Population Distribution Map of Greece

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
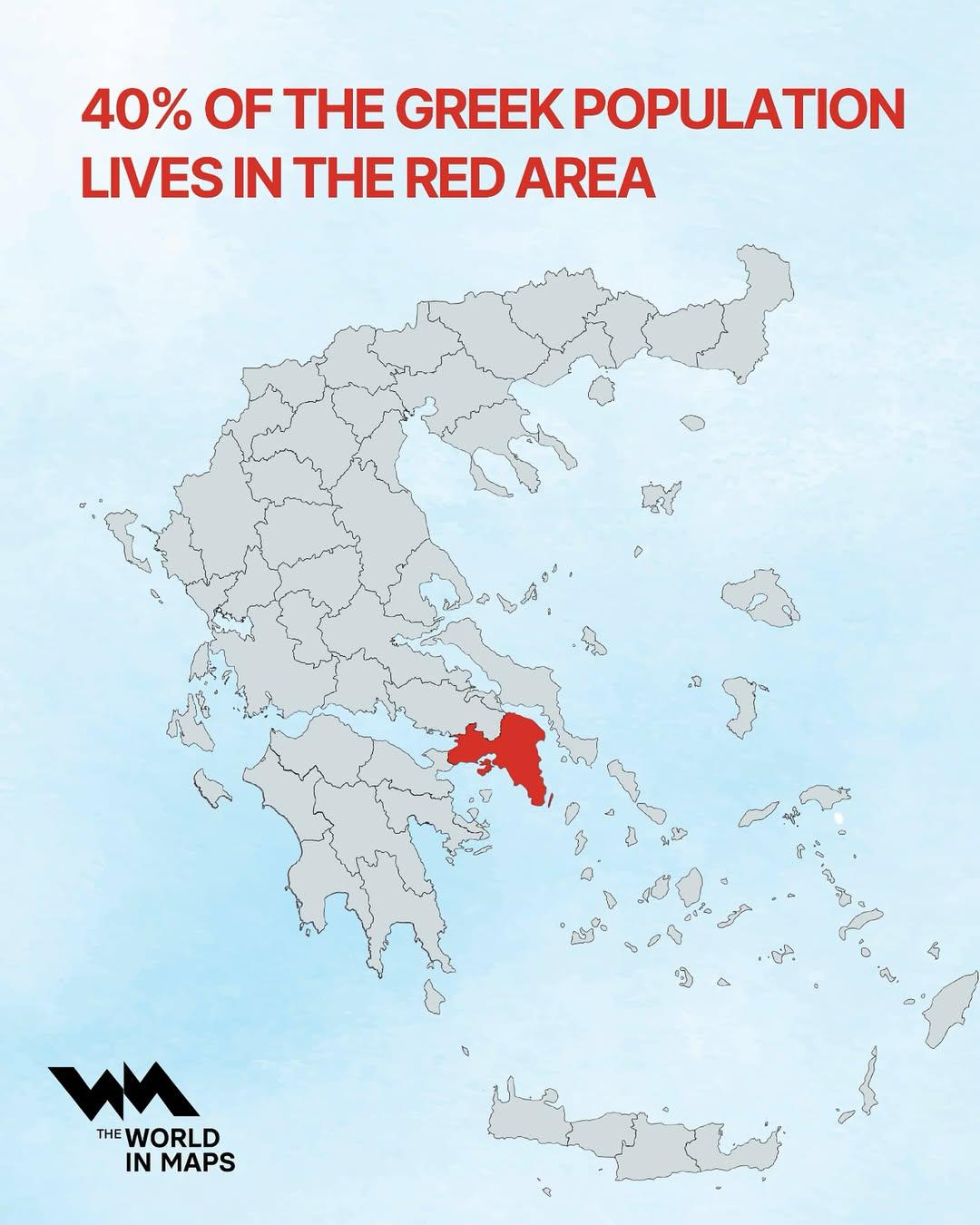
What This Map Shows
This map illustrates a striking demographic trend in Greece: approximately 40% of the nation's population resides within the designated red area. This visualization highlights significant urban centers and their expansive influence on the population distribution across the country. The red area typically encompasses major cities, particularly Athens and Thessaloniki, which are pivotal in shaping Greece's socio-economic landscape.
Deep Dive into Population Distribution in Greece
Population distribution is a critical aspect of geography that reveals much about a country's demographics, urbanization, and development patterns. In Greece, population density is not evenly spread; instead, it is heavily concentrated in urban areas. The capital, Athens, is a prime example, being one of the most densely populated cities in Europe. As of 2023, Athens houses around 3 million residents, which is nearly a third of the total Greek population.
Interestingly, the reasons behind this urban concentration are multifaceted. Historically, Athens has been the cultural, political, and economic heart of Greece. The city offers a wealth of job opportunities, educational institutions, and healthcare facilities, attracting individuals from rural areas in search of better prospects. Conversely, many of the rural regions in Greece face challenges, including limited job opportunities and access to services, which can lead to population decline.
In addition to Athens, Thessaloniki, the second-largest city, plays a crucial role in this demographic trend. With a population of approximately 1 million, it acts as a significant hub for trade and commerce in Northern Greece. The map's red area likely highlights these urban centers, where infrastructure development and investment have fostered growth and attracted migration.
Another interesting aspect is the impact of Greece's geography on population distribution. The country is characterized by its mountainous terrain and numerous islands, which contribute to isolated communities and hinder the development of transportation networks. As a result, many inhabitants in these remote areas have migrated to urban centers, further exacerbating the population concentration.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map closely, we can discern distinct regional patterns in population distribution. For instance, the Peloponnese and many of the Aegean islands show significantly lower population densities compared to Attica, where Athens is located. This discrepancy can be attributed to economic factors, such as the availability of jobs, as well as social factors like access to education and healthcare.
In the region of Central Macedonia, where Thessaloniki is situated, the population density is more favorable compared to the more rural areas of Western Greece. Here, urbanization has led to a flourishing economy, with industries and services attracting individuals from surrounding regions. Furthermore, the Ionian Islands, while known for their stunning landscapes, experience lower population density due to their geographic isolation and limited economic opportunities, leading to a reliance on tourism.
Additionally, the map indicates that certain areas, particularly in the north and rural parts of the country, are experiencing demographic decline. Factors such as aging populations and youth migration to urban centers are prevalent in these regions. This demographic shift not only impacts local economies but also poses challenges for community sustainability and development.
Significance and Impact
Understanding population distribution in Greece is vital for several reasons. Firstly, it aids in urban planning and resource allocation, ensuring that infrastructure and services meet the needs of residents, particularly in overcrowded urban areas. Secondly, it highlights the socio-economic disparities between urban and rural regions, prompting discussions on how to revitalize rural communities and improve living conditions.
Moreover, the concentration of population in urban centers has implications for environmental sustainability. Increased urbanization often leads to challenges such as pollution, traffic congestion, and strain on public services. Policymakers must address these issues to create a balanced approach to urban growth.
Looking ahead, trends suggest that urban migration will continue, influenced by economic opportunities and lifestyle choices. However, there is a growing awareness of the importance of revitalizing rural areas, ensuring that all regions can thrive and contribute to the nation's overall prosperity. This focus on balanced development could reshape Greece's demographic landscape in the coming years, making it a vital area for future research and policy-making.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 13, 2025
- Views
- 242
Comments
Loading comments...