Sunshine Duration Map of the United States and Europe

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
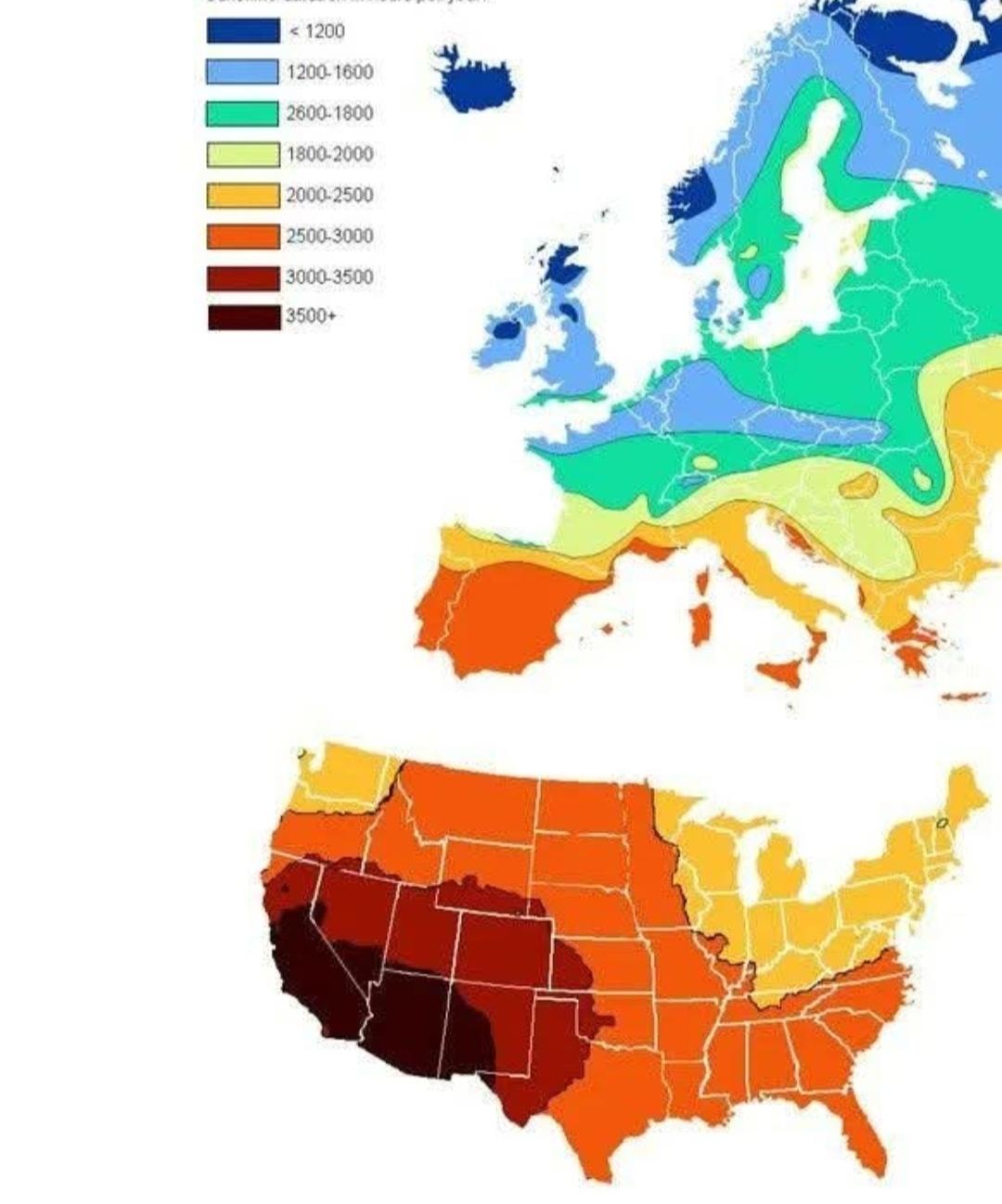
The "Sunshine Duration Map of the United States and Europe" visually represents the average annual hours of sunshine received across various regions in both the U.S. and Europe. This map offers a clear comparative view of how sunlight varies geographically, highlighting areas that bask in sunshine throughout the year versus those that experience more overcast conditions. Understanding sunshine duration is not just about weather; it can influence lifestyle, agriculture, tourism, and even energy consumption patterns.
Deep Dive into Sunshine Duration
Sunshine duration refers to the number of hours that a location receives direct sunlight over a year. It's an essential climatic factor that affects various ecological and human systems. Interestingly, the distribution of sunshine is not uniform; it varies significantly due to geographical features, climate zones, and atmospheric conditions.
For instance, regions closer to the equator typically enjoy longer sun hours year-round compared to those situated at higher latitudes. In the United States, states like Arizona and New Mexico lead the pack, boasting upwards of 3,800 hours of sunshine annually. This abundance of sunlight not only makes these states popular tourist destinations but also enhances their agricultural productivity, particularly for crops like tomatoes and peppers that thrive in sunny environments.
On the other hand, states in the Pacific Northwest, such as Washington and Oregon, experience significantly less sunshine, often averaging around 2,000 to 2,400 hours per year. The dense forests and lush landscapes of this region are largely due to the high levels of precipitation and cloud cover that inhibit sunlight.
In Europe, the variance in sunshine duration is equally pronounced. Southern countries like Spain and Italy enjoy long hours of sunshine, often exceeding 3,000 hours annually. This bright climate supports a vibrant outdoor lifestyle and a robust agricultural sector, particularly in wine production. Conversely, northern European countries, such as Sweden and Norway, experience much shorter sunshine durations, particularly in winter months when daylight can be scarce. The phenomenon of polar nights, where the sun does not rise above the horizon for several weeks, has profound impacts on lifestyle, mood, and energy usage in these regions.
Regional Analysis
When examining the U.S., the Southwest and Southeast regions stand out due to their significantly higher sunshine durations. Florida, known as the Sunshine State, boasts an impressive average of 3,200 hours of sunshine per year, contributing to its popularity as a vacation hotspot. In contrast, the Northeast U.S., with states like New York and Pennsylvania, typically sees only about 2,500 hours, leading to a more varied seasonal climate.
In Europe, the Mediterranean region is a stark contrast to the northern countries. For example, while cities like Athens and Rome bask in sunlight for over 3,000 hours annually, cities like Oslo or Reykjavik can average less than 1,500 hours. This difference not only influences local economies, particularly tourism, but also the cultural practices of these regions. While northern European countries might emphasize winter sports and indoor activities, southern European nations tend to focus on outdoor festivals and beach tourism, capitalizing on their sunny weather.
Significance and Impact
Understanding sunshine duration extends beyond mere weather patterns; it has real-world implications. For instance, regions with prolonged sunlight often see advantages in solar energy production. States like California are harnessing their abundant sunshine to meet renewable energy goals, while countries like Germany, despite having less sunshine, are investing heavily in solar technologies to maximize energy efficiency.
Moreover, the effects of sunshine on mental health are significant. Regions with long periods of sun can foster outdoor activities and social interactions, contributing to higher overall happiness and well-being. Conversely, areas with extended cloudy seasons may face challenges related to Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD), prompting communities to find innovative ways to cope with reduced sunlight.
As climate change continues to alter weather patterns globally, understanding sunshine duration could become increasingly vital. Shifts in climate may lead to changes in agricultural productivity, energy consumption, and even population movements as people seek sunnier locales. The importance of this map lies in its ability to inform us about these dynamics, allowing us to appreciate how sunshine shapes our environments, economies, and lives.
Comments
Loading comments...