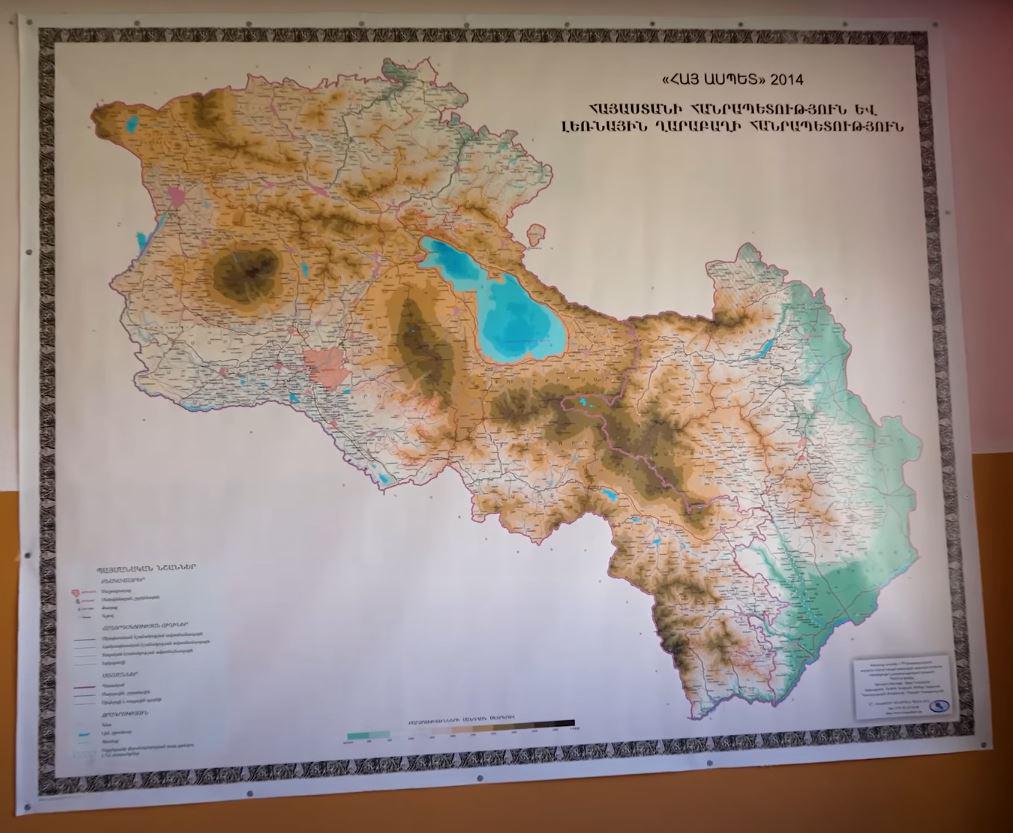
Map of Armenia in an Armenian School

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map provides a detailed overview of Armenia, highlighting its geographical features, political boundaries, and significant landmarks. It illustrates the country’s diverse topography, including mountains, rivers, and urban centers. The visualization serves as a comprehensive tool for understanding Armenia’s geography, especially in an educational setting like a school, where students can learn about their country's layout and its historical context.
Deep Dive into Armenia’s Geography
Armenia, a landlocked country in the South Caucasus region, is characterized by its rugged terrain and a rich tapestry of geographical features. Covering an area of approximately 29,743 square kilometers, Armenia is situated at the crossroads of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. One of the most notable features of the country is the Armenian Highlands, which are renowned for their scenic beauty and geological significance. The highest point in Armenia is Mount Ararat, standing at 5,137 meters, a national symbol that holds immense cultural and historical importance for Armenians.
Interestingly, the country is crisscrossed by various rivers, with the Hrazdan and the Arax being the most prominent. The Hrazdan River, flowing through the capital city of Yerevan, is vital for irrigation and has shaped the surrounding landscapes. The Arax River, which forms part of the border with Turkey and Iran, plays a crucial role in the region's biodiversity and ecology.
Armenia's climate is primarily continental, with hot summers and cold winters, making its climate zones diverse. This variability directly impacts the agricultural practices in the country. The fertile Ararat Plain, for instance, is renowned for its fruit production, particularly apricots and grapes. Have you ever wondered why Armenia is often referred to as the Land of the Stone? This nickname stems from the use of volcanic tuff in most of its architecture, giving cities like Yerevan their unique pink hue.
Moreover, Armenia's unique geographical location has made it a historical crossroads for trade routes, particularly the Silk Road. This has contributed to its rich cultural heritage, with numerous ancient monasteries and churches dotting the landscape, such as the UNESCO World Heritage Site of Geghard Monastery and the Etchmiadzin Cathedral, one of the oldest churches in the world.
Regional Analysis
Looking at the map, we can observe distinct regional characteristics throughout Armenia. The northern region, which includes cities like Vanadzor and Dilijan, is noted for its lush forests and mountainous terrain, making it a popular destination for eco-tourism and outdoor activities. In contrast, the central part of the country, particularly the capital Yerevan, serves as the political, economic, and cultural hub. Here, urban development has significantly transformed the landscape, with modern infrastructure coexisting alongside historical landmarks.
The southern regions, including Syunik Province, are characterized by their rugged mountains and strategic importance due to border proximity with Azerbaijan and Iran. This area not only holds natural beauty but is also crucial for national security and economic activities, including mining and agriculture. Interestingly, the southern city of Goris is famed for its ancient cave dwellings, showcasing a unique aspect of Armenia's historical and geographical narrative.
Significance and Impact
Understanding Armenia’s geography is essential, especially in today's global context where geographical knowledge can influence economic, political, and social decisions. The country’s strategic location continues to impact its international relations, particularly with neighboring countries. As Armenia navigates its path towards development, the interplay of geography, history, and culture remains pivotal.
Current trends such as climate change are also affecting Armenia's environment, with rising temperatures impacting agricultural yields and water resources. The government and local communities are increasingly focused on sustainable practices to mitigate these effects. Moreover, as tourism grows, there is a renewed interest in preserving Armenia's natural landscapes and historical sites, ensuring that future generations can appreciate their rich heritage.
In conclusion, the map of Armenia in an Armenian school serves not just as a tool for education, but as a gateway to understanding the intricate relationship between geography and culture in this fascinating region.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 16, 2025
- Views
- 152
Comments
Loading comments...