Agricultural Employment Percentage Map of Europe

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
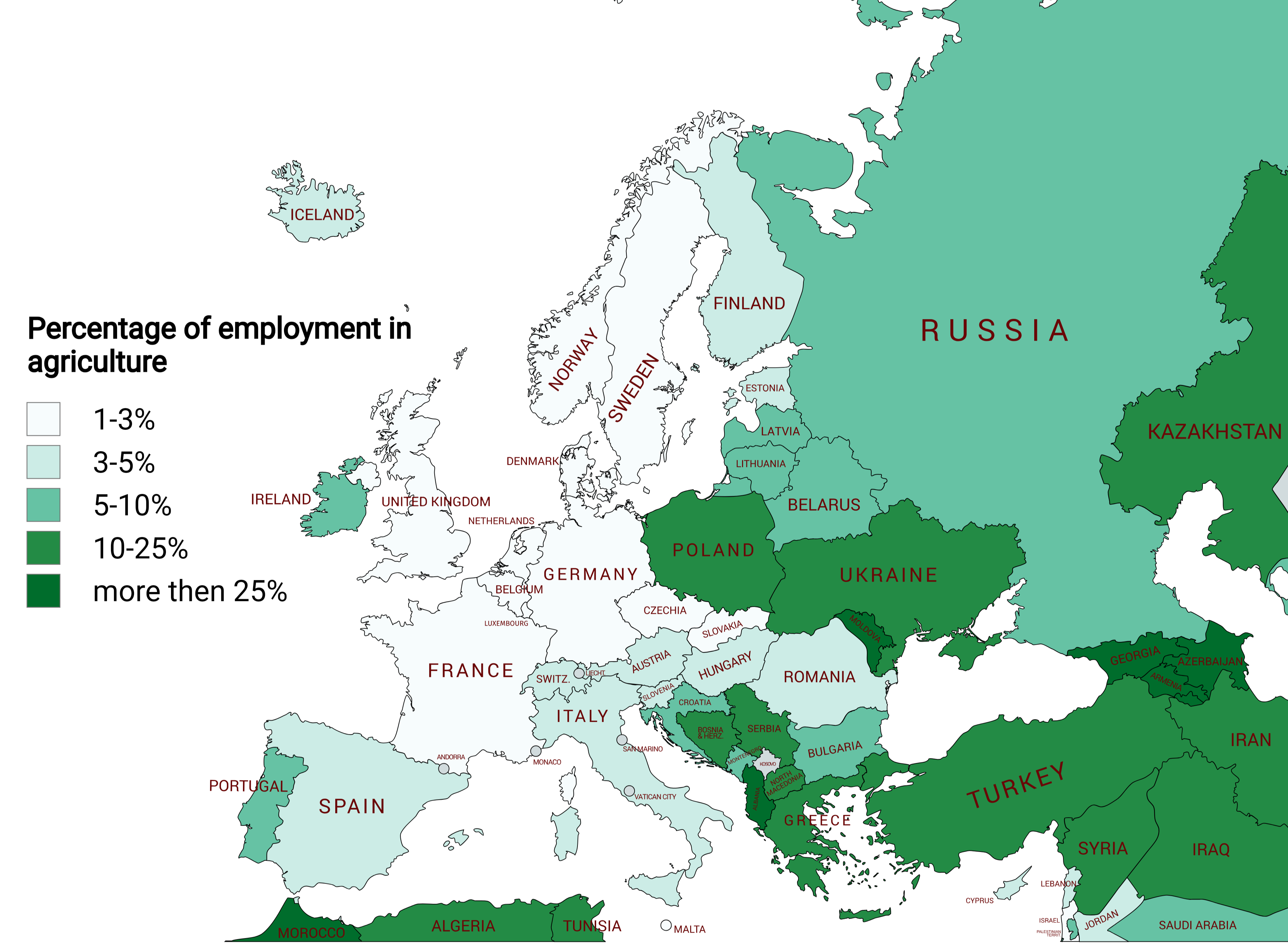
The "Agricultural Employment Percentage Map of Europe" provides a clear visual representation of the proportion of total employment that is dedicated to agriculture across various European countries. This map highlights significant differences in agricultural employment rates, offering insights into the economic structures of different nations. While some countries show a high reliance on agricultural jobs, others exhibit a much lower percentage, reflecting diverse economic activities and priorities within the continent.
Deep Dive into Agricultural Employment in Europe
Agriculture has long been a cornerstone of human civilization, providing not just food but also livelihoods for millions. Across Europe, the agricultural sector remains essential, but its significance varies widely. Have you ever wondered why some countries have a higher percentage of their workforce engaged in agriculture? This disparity can be attributed to numerous factors, including geography, economic development, and cultural practices.
In countries like Romania and Bulgaria, for example, the agricultural sector employs a substantial portion of the workforce—often exceeding 20%. This high percentage is indicative of their economies, which still rely heavily on traditional farming practices. In contrast, more industrialized nations such as Germany and the United Kingdom show significantly lower percentages, often below 2%. The emphasis in these countries has shifted toward urbanization and industrialization, leading to a decrease in agricultural employment.
Interestingly, the map also reveals the role of agriculture in Mediterranean countries such as Greece and Italy, where the sector plays a vital role not only in employment but also in cultural identity and tourism. The Mediterranean climate supports a variety of crops, leading to a diverse agricultural output. In these regions, the agricultural workforce is often engaged in both traditional farming and modern agribusiness, showcasing a blend of old and new practices.
Moreover, the European Union's Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) plays a critical role in shaping agricultural employment. This policy aims to support farmers, promote sustainable agriculture, and ensure food security across member states. With ongoing reforms, the CAP influences employment trends, encouraging younger generations to engage in innovative agricultural practices while supporting rural communities.
Regional Analysis
When diving into regional specifics, the map illustrates stark contrasts. Northern European countries, particularly the Scandinavian nations, have a minimal agricultural workforce percentage. These countries, characterized by advanced technological integration and high productivity, have moved to mechanized farming, requiring fewer laborers. The focus here has shifted to enhancing efficiency rather than expanding the workforce.
In contrast, Eastern Europe shows a different trend. Countries like Poland and Hungary maintain a significant agricultural employment rate, driven by a combination of traditional methods and EU subsidies aimed at revitalizing rural economies. The cultural heritage of farming practices in these countries also contributes to the relatively high percentage of agricultural employment.
Southern Europe presents a mixed bag. Italy, with its rich culinary traditions and diverse agricultural products, sees a higher employment rate in agriculture compared to its northern counterparts. However, the challenges posed by climate change and economic pressures are prompting shifts in agricultural employment patterns.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the employment landscape in agriculture across Europe carries significant implications. As we face global challenges such as climate change, food security, and rural depopulation, the role of agriculture becomes even more critical. Countries with a higher percentage of agricultural employment may be more vulnerable to economic fluctuations caused by environmental factors. Conversely, nations with lower agricultural employment may face challenges in ensuring food security, relying on imports to meet their needs.
Looking forward, trends indicate a potential shift in agricultural employment due to technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. The rise of sustainable practices and organic farming is creating new job opportunities within the agricultural sector, potentially altering the employment landscape. As Europe continues to navigate these changes, the data reflected in this map will be essential for policymakers, economists, and communities alike, emphasizing the ongoing relevance of agriculture in shaping the continent's future.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 16, 2025
- Views
- 128
Comments
Loading comments...