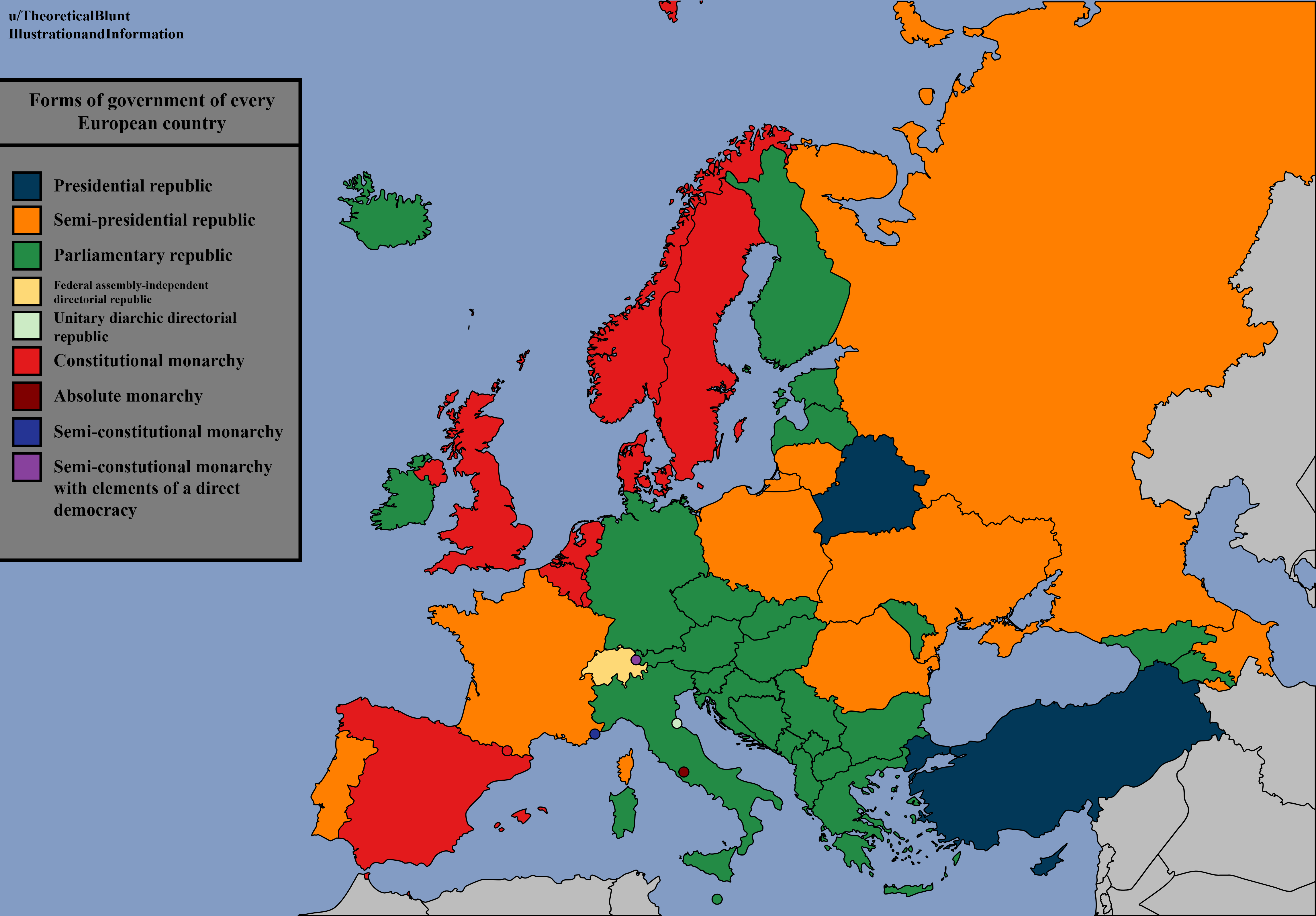
Forms of Government of Every European Country Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The "Forms of Government of Every European Country Map" provides a comprehensive visual representation of the various political systems in place across the continent of Europe. This map categorizes each European nation according to its form of government—be it a republic, monarchy, or another system—allowing viewers to quickly grasp the political landscape of Europe at a glance. By examining this map, one can appreciate not only the diversity of governance in Europe but also the historical and cultural contexts that have shaped these systems over time.
