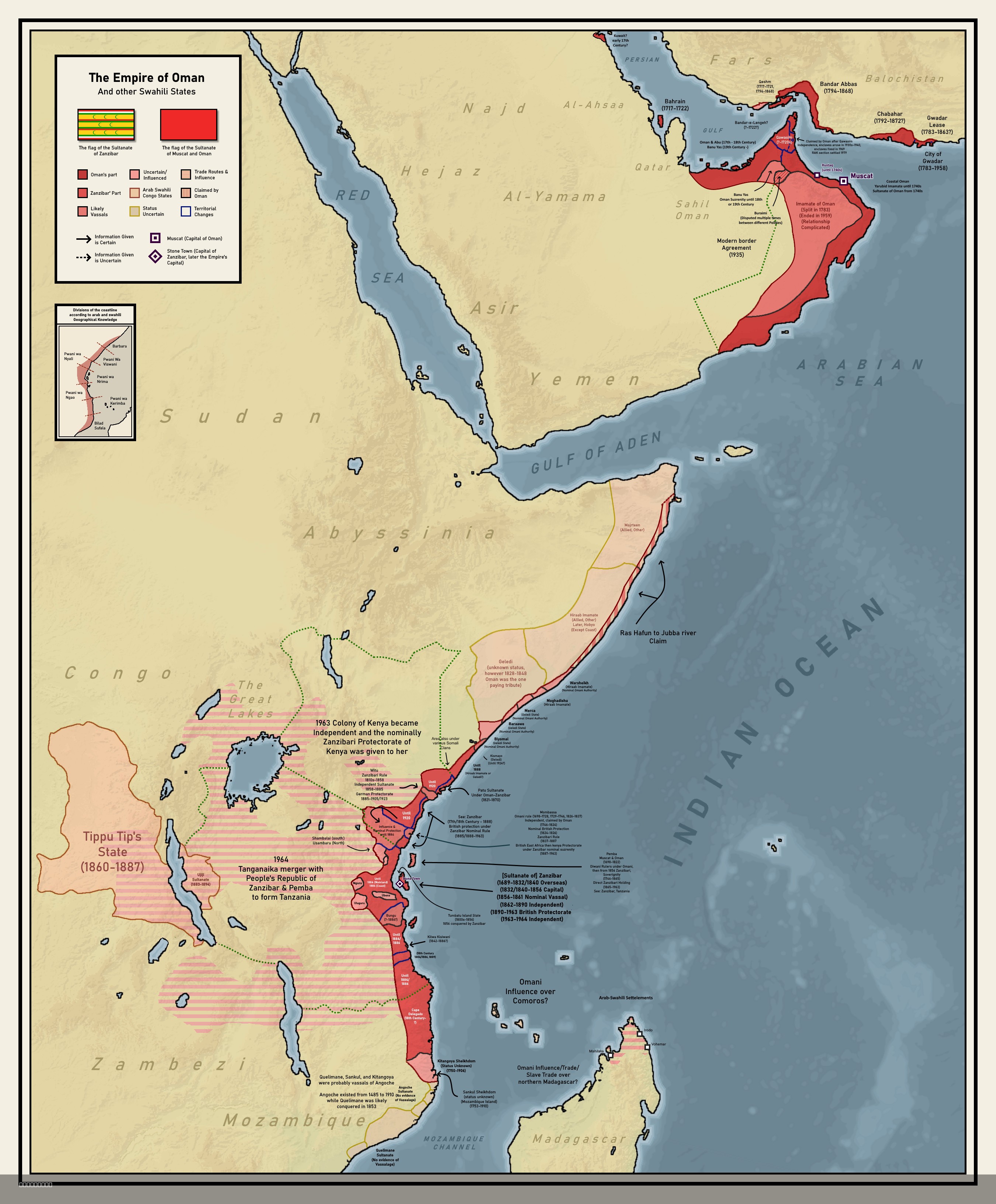
Colonial Empire of Oman Map 1696 to 1856

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The map titled "Forgotten Colonial Empire of Oman from 1696 to 1856" illustrates the extensive territorial reach of the Omani Empire during a significant period of its history. Covering parts of modern-day Oman, the East African coast, and the Persian Gulf, this visualization highlights the areas where Omani influence was prominent, showcasing not only the geographical expanse but also the strategic maritime routes that were crucial for trade and military endeavors. This map provides a visual understanding of how Oman emerged as a formidable maritime power, participating in Arab colonialism in the Indian Ocean region.
