Dominant Land Use in the European Union Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
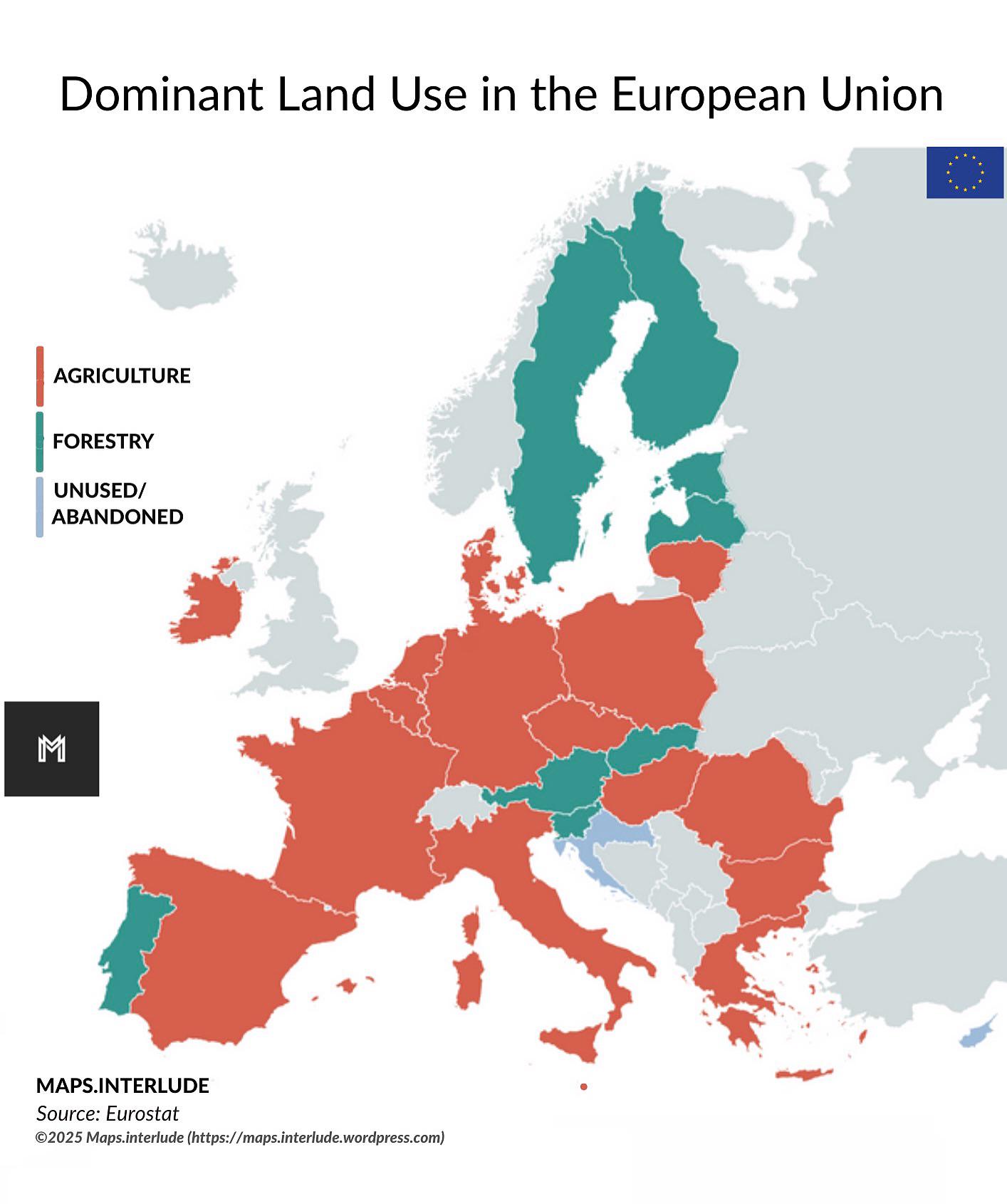
What This Map Shows
The "Dominant Land Use in the European Union" map provides a comprehensive visualization of how land is utilized across the EU member states. It categorizes land use into various segments such as agriculture, forestry, urban development, and industrial areas. Each region is color-coded to represent the predominant type of land use, allowing viewers to quickly grasp the agricultural landscapes of France, the industrial zones of Germany, or the urban sprawl of Spain.
Deep Dive into Land Use Patterns in the EU
Land use is a crucial aspect of geography that reflects the interaction between humans and their environment. In the European Union, land use is predominantly categorized into three main sectors: agriculture, forestry, and urban development. Interestingly, the EU has one of the most diverse land-use patterns in the world, shaped by history, climate, and socio-economic factors.
Agriculture remains the most significant land use type across the EU, accounting for approximately 40% of the total land area. The map highlights that countries like France and Spain have extensive agricultural lands, primarily dedicated to crop production and livestock farming. France, known as the breadbasket of Europe, has vast areas devoted to wheat, maize, and vineyards, while Spain's Mediterranean climate supports olive groves and citrus fruit cultivation.
Forestry is another critical component of land use in Europe, covering about 38% of the total land area. Countries like Sweden and Finland, rich in coniferous forests, showcase the importance of timber and paper industries. Interestingly, forested areas in these countries are not only vital for the economy but also play a significant role in carbon sequestration and biodiversity conservation.
Urban areas, while covering a smaller percentage of total land use, are expanding rapidly. The map indicates that cities like Amsterdam, Berlin, and Paris have significant urban footprints, reflecting trends in population growth and economic development. Urbanization leads to increased demand for housing, infrastructure, and services, which can put pressure on surrounding agricultural and natural lands. The EU's commitment to sustainable development aims to address these challenges by promoting smart growth strategies that balance urban expansion with the preservation of green spaces.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the map reveals fascinating regional differences in land use across the European Union. For instance, Southern Europe tends to have a higher concentration of agricultural land due to its favorable climate and historical reliance on farming. Countries like Italy and Greece showcase diverse agricultural practices, from vineyards to olive oil production, which are integral to their economies and cultural identities.
In contrast, Northern European countries, such as Denmark and the Netherlands, exhibit a blend of agriculture and urban development. The Netherlands, known for its advanced agricultural technologies, has a unique landscape where farming coexists with urban centers, resulting in a highly efficient land-use model.
Central and Eastern Europe show a mix of land uses, with countries like Poland and Hungary still transitioning from traditional agricultural practices to more modern land use patterns. The map indicates that urban areas in these regions are growing, but agricultural activities still dominate significant portions of land, showcasing the ongoing evolution of land use in response to economic changes.
Significance and Impact
Understanding dominant land use in the European Union is vital for several reasons. Firstly, it provides insights into food security, environmental sustainability, and economic development. As the EU strives towards more sustainable practices, recognizing how land is utilized can inform policies aimed at mitigating climate change and preserving natural resources.
Moreover, current trends show a shift towards urbanization, with projections indicating that by 2050, nearly 80% of the EU's population will reside in urban areas. This transformation poses challenges, such as increased pressure on land resources and the potential loss of agricultural land to urban sprawl. Therefore, it is crucial for policymakers to develop integrated land-use strategies that promote sustainability and resilience in both urban and rural landscapes.
In conclusion, the "Dominant Land Use in the European Union" map is not just a visualization; it's a reflection of the complex interplay between human activity and the natural environment. By understanding these patterns, we can better appreciate the diverse landscapes of Europe and the implications they hold for the future.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 12, 2025
- Views
- 194
Comments
Loading comments...