Literal Translations of Chinese Provinces Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
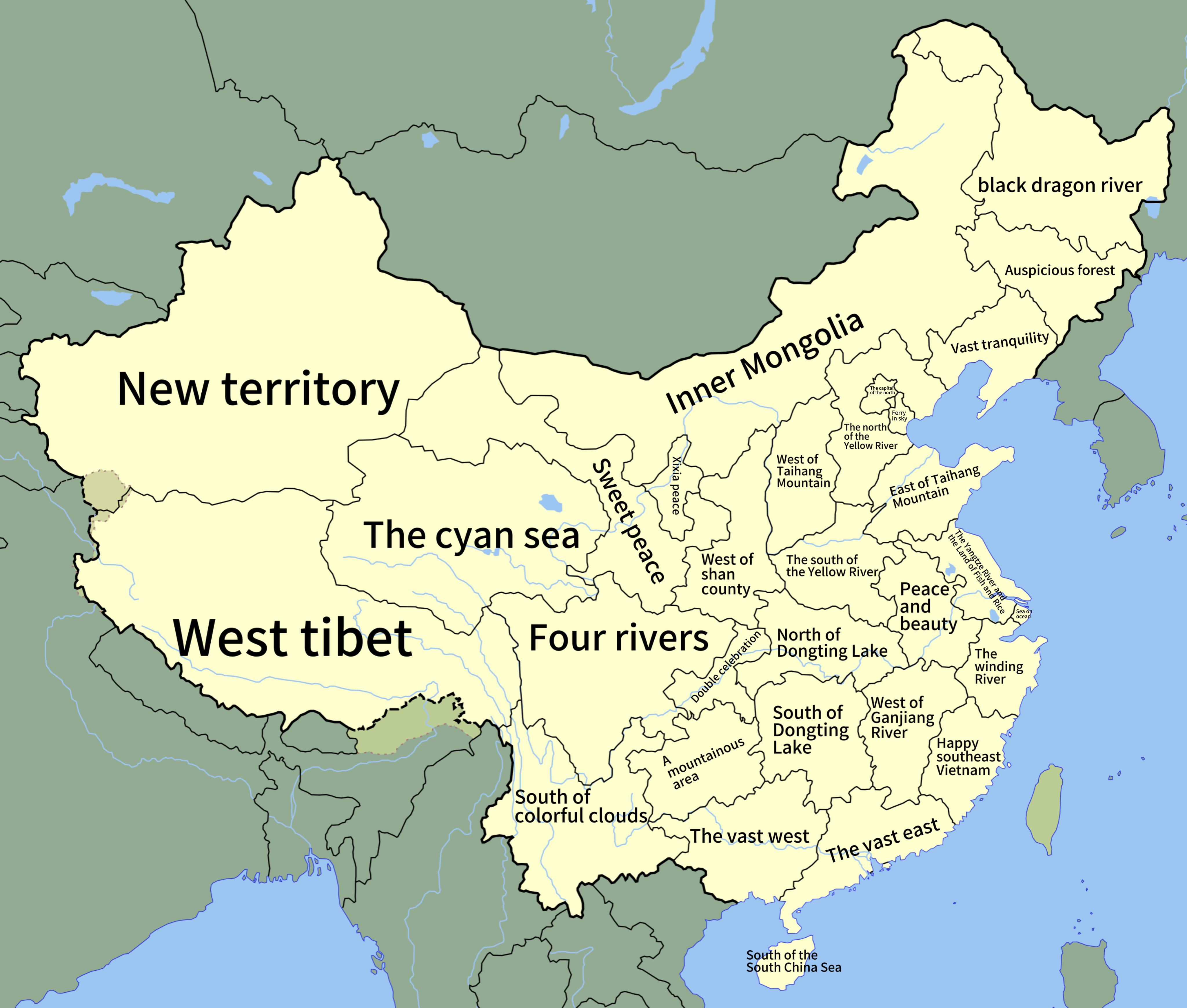
This map presents a fascinating look at the literal translations of the names of every province in China. From the sprawling landscapes of the north to the lush, tropical regions in the south, each province carries a name that tells a story, often reflecting geographical features, historical events, or cultural significance. By translating these names literally, we gain deeper insights into the identity and character of each region, enriching our understanding of China's diverse provinces.
Deep Dive into Literal Translations
Have you ever wondered what the names of Chinese provinces really mean? The literal translations provide a unique glimpse into the country's geography and culture. For instance, the province of Guangdong translates to "East of the River," which highlights its location east of the Pearl River. This river has been central to the development and economy of the area. Similarly, Hunan means "South of the Lake," referring to its position south of Dongting Lake.
Interestingly, some names reflect natural features. For example, Xinjiang translates to "New Frontier," a nod to its borderland status and the diverse landscapes that include deserts and mountains. Meanwhile, Sichuan means "Four Rivers," indicating the numerous rivers that flow through the province, which is crucial for its agriculture and irrigation systems.
It's also worth noting that many provinces have historical connotations. For instance, the name Shanxi means "West of the Mountains," which relates to its location relative to the Taihang Mountains. This geographical positioning has played a significant role in shaping the province's culture and economy over the centuries.
Moreover, the literal translations often provide clues about the province’s resources and economic activities. For example, the name Heilongjiang, which means "Black Dragon River," refers to the Amur River that forms the border with Russia and highlights the province's rich natural resources and strategic importance.
Understanding these names not only enhances our geographical knowledge but also connects us to the historical narratives and identities of the places they represent. The translations serve as a bridge between language and geography, illustrating how intimately intertwined they are.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the provinces by region reveals interesting patterns in naming conventions. In the northeastern provinces, such as Heilongjiang and Jilin, names are often tied to significant rivers and the surrounding natural environment, reflecting the importance of these waterways in local culture and economy.
In contrast, provinces in the south, like Yunnan and Guangxi, emphasize geographical features such as mountains and rivers, which are integral to the livelihoods of the local populations. Yunnan translates to "South of the Clouds," suggesting its high elevation and picturesque landscapes, while Guangxi, meaning "Expansive West," hints at its vast territory and the importance of its geographical position in trade routes.
Central provinces, like Hubei and Hunan, share a similar linguistic structure that highlights their locations relative to major lakes and rivers. This connection isn't just linguistic but also cultural, as these provinces have historically been significant in terms of agriculture and trade.
Meanwhile, provinces in the west, such as Tibet (Xizang, meaning "Western Treasure House") and Xinjiang, embody the rich cultural diversity and ethnic groups found in these areas, often reflecting their unique geographical and historical contexts.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the literal translations of Chinese provinces is not merely an academic exercise; it has real-world implications. These names are a reflection of the cultural heritage and geographical realities that shape the identities of the regions. As China continues to develop and modernize, the historical significance embedded in these names reminds us of the deep connections people have with their land.
Additionally, as global interest in China grows, especially in terms of economic investment and tourism, being aware of the meanings behind these names can enhance cultural appreciation and tourism experiences. Future projections indicate that as urbanization increases, the narrative behind these names may evolve, but their roots will remain significant in understanding the country’s past and future.
In conclusion, the literal translations of the names of China's provinces offer a window into the rich tapestry of its cultural and geographical landscape. Each name is a story waiting to be told, and understanding these stories can deepen our appreciation for one of the world's most diverse and historically rich countries.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 10, 2025
- Views
- 176
Comments
Loading comments...