Deep Dive into Forms of Government
The forms of government in Europe are as varied as its landscapes and cultures, reflecting centuries of history, conflict, and evolution. At the broadest level, European countries can be classified into three primary categories: republics, monarchies, and hybrid systems.
**Republics** are prevalent in Europe and can take several forms, including parliamentary and presidential systems. For instance, France is a semi-presidential republic, where the president shares powers with a prime minister. In contrast, Germany operates as a federal parliamentary republic, emphasizing a decentralized power structure across its states, known as Bundesländer. Interestingly, there are also countries like Italy which, despite being a parliamentary republic, have a complex political landscape characterized by coalition governments.
On the other side of the spectrum, **monarchies** are still significant in Europe, with countries such as the United Kingdom, Spain, and Sweden maintaining royal families. The British monarchy, while largely ceremonial, plays a crucial role in national identity and continuity. Conversely, in constitutional monarchies like Sweden, the monarch’s powers are limited by a constitution, with real political power resting in an elected parliament.
Interestingly, some countries exhibit a combination of these systems, known as **hybrid governments**. For instance, Belgium is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system, which has led to a unique political dynamic, especially given its linguistic divisions between the Dutch-speaking Flanders and French-speaking Wallonia.
Additionally, it's worth noting that some nations, such as Belarus, operate under authoritarian regimes, which often suppress political opposition and limit democratic processes. This starkly contrasts with the more democratic nations in the European Union, where the rule of law and civil liberties are upheld as fundamental principles.
The diversity of government forms in Europe reflects not just historical circumstances but also contemporary political ideologies and cultural values. For example, countries with a strong emphasis on social welfare, like the Nordic nations, tend to have robust democratic frameworks that prioritize citizen participation and equitable distribution of resources.
Regional Analysis
When examining Europe regionally, notable differences in governance become apparent. In **Northern Europe**, countries like Denmark and Norway exemplify strong democratic traditions with high levels of political engagement and transparency. The Nordic model emphasizes social welfare and egalitarianism, resulting in some of the highest quality-of-life indices in the world.
In **Southern Europe**, we see a mix of parliamentary republics and constitutional monarchies. Spain, for example, has a rich monarchy with a parliamentary system, while Italy grapples with a political system characterized by frequent changes in government and coalition politics. This instability contrasts sharply with the more steadfast governance seen in the north.
**Eastern Europe** presents a diverse political landscape as well. The Baltic states (Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania) have embraced democratic reforms post-Soviet Union, whereas countries like Hungary have experienced a shift toward more authoritarian governance, raising concerns about the erosion of democratic norms. Meanwhile, countries in the **Western Balkans**, such as Serbia and Montenegro, are navigating their own paths toward democratic consolidation amidst historical tensions and socio-economic challenges.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the forms of government in Europe is crucial not only for political science enthusiasts but also for anyone interested in international relations, economics, and social issues. Governance structures profoundly influence policy decisions, international cooperation, and the overall quality of life for citizens. For instance, countries with stable governments typically have better economic performance, higher levels of foreign investment, and greater social cohesion.
Moreover, the current trends in European governance reveal shifts toward populism and nationalism in some areas, challenging established democratic norms. As countries grapple with issues like immigration, economic disparities, and climate change, the forms of government will play a significant role in how effectively they respond to these challenges. As we look to the future, understanding the governmental frameworks of Europe will be essential in predicting political stability and cooperation across the continent.
Ultimately, this map serves as a vital tool for visualizing the complex political tapestry of Europe, where history, culture, and governance intertwine to shape the lives of millions. By recognizing the diversity of forms of government, we can better appreciate the unique challenges and opportunities that each European country faces today.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 10, 2025
- Views
- 114
Comments
Loading comments...