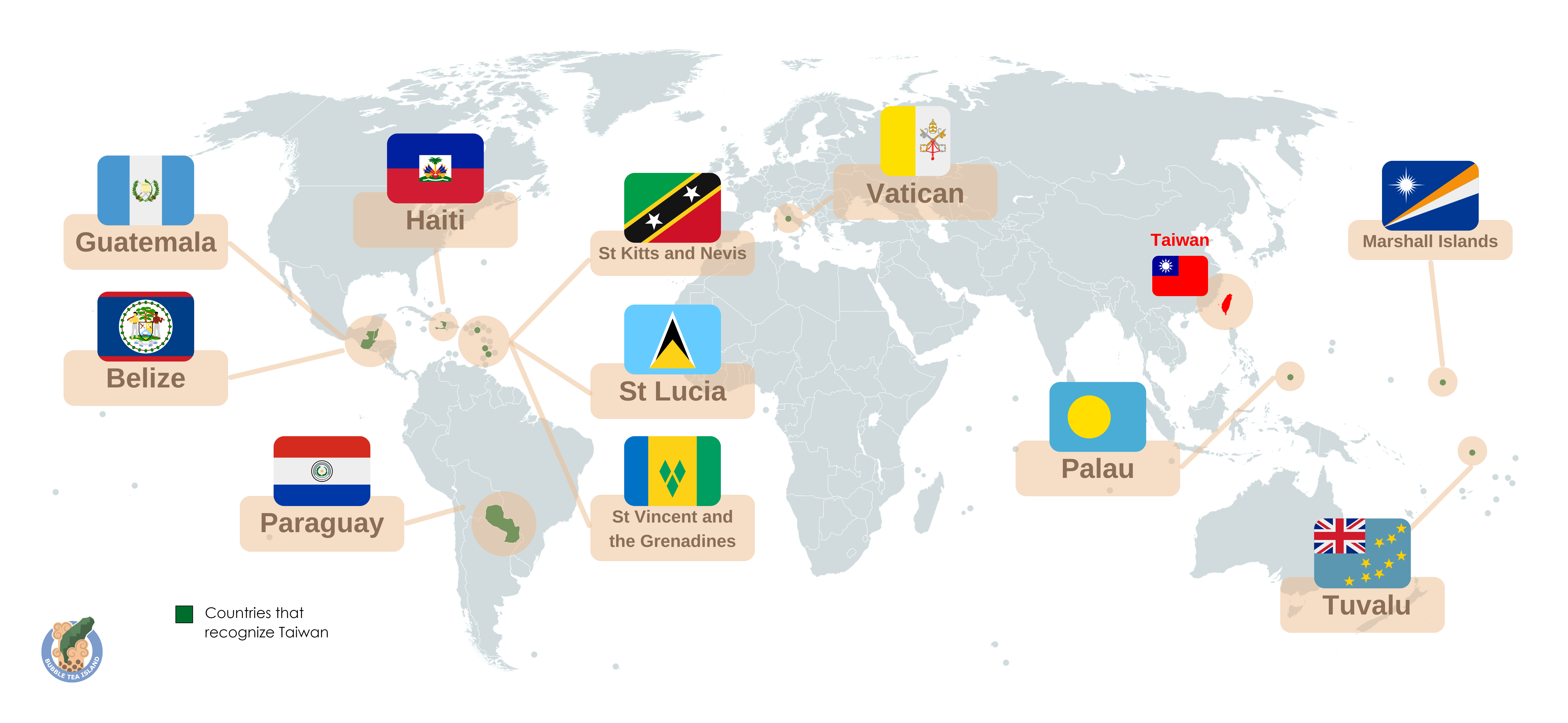
Countries that Recognize Taiwan Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map highlights the countries that officially recognize Taiwan as a sovereign nation. In a world where diplomacy is often dictated by political alliances and economic interests, the status of Taiwan remains a contentious issue. While some countries acknowledge Taiwan's independence, many others adhere to the One China policy, leading to a complex international landscape. This visualization showcases the nations that have chosen to recognize Taiwan, providing insight into their geopolitical stance and the implications of such recognition.
