heavy seasonal rains that can disrupt livelihoods and infrastructure.
In contrast, the southeastern parts of Australia, particularly Victoria and New South Wales, are highlighted as highly habitable regions. Notably, Melbourne is not only the second-largest city but also boasts a diverse economy, thriving cultural scene, and high standards of living. The infrastructure in these areas supports large populations, with well-developed public transport systems and healthcare facilities.
The southwestern part of Australia, including Perth, showcases another interesting case. While it is geographically isolated from the eastern cities, it has developed into a major urban center. The climate here is Mediterranean, which is conducive to a variety of agricultural practices, reinforcing its habitability.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the habitability of different regions in Australia is crucial for urban planning, resource management, and environmental conservation. As climate change continues to impact weather patterns and natural resources, the areas highlighted in the 1946 map may see shifts in their livability. For instance, some coastal areas might face rising sea levels, while the Outback may become even less hospitable due to prolonged droughts.
The implications of this map extend beyond mere geography; they touch upon social and economic aspects as well. Regions marked by low habitability could face population decline, leading to challenges in service provision, economic sustainability, and cultural preservation. Conversely, as urban centers grow, they may grapple with issues like overpopulation, housing shortages, and infrastructure strain.
In conclusion, the 1946 Map of Australia serves as a historical lens through which we can assess habitability. It not only informs us about the past but also urges us to consider future trends and challenges related to living conditions in different regions. Have you noticed how our understanding of geography can shape our response to environmental changes? As we move forward, this kind of geographic insight will play a vital role in shaping sustainable practices and policies in Australia and beyond.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 21, 2025
- Views
- 184
Comments
Loading comments...