Holocaust Concentration Camps Estimated Deaths Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
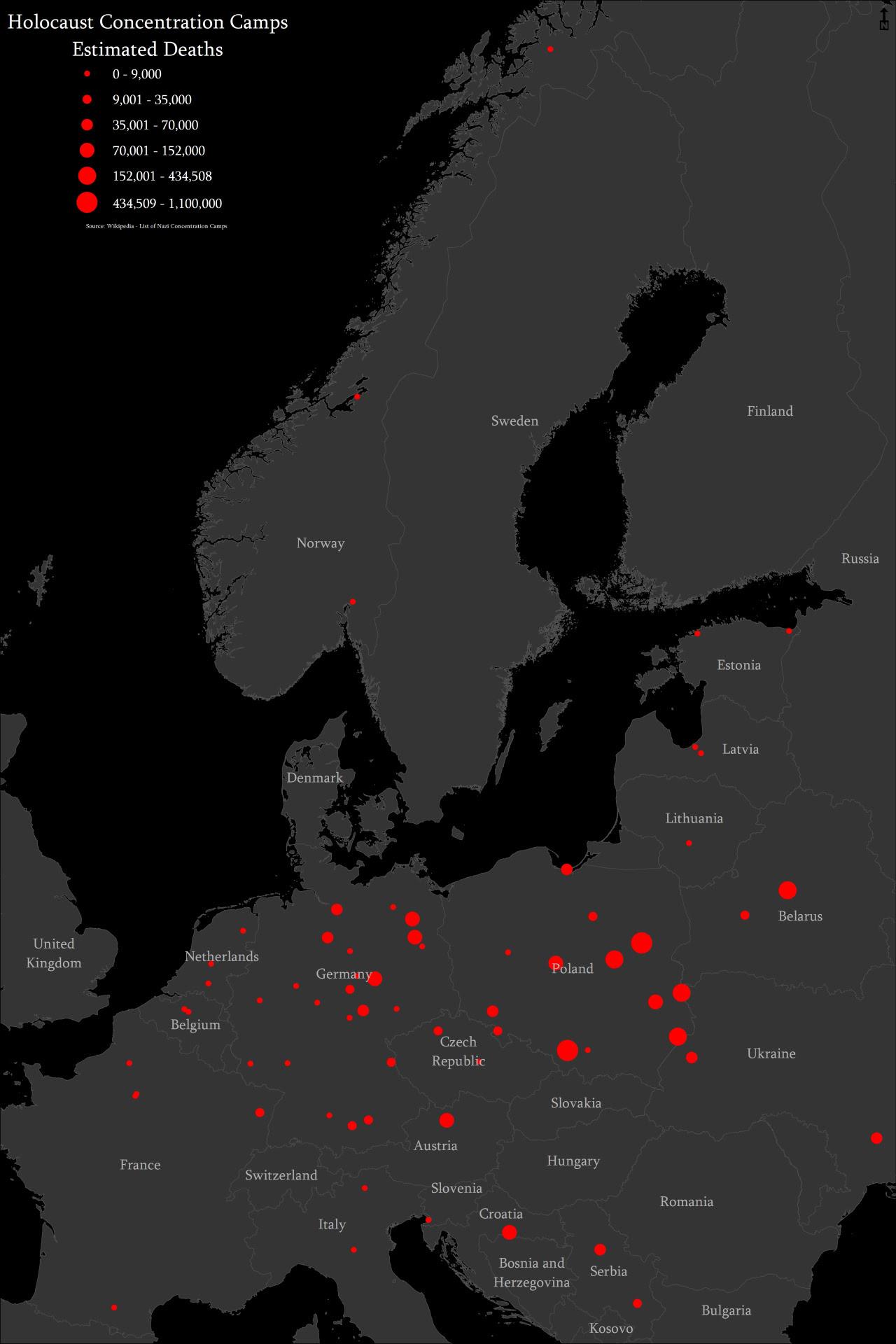
What This Map Shows
This map visualizes the estimated deaths at various Holocaust concentration camps across Europe during World War II. It provides a stark representation of the scale of human suffering and loss experienced in these camps, illustrating not only the geographical distribution of these locations but also the tragic toll they took on countless lives. Each dot or area on the map corresponds to a different camp, with varying intensities representing the estimated number of deaths, creating a powerful visual impact that serves as a reminder of this dark chapter in history.
Deep Dive into Holocaust Concentration Camps
The Holocaust is one of the most harrowing events in human history, marked by the systematic extermination of six million Jews, along with millions of others deemed undesirable by the Nazi regime. Concentration camps were a central element of this atrocity, serving multiple purposes from forced labor to mass execution.
Interestingly, the term "concentration camp" can refer to various types of camps, including labor camps, extermination camps, and transit camps. Each type had its own specific function, yet they all contributed to the overall goal of the Nazi regime to annihilate entire populations. The sheer scale of death in these camps is staggering; for instance, Auschwitz, one of the most notorious camps, is estimated to have claimed the lives of over 1.1 million people, predominantly Jews, but also Poles, Romani people, and Soviet prisoners of war.
What's fascinating is how the Nazis managed to create such an extensive network of camps across Europe. By the end of the war, there were approximately 40,000 camps and subcamps across Nazi-occupied territories. These camps were not only in Germany; they spanned across Poland, Austria, Czechoslovakia, and even as far as France and the Netherlands, showcasing the breadth of Nazi brutality.
The deaths in these camps happened through various means: gas chambers, starvation, forced labor, and medical experiments. In some camps, like Treblinka and Sobibor, the primary function was mass murder, where victims were often killed upon arrival. In others, such as Dachau, although it began as a camp for political prisoners, it evolved into a site of intense suffering where inmates faced brutal conditions and death through work.
The numbers are not just statistics; they represent families, communities, and cultures that were obliterated. The impact of this genocide is felt even today, as it serves as a cautionary tale about the consequences of hatred and intolerance.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map more closely, we can see how different regions experienced varying scales of devastation. For example, Poland, which hosted the largest number of concentration and extermination camps, is depicted with the highest estimates of deaths. Camps like Auschwitz and Majdanek are stark reminders of the brutal efficiency of the Nazi death machine.
In contrast, Western Europe, while still experiencing atrocities, had fewer camps and lower estimated deaths. For instance, camps in France, such as Drancy, were primarily transit camps where Jews were held before being deported to extermination camps in the East. The death tolls here, while significant, were not on the same scale as those in Poland.
Moreover, the map also highlights the differences in camp types across regions. In Eastern Europe, the focus was predominantly on extermination, while in Western Europe, labor camps played a more critical role. The variation in camp types and their locations reflects the broader strategies of the Nazi regime and their logistical capabilities at different stages of the war.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the geographical distribution and estimated deaths in Holocaust concentration camps is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it serves as a grim reminder of the depths of human cruelty and the consequences of unchecked hatred. Furthermore, it emphasizes the importance of historical memory and education in preventing future atrocities. By studying these maps and the stories behind them, we can honor the lives lost and ensure that such horrors are never repeated.
Moreover, in today's context, the lessons from the Holocaust resonate deeply with ongoing global issues such as refugee crises, ethnic cleansing, and genocides. The map serves as a powerful educational tool, encouraging discussions about tolerance, human rights, and the need to stand against oppression in all its forms. As we look forward, it is vital to remember that while the Holocaust is a historical event, its implications are very much alive in contemporary society. The future depends on our commitment to remembrance and vigilance against hatred, ensuring that the past informs our present and shapes a more compassionate world for generations to come.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 31, 2025
- Views
- 6
Comments
Loading comments...