Deep Dive into Taiwan's International Recognition
Taiwan's status as a separate entity from mainland China has been a significant topic in international relations. Officially known as the Republic of China (ROC), Taiwan has its own government, military, and constitution. However, due to pressure from the People's Republic of China (PRC), which claims Taiwan as part of its territory, many countries have refrained from formal recognition.
Currently, only a small number of countries maintain formal diplomatic relations with Taiwan. These include nations such as Palau, Nauru, and the Vatican City, among others. Interestingly, these countries often have historical or cultural ties with Taiwan, which contribute to their decision to recognize its sovereignty. For instance, Palau has a long-standing relationship with Taiwan, stemming from earlier diplomatic engagements and mutual benefits in areas such as education and healthcare.
Moreover, the recognition of Taiwan is not merely a formality; it has real consequences for international relations, trade, and security. Countries that recognize Taiwan often face diplomatic repercussions from China, which can include economic sanctions or reduced trade opportunities. For example, countries like Nicaragua and El Salvador have switched their recognition from Taiwan to China in recent years, likely due to the incentives provided by Beijing, such as investment and development aid.
Statistics reveal that as of now, only 15 countries officially recognize Taiwan, which is a stark contrast to the 180+ countries that recognize the PRC. This disparity underscores the complex dynamics of international diplomacy, where economic leverage often outweighs ideological alignment. Furthermore, the global debate surrounding Taiwan's status is not just limited to formal recognition; it also encompasses informal relationships and support through trade agreements, cultural exchanges, and unofficial diplomatic channels.
Regional Analysis
When examining the countries that recognize Taiwan, it's essential to consider geographic and political contexts. Most of these nations are small island states or countries with limited economic clout, often in the Pacific region. For example, the Pacific island nations of Tuvalu and the Marshall Islands have opted to maintain ties with Taiwan, likely influenced by their historical relationships and the aid they receive from Taipei.
In contrast, larger nations like the United States do not officially recognize Taiwan but maintain a robust unofficial relationship. This nuanced stance allows the U.S. to support Taiwan's democratic aspirations while also managing its relationship with China. The U.S. has been a vocal advocate for Taiwan's participation in international organizations, often calling for greater inclusion in forums where Taiwan’s input could be beneficial.
Interestingly, the European Union's position on Taiwan is also complex. While individual EU member states may have their own diplomatic stances, the EU as a whole does not recognize Taiwan as a separate state. However, recent trends show an increasing willingness among some EU countries to engage with Taiwan, especially concerning trade and technology.
Significance and Impact
The recognition of Taiwan is not just a geopolitical puzzle; it has profound implications for global politics, security, and economics. As the debate surrounding Taiwan's sovereignty continues, the responses from other nations can shape the future of international relations in the Asia-Pacific region. The growing assertiveness of China, combined with Taiwan's strategic importance in global supply chains—particularly in semiconductor manufacturing—means that the stakes are high.
Have you noticed how Taiwan's situation has increasingly become a focal point in U.S.-China relations? With tensions rising, the question of Taiwan's recognition may come to the forefront, influencing not only bilateral relations but also the dynamics of global alliances. Additionally, as Taiwan continues to push for greater international presence and recognition, we may see shifts in diplomatic relations that could redefine alliances in the coming years.
In conclusion, the map of countries recognizing Taiwan is not just a snapshot of diplomatic ties; it reflects broader themes of international politics, economic dependencies, and the struggle for identity within a complex global framework. As these dynamics evolve, the world watches closely, and Taiwan's status may very well serve as a bellwether for future geopolitical shifts.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 24, 2025
- Views
- 16
Comments
Loading comments...