Races of Mankind Map Before European Expansion

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
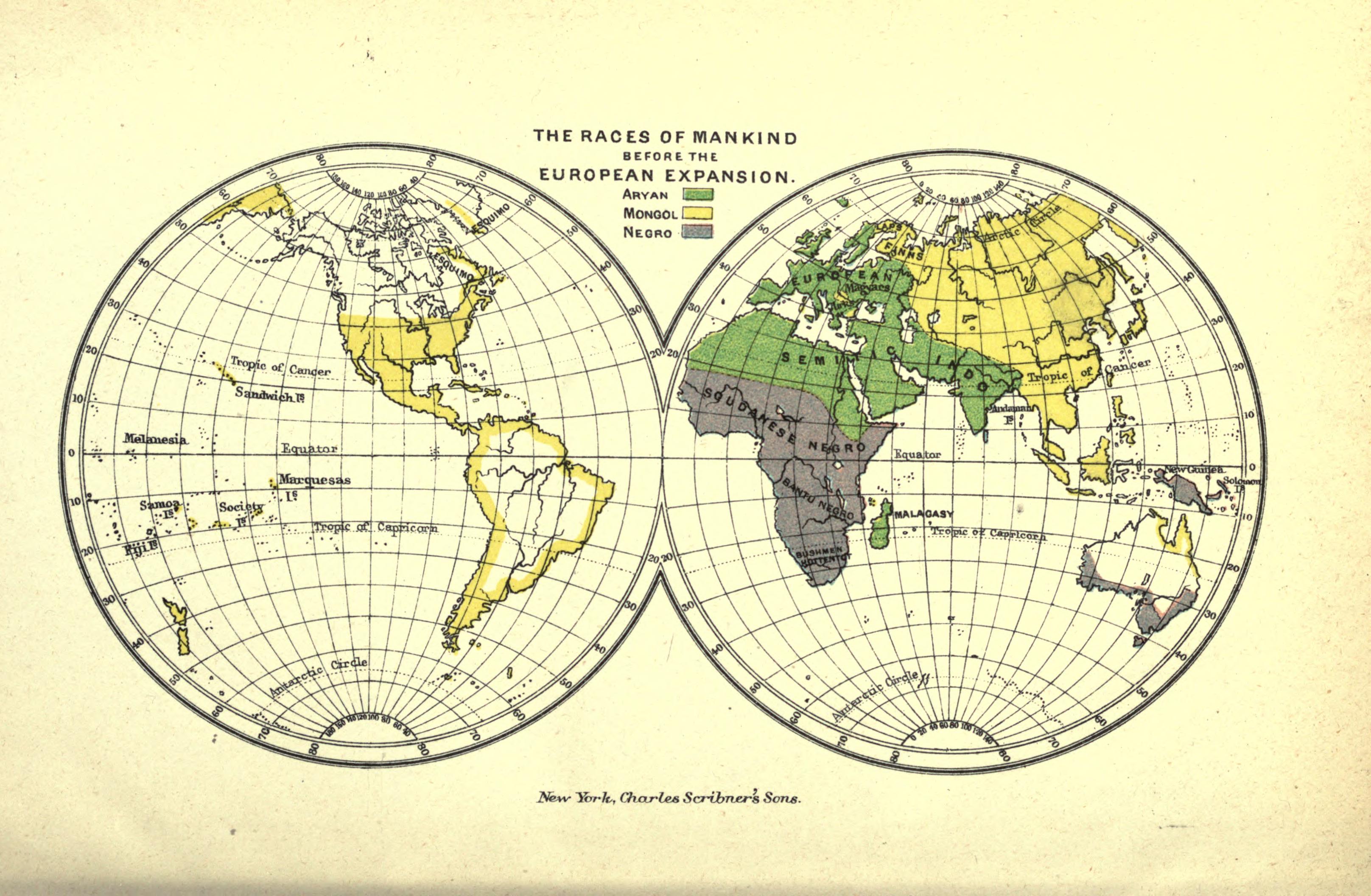
The 1891 map titled "The Races of Mankind Before European Expansion" published by Charles Scribner's Sons provides a visual representation of human populations categorized by race across the globe during a time when scientific racism was prevalent. This map illustrates how different groups were perceived and classified based on physical characteristics and cultural traits, reflecting the prevailing attitudes and beliefs of the era.
Interestingly, rather than just a geographical representation, this map serves as a historical artifact that offers insights into the social and scientific ideologies of the late 19th century. It showcases various regions of the world, delineating boundaries that were often arbitrary and based on the misconceptions of racial superiority.
Deep Dive into Racial Classification
The concept of race has been a complex and often contentious topic throughout history. In the context of the map, racial classification during this period was heavily influenced by the prevailing theories of the time, which often sought to categorize human beings into distinct groups based on perceived biological differences. The map presents several racial categories, including Caucasian, Mongolian, Malay, Ethiopian, and American, among others. Each of these classifications was based not only on physical traits but also on cultural stereotypes that were widely accepted at the time.
One of the most significant aspects of this map is how it reflects the social hierarchies that were constructed around these classifications. For instance, the Caucasian race was often viewed as superior, which led to a skewed understanding of other races. This hierarchy influenced policies, social structures, and even scientific research, leading to a legacy of discrimination and prejudice that can still be observed today.
What's fascinating is how these classifications were often used to justify colonial expansion. As European powers ventured into Africa, Asia, and the Americas, they often rationalized their conquests through a belief in their own racial superiority. The portrayal of non-European races on this map can be seen as a reflection of those justifications. Moreover, this categorization had real-world implications, influencing everything from economic policies to social interactions.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map regionally, we can observe notable differences in the classification of races. For example, in Africa, the map predominantly categorizes inhabitants as members of the Ethiopian race, which encompasses a wide range of ethnic groups and cultures. However, this oversimplification fails to recognize the continent's immense diversity. From the Berbers in North Africa to the Zulu in the south, Africa is home to thousands of distinct groups with unique languages and traditions.
In contrast, the Americas are represented by the American race, which includes indigenous populations. This classification is particularly problematic, as it overlooks the rich tapestry of cultures and identities that existed long before European contact. The map's depiction of indigenous peoples as a singular race ignores the thousands of tribes, each with their own languages, customs, and histories.
Additionally, regions such as Asia are grouped under the Mongolian race, which again represents a vast number of cultures, from the Chinese and Japanese in the East to the various ethnic groups in Central Asia. The map misses an opportunity to appreciate the complexity and richness of these societies, reducing them to a single label that lacks nuance.
Significance and Impact
The significance of this map extends beyond mere historical interest; it highlights the lasting impact of racial classification on modern society. The ideologies that shaped the creation of such maps have influenced contemporary issues related to race, identity, and social justice. Today, as we engage in discussions about race, it is essential to understand the historical context that informs these conversations.
Moreover, the legacy of scientific racism continues to affect societal structures and policies around the world. Racial stereotypes that originated from such classifications can still be seen in media portrayals, educational curricula, and even in the justice system. The fight against racism today is a direct response to the historical injustices rooted in ideologies like those represented in this map.
As we move forward, it is crucial to acknowledge the complexities of human identities and to celebrate diversity rather than oversimplifying it into categories that serve to divide us. Understanding the past helps us to create a more equitable future, where every individual is seen for their unique contributions rather than being confined to outdated and inaccurate classifications.
In conclusion, the "Races of Mankind Before European Expansion" map serves as a reminder of the dangers of oversimplification and the importance of embracing the rich diversity of human culture. By engaging with the historical context of such representations, we can foster a deeper understanding of race and its implications in our world today.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 7, 2025
- Views
- 108
Comments
Loading comments...