Nepal's Forest Area Map: 1992 vs 2016

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
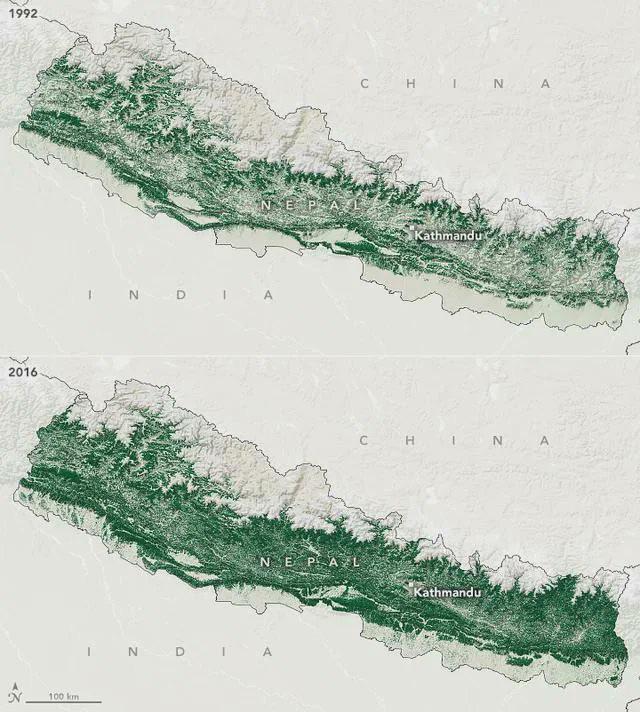
The visualization titled "Nepal's Forest Area in 1992 vs 2016" presents a stark contrast in the forest cover of Nepal over a 24-year period. By comparing these two snapshots in time, we can observe the changes in forest area, which reflect broader environmental and socio-economic trends in the region. This map serves as a vital tool in understanding not just the forest cover itself, but the various factors contributing to its loss or growth, including policy changes, population dynamics, and climate impacts.
Deep Dive into Nepal's Forest Areas
Nepal is renowned for its rich biodiversity and varied ecosystems, largely due to its diverse topography and climate zones. Forests cover approximately 40% of Nepal’s total land area, playing a crucial role in the ecological balance and economy of the country. Interestingly, forests are not only vital for wildlife but also serve as a significant resource for local communities, providing timber, fuelwood, and non-timber forest products.
In 1992, Nepal's forests were under significant pressure due to various factors, including deforestation driven by agriculture expansion and the demand for fuelwood. The socio-political climate of the early 1990s, marked by the transition to democracy, saw increased migration to urban areas, leading to a rise in timber extraction for housing and infrastructure. At that time, the deforestation rate was alarmingly high, with estimates suggesting a loss of around 1% of forest cover per year.
Fast forward to 2016, and the map indicates a remarkable transformation. Interestingly, during this period, Nepal made significant strides in forest conservation, largely due to community forestry initiatives. These programs have empowered local communities to manage forest resources sustainably, resulting in an increase in forest cover in many regions. Reports indicate that between 2000 and 2016, Nepal's forest area increased by approximately 4%, reversing the trend of previous decades.
This positive trend can also be attributed to a growing awareness of the ecological importance of forests, supported by government policies and international aid aimed at reforestation and sustainable land management. However, challenges remain, including illegal logging, land encroachment, and the impacts of climate change, which can threaten these gains.
Regional Analysis
When we break down the forest area by regions shown in the map, we can identify distinct patterns and variations. For instance, the Terai region, which is characterized by its flat plains, has historically faced severe deforestation due to agricultural expansion. However, recent community forestry programs have seen a resurgence of forest cover in parts of this region. In contrast, the mountainous regions, such as the Himalayas, have seen a slower but steady recovery of forest areas, thanks in part to conservation efforts that prioritize biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Moreover, the map highlights areas where forest loss is still prevalent. Regions experiencing high population growth, such as the Kathmandu Valley, have shown significant declines in forest cover due to urbanization and infrastructure development. This stark contrast illustrates the complexity of managing forest resources in a country balancing development with conservation.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the changes in Nepal's forest areas is critical not just for environmentalists but for all of us. Forests are essential for carbon sequestration, which helps mitigate climate change effects. They also play a vital role in maintaining water cycles and supporting agriculture, which many communities depend on. As the world grapples with climate change, preserving and expanding forest areas becomes increasingly significant.
Moreover, the success of community forestry in Nepal serves as a model for other developing nations facing similar challenges. By involving local populations in conservation efforts, there is a greater chance of sustainable outcomes that benefit both people and the environment.
Looking forward, it’s crucial for Nepal to continue investing in forest management and conservation policies while addressing the challenges posed by climate change and urbanization. The trends observed in the map from 1992 to 2016 provide both a cautionary tale and a beacon of hope, showing that with the right initiatives, it is possible to reverse the tide of deforestation and foster a healthier environment for future generations.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 19, 2025
- Views
- 34
Comments
Loading comments...