Deep Dive into Omani Colonialism
What’s fascinating about Oman’s colonial history is its maritime roots. Unlike many other colonial powers that predominantly relied on land conquests, Oman established its empire through its naval prowess. The period from 1696 to 1856 saw Oman transforming into a powerful entity, controlling key trade routes between Africa, the Middle East, and Asia. This era marked the zenith of Omani power, largely attributed to the rise of the Al Ya'rubi dynasty, which played a pivotal role in expanding Oman's influence.
Oman's colonial efforts were largely focused on the East African coast, particularly in areas like Zanzibar and Mombasa. These coastal cities became vital trade hubs, where Omani merchants engaged in the lucrative trade of spices, ivory, and slaves. Interestingly, during this time, Oman also established a significant presence in the Persian Gulf, asserting its dominance over trade routes that were critical for the movement of goods and resources.
The Omani Empire was not just about commerce; it also involved cultural exchanges. As Omani traders and settlers moved to the East African coast, they brought with them Islamic culture, architecture, and governance practices, which significantly influenced local societies. The Swahili culture, for instance, reflects a blend of Arab, Persian, and African influences, showing how Oman's colonial legacy extended beyond mere trade.
However, Oman's expansion was met with resistance, particularly from European colonial powers. The Portuguese and British, in particular, posed significant challenges to Oman's ambitions. The British, in the 19th century, recognized the strategic importance of controlling the Indian Ocean and sought to diminish Omani influence, eventually leading to treaties that curtailed Omani sovereignty in some regions. Despite these challenges, Oman managed to maintain a degree of independence and influence, especially in regions like Zanzibar until the late 19th century.
Regional Analysis
On the map, we can observe several distinct regions that were affected by Omani colonialism. The coastal areas of East Africa, particularly the islands of Zanzibar and Pemba, illustrate the depth of Omani influence. Zanzibar, often referred to as the “Spice Island,” became a melting pot of cultures and a center for the spice trade, with Omani sultans ruling over it.
In contrast, looking at the interior regions of East Africa reveals a different story. While Omani influence was felt along the coasts, the interior areas remained largely unaffected by direct Omani control. This dichotomy highlights the nature of Omani colonial practices, which were predominantly maritime and trade-focused, rather than land-based conquests typical of European powers.
Moreover, the Persian Gulf region, visible on the map, showcases Oman's historical competition with the Portuguese and later the British. The Omani-controlled territories in this area were crucial for maintaining trade routes, and major ports like Muscat served as significant naval bases.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the colonial history of Oman is essential for contextualizing the broader narrative of Arab colonialism and its impact on global trade networks. This topic matters not only for historians but also for contemporary discussions about cultural exchanges and the legacies of colonialism. The interactions that took place during this period paved the way for modern socio-economic dynamics in the Indian Ocean region.
Interestingly, the remnants of Oman's colonial past can still be seen today in the cultural practices, languages, and architectural styles found in East Africa. As we look towards the future, examining such historical contexts becomes crucial for fostering a deeper understanding of regional identities and the complexities of colonial legacies.
In conclusion, the map of the Forgotten Colonial Empire of Oman from 1696 to 1856 serves as a vivid reminder of the empire's extensive maritime reach and influence during a time when global trade was beginning to reshape economies and cultures. Oman's story is one of resilience and adaptation in the face of colonial challenges, and it remains a significant chapter in the history of Arab colonialism in the Indian Ocean.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 6, 2025
- Views
- 132
Comments
Loading comments...