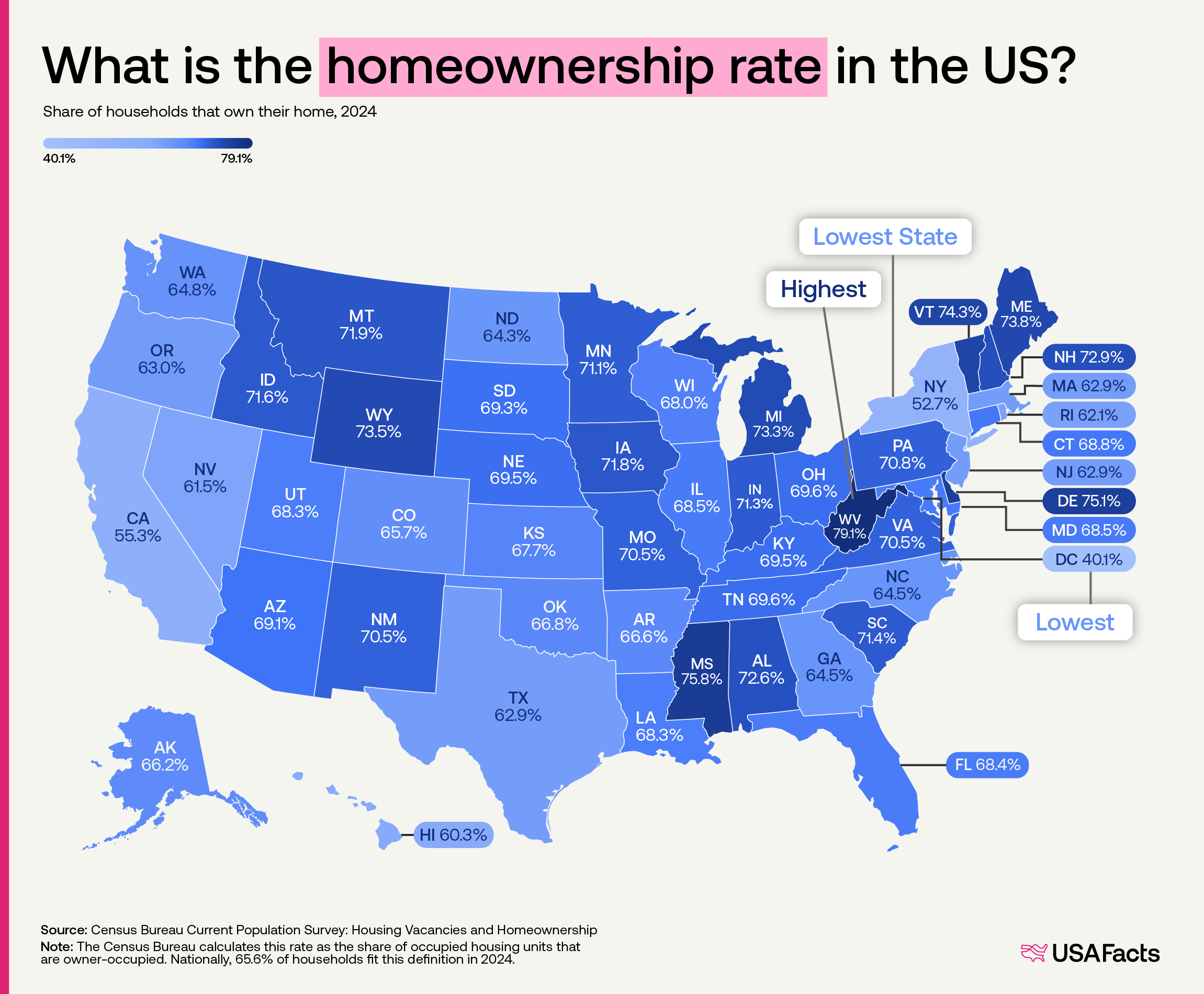
Homeownership Rates in the US Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows\nThis map displays the homeownership rates across the United States, providing a visual representation of how many people own their homes compared to those who rent. Homeownership is often considered a key indicator of economic stability and personal investment in one’s community. As we dive deeper into this topic, it’s essential to understand the factors that influence these rates and what they signify for American families and the economy as a whole.
Deep Dive into Homeownership Rates\nHomeownership has long been a cornerstone of the American Dream, symbolizing personal success and financial security. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the national homeownership rate has fluctuated over the decades, influenced by economic conditions, government policies, and demographic shifts. As of the most recent data, the overall homeownership rate in the United States stands around 65%, a figure that shows some variability when broken down by age, ethnicity, and geographic location.
Interestingly, age plays a significant role in homeownership statistics. Younger individuals, particularly those aged 25 to 34, have seen a decline in homeownership rates in recent years, thanks in part to rising student debt and a challenging job market. In contrast, older generations are more likely to own homes outright, often benefiting from years of equity buildup.
Moreover, ethnic and racial disparities also impact homeownership rates. For instance, while approximately 75% of White Americans owned homes in recent years, the rates for Black Americans lagged significantly behind, hovering around 44%. This gap highlights ongoing challenges related to systemic inequality and access to affordable housing.
Economically, homeownership is not just a personal milestone; it also contributes to economic stability. Homeowners are more likely to invest in their communities, leading to improvements in local infrastructure and services. Furthermore, homeownership can create a buffer against economic downturns, as owning real estate often provides families with a sense of security and a physical asset that can appreciate over time.
Regional Analysis\nWhen examining homeownership rates regionally, significant variations emerge. For instance, states in the Midwest, such as Iowa and Indiana, typically showcase higher homeownership rates, often exceeding 70%. These areas benefit from lower housing costs and a more stable job market that encourages families to invest in home purchases.
Conversely, coastal states like California and New York often struggle with lower homeownership rates, often around 55% or even lower in some urban areas. The high cost of living and competitive real estate markets mean that many residents must rent, sometimes for their entire lives. Interestingly, cities like San Francisco and New York City have some of the lowest homeownership rates due to skyrocketing property values and limited housing supply.
Additionally, the South has seen a surge in homeownership, with states like Texas and Florida reporting rates above 70%. The allure of a warmer climate, coupled with more affordable housing options, has attracted many new residents, making these regions increasingly popular for families looking to settle down.
Significance and Impact\nWhy does understanding homeownership rates matter? The implications are profound, touching on economic health, social stability, and individual well-being. Homeownership is often linked to wealth accumulation, with homeowners typically enjoying greater financial security than renters over time. However, as we see shifting trends, it raises questions about the future of housing policies and economic inequality.
Current trends suggest that as the younger generation faces challenges in the housing market, we may see a continued divergence in homeownership rates. With rising interest rates and inflation, prospective homeowners find themselves at a crossroads, weighing the benefits of buying against the escalating costs of homeownership.
Looking ahead, it will be crucial for policymakers to address these disparities and work toward creating a more equitable housing market. Programs that support affordable housing initiatives and assist first-time homebuyers could play a pivotal role in closing the existing gaps. Understanding the dynamics of homeownership will enable us to advocate for solutions that allow more Americans to achieve the dream of owning a home, fostering stronger communities in the process.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 23, 2025
- Views
- 18
Comments
Loading comments...