Global GDP Distribution by Region Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
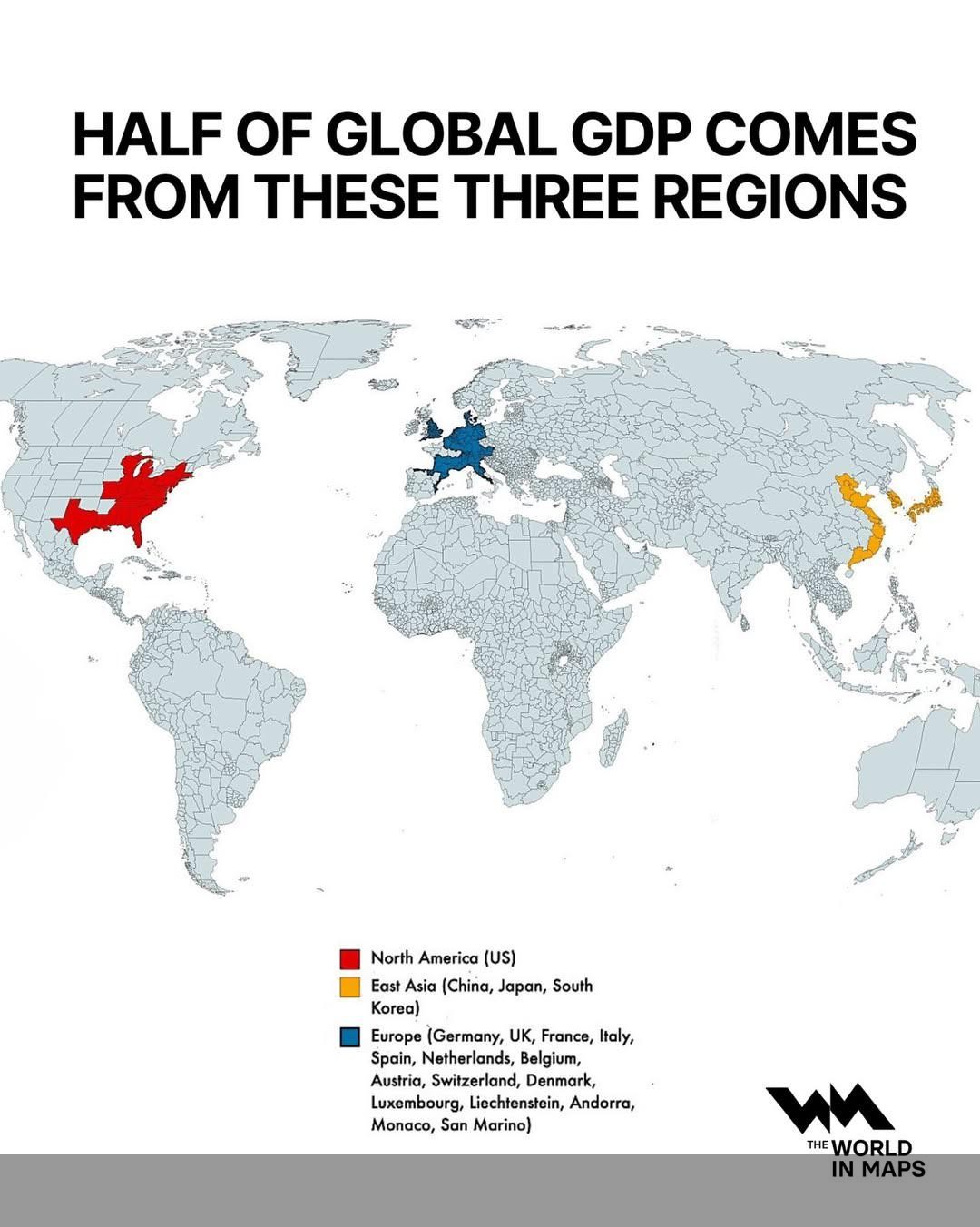
What This Map Shows
This map illustrates a significant economic reality: half of the world's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) originates from just three key regions. These regions, which include North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, dominate global economic output, highlighting the concentrated nature of wealth creation and production in specific areas. As you delve into this visualization, you'll notice the stark disparities in economic contributions across the globe, prompting deeper questions about the underlying factors that drive these distributions.
Deep Dive into Global GDP
Gross Domestic Product is a crucial metric that reflects the economic performance of a country or region, serving as a comprehensive measure of economic activity. It encompasses all goods and services produced over a specific time period, providing insight into the overall health of an economy. The concentration of GDP in North America, Europe, and the Asia-Pacific region raises interesting questions about the characteristics of these areas that contribute to such economic prowess.
North America, particularly the United States, stands out as a leader in technology, finance, and consumer markets. The U.S. alone accounts for a significant percentage of global GDP, thanks to its vast resources, innovative industries, and strong consumer spending. Silicon Valley, for instance, is a hub for technological innovation that has reshaped global markets and created substantial economic value.
Europe, on the other hand, benefits from a diverse economy that ranges from manufacturing powerhouses like Germany to financial centers like London. The European Union (EU) facilitates trade among member countries, boosting economic integration and stability. Interestingly, the EU's commitment to sustainability and green technologies is also shaping future economic growth, as countries invest in renewable energy and environmentally friendly practices.
Asia-Pacific, which includes rapidly growing economies such as China and India, is a powerhouse of production and consumption. China, as the world's second-largest economy, has transformed into a global manufacturing leader with a significant impact on international trade. India, with its burgeoning tech sector and youthful population, is poised to contribute even more to global GDP in the coming years. What’s fascinating is how these regions are not just growing economically; they are also reshaping global trade dynamics, presenting new opportunities and challenges.
Regional Analysis
When we break down the three regions represented in the map, we notice distinct characteristics and trends. In North America, the U.S. contributes approximately 24% of global GDP, which is a testament to its robust economic infrastructure. Canada and Mexico, while smaller players, also contribute significantly through natural resources and manufacturing.
In Europe, Germany leads with the largest GDP in the EU, followed closely by the UK and France. The region benefits from a highly skilled workforce and a strong emphasis on innovation and technology. However, the economic performance varies greatly; for instance, Southern European countries like Greece and Italy face economic challenges that contrast sharply with their Northern counterparts.
Asia-Pacific showcases the most dynamic growth, with China's economy expanding rapidly, accounting for about 17% of global GDP. India’s growth trajectory is equally impressive, with projections indicating it could surpass the UK in GDP over the next few years. Interestingly, the economic rise of Southeast Asian nations, such as Vietnam and Indonesia, reflects a shift in manufacturing and service industries, contributing to a diversified economic landscape.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the distribution of GDP by region is crucial for grasping global economic trends and their implications. This concentration of wealth raises important questions about inequality, access to resources, and future growth trajectories. For instance, as emerging economies in Asia continue to grow, they are likely to reshape global trade patterns, impacting everything from supply chains to labor markets.
Moreover, the emphasis on technology and innovation in these leading GDP regions suggests a future where digital economies will play an increasingly central role. The pandemic has accelerated trends towards remote work and e-commerce, further entrenching the economic dominance of these regions.
As the world continues to evolve, keeping an eye on these economic powerhouses will be vital for understanding global dynamics. What remains to be seen is how these regions will adapt to challenges such as climate change, labor market shifts, and geopolitical tensions, all of which could influence their GDP contributions in the years to come.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 5, 2025
- Views
- 216
Comments
Loading